Preparation method and application of molybdenum carbide microspheres
A micro-sphere, molybdenum carbide technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, carbides, tungsten/molybdenum carbides, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable size and morphology, reduced electrocatalyst activity, and easy catalyst detachment. High stability, high current density, and low requirements for preparation conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
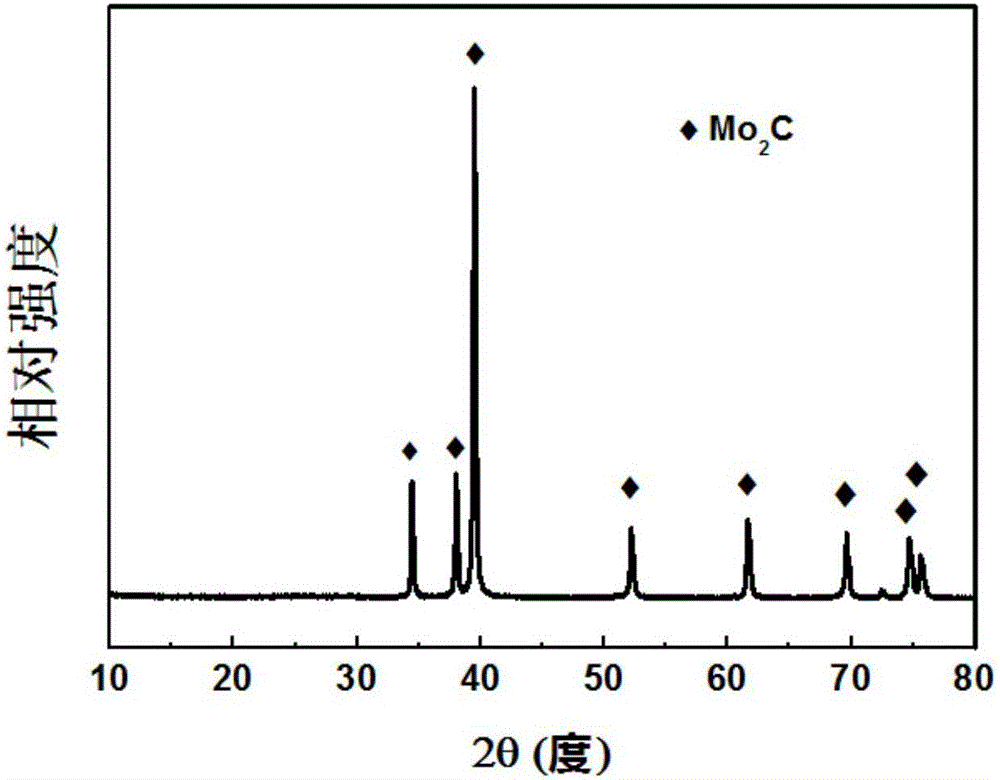
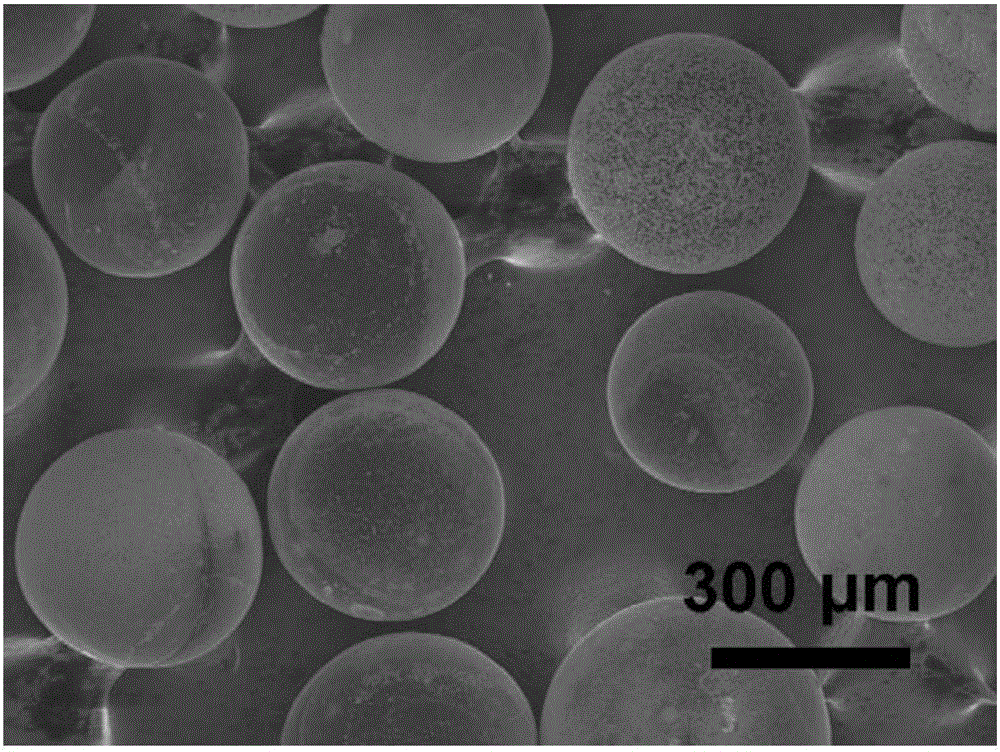
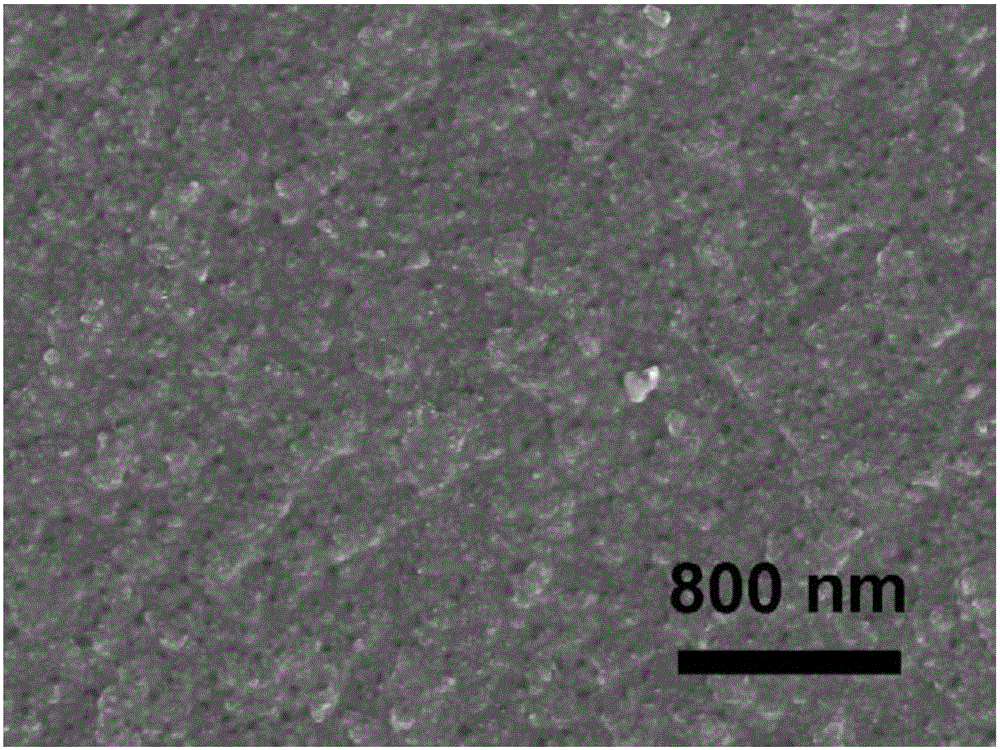
[0041] Weigh 5 grams of D201 type anion exchange resin and add to 20 milliliters, 0.5 mole per liter of sodium molybdate solution, add a stirring bar and stir for 24 hours at room temperature. Slowly add the solution into a suction filter bottle for suction filtration, and dry the obtained solid at 100° C. for 24 hours to obtain an ion exchange resin adsorbing molybdenum ions. Put the obtained powder into a ceramic crucible, place it in an atmosphere tube furnace, and under the protection of nitrogen gas, heat up to 900 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C per minute in the tube type furnace for 2 hours, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain molybdenum carbide Microspheres. The microspheres were characterized by X-ray electron diffraction as a molybdenum carbide component, as figure 1 ; Observing micron spherical shape by scanning electron microscope, diameter is 200-500 micron (as figure 2 ), the surface of the microspheres has a granular composition and a porous struct...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Weigh 2g of 201×4 type anion exchange resin and add it into 40 ml of sodium molybdate solution with 2 moles per liter, add a stirring bar and stir for 12 hours at normal temperature. The obtained solution was filtered with suction, and the obtained solid was dried at 100° C. for 48 hours. Under the protection of argon gas, the obtained solid was heated up to 1000°C for 2 hours at a heating rate of 5°C / min, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain molybdenum carbide microspheres. The X-ray diffraction results were as follows: Figure 8 ; The morphology of molybdenum carbide is obtained by grinding and pulverizing, such as Figure 9 .
[0049] With the molybdenum carbide prepared in this example as electrocatalyst, the result of its polarization curve Figure 10 , the hydrogen overpotential is 0.22 volts.
Embodiment 3
[0051] The preparation steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the anion exchange resin is D202 type, and the temperature is raised to 800° C. for 2 hours in a tube furnace at a heating rate of 5° C. per minute. The morphology of the obtained molybdenum carbide microspheres is as follows: Figure 11 , the X-ray powder diffraction results are as follows Figure 12 . Its specific surface area obtained by nitrogen absorption and desorption test is 42.8 square meters per gram ( Figure 13 ), indicating that the molybdenum carbide microspheres are porous.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com