A strain of Sphingomonas and its application
A technology of sphingomonas and bacteria agent, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of chlorpyrifos residual ecological environment, excessive pesticide residues, unreasonable use, etc., and achieve the goal of being suitable for widespread promotion and use, efficiently degrading pesticide residues, and enhancing activity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
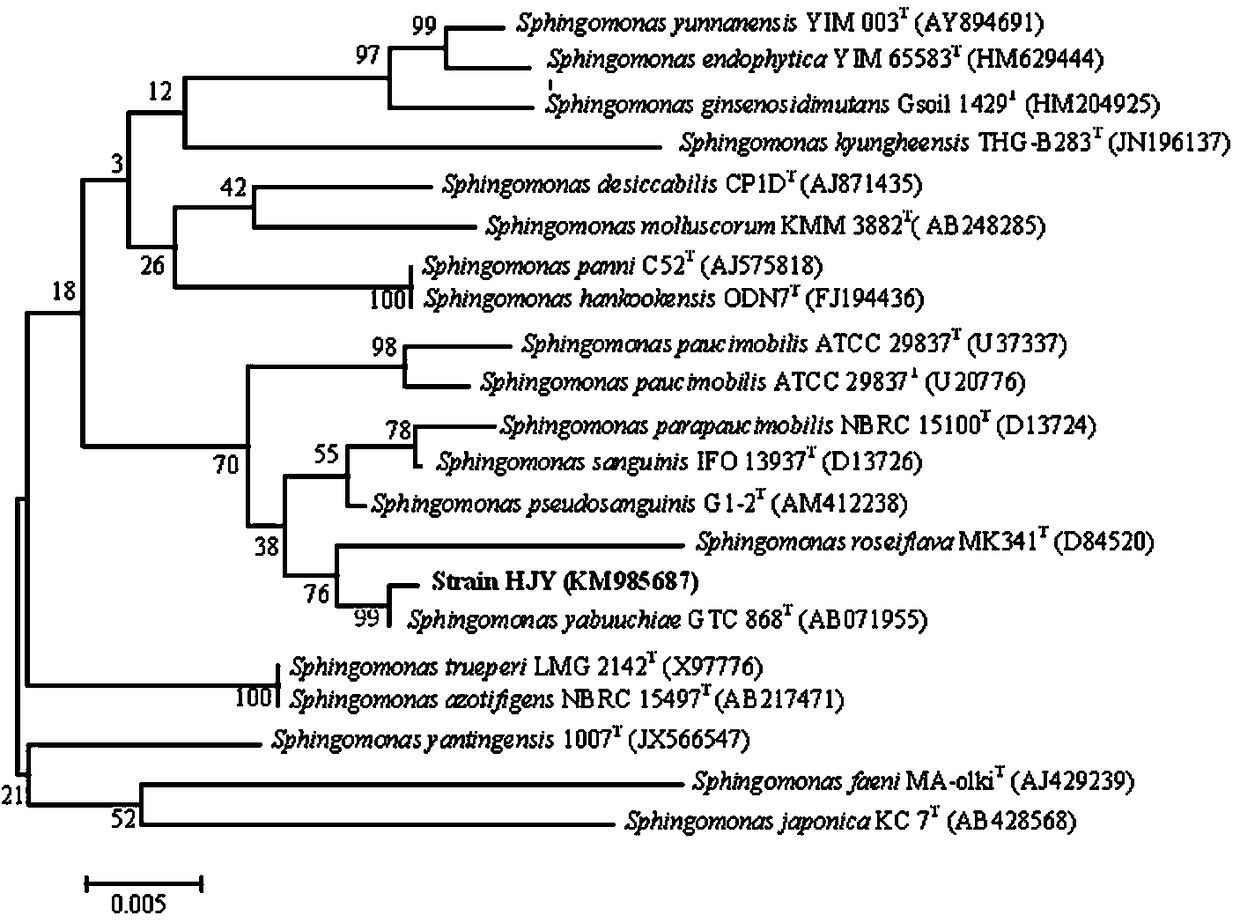
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Screening strains
[0031] 1. Obtaining the strain
[0032] (1) Sample collection: In October 2012, fresh plant samples of chives domesticated by chlorpyrifos selective pressure were collected in the experimental field of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. The dust and soil attached to the plant surface were washed with tap water, dried naturally, and pressed. Surface disinfection according to the above procedure: soak in 75% alcohