On-site Implementation Method of Dynamic Rod Engraving in Nuclear Power Plant
A technology of dynamic rod cutting and nuclear power plants, applied in nuclear power generation, nuclear engineering, nuclear reactor monitoring, etc., can solve the problems of exceeding acceptance standards, loss of economic benefits of commercial power plants, and failure to optimize the sequence of zero-power physical tests, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
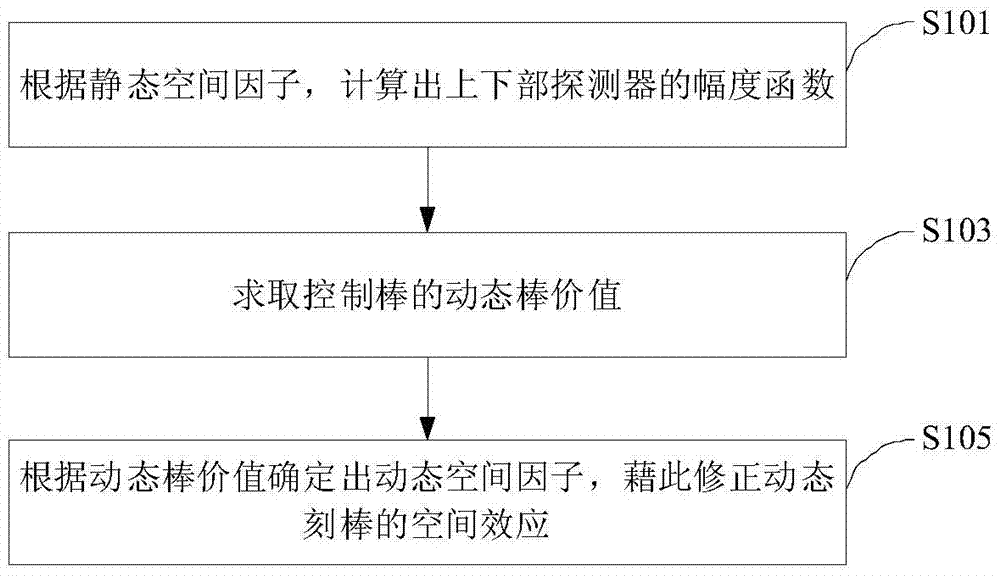
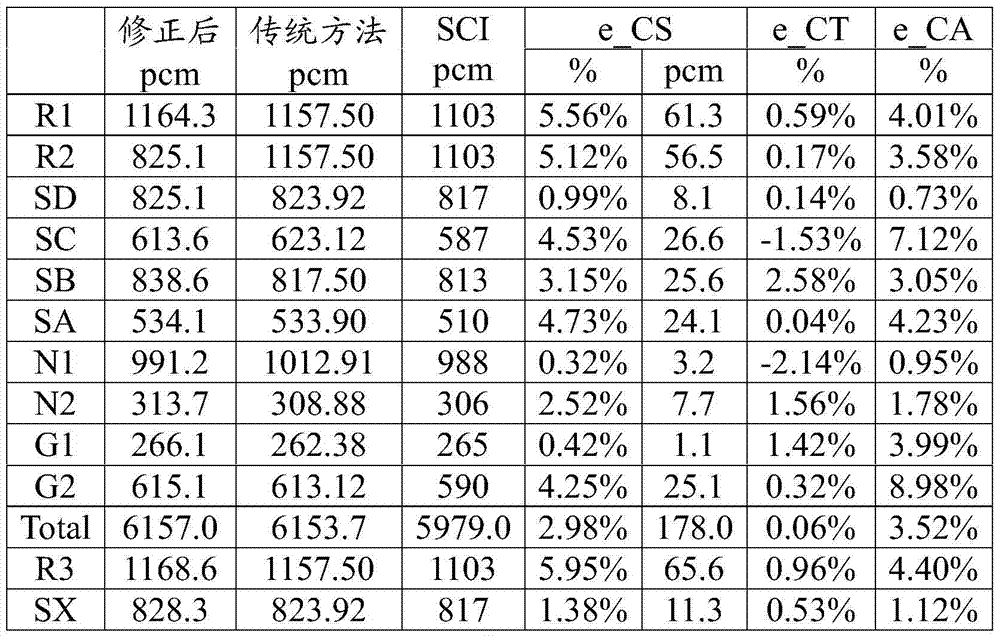
[0027]This embodiment provides a method for correcting space effects in the on-site implementation method of dynamic rod carving in a nuclear power plant, by introducing static space factors and dynamic space factors to ensure that the dynamic rod carving method can obtain correct reactivity measurement values during field tests.
[0028] The static space factor is actually a normalized space distribution function. Generally, the static space factor = the simulated static detector signal when inserting rods / the simulated static detector signal when all rods are pulled out (ARO, All Rods Out).
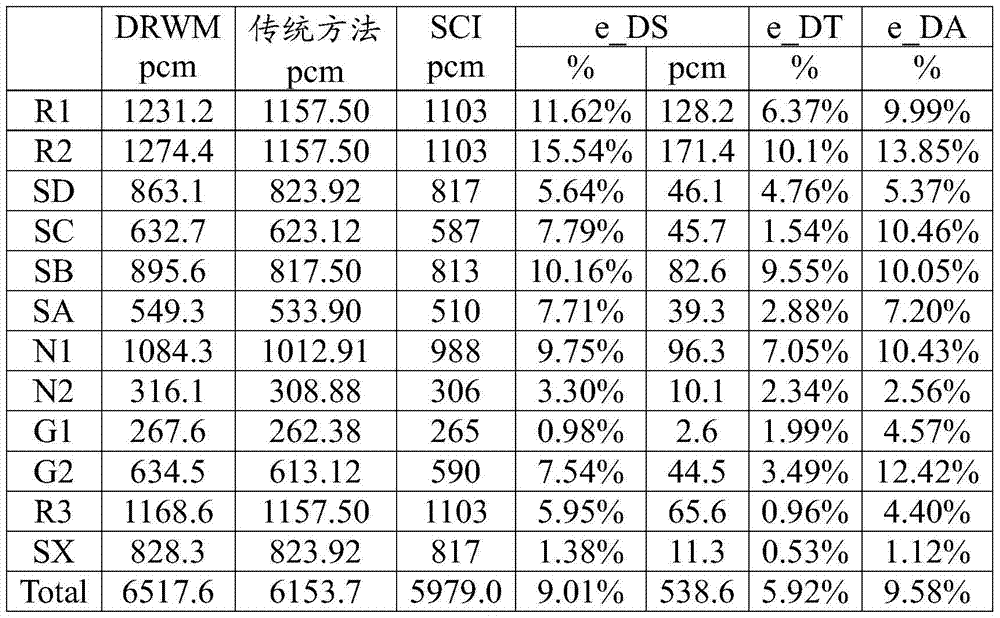
[0029] The rod value corresponding to the reactivity obtained by the static space factor is not completely equal to the rod value obtained by the traditional method, because the spatial distribution of delayed neutrons has not yet reached the progressive equilibrium. Here, the rod value obtained by dynamic carving rod through static space factor and reactivity equation is called (calc...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This embodiment provides a method for determining the background compensation current in the on-site implementation method of dynamic rod marking in nuclear power plants, which is implemented based on the ADRC with DRWM mode developed by Westinghouse Corporation of the United States, and includes the following steps S201-S206.
[0051] Step S201: Confirm that all the control rods are set to manual (automatic is prohibited), and the maximum moving speed of all control rods has been set, for example, 72 steps / min. The control rod group is divided into three categories, namely, the power compensation rod group (G rod and N rod, including such as G1, G2, N1, N2), the temperature regulation rod group (R rod) and the shutdown rod group (S rod, including such as SA, SB, SC and SD).
[0052] Step S202: Set the ADRC to the DRWM mode, and adjust the range setting of the multi-stroke recorder.
[0053] Step S203: Manually analyze and record the boron concentration of the main cir...
Embodiment 3
[0063] In order to explore the influence of the background current setting on the rod value measurement results, sensitivity analysis was carried out by using different background current correction test fluxes. Figure 4 It schematically shows the trend of the background compensation current changing with the state of the core during the overhaul of a nuclear power plant, where "diluted to about CBcri+125ppm" means that the theoretical boron concentration is 125ppm higher, and "R1 value is too large, Rin" means R The control rod group is inserted into the 5-step withdrawal position of the reactor core, and "R+G2in" means that both the R and G2 control rod groups are inserted into the 5-step withdrawal position of the reactor core. It can be seen that when the unit is in thermal shutdown and ARI state (non-standard thermal shutdown), the PRC background is measured, and it is found that when the background compensation current has just been set, the readings of the upper and low...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com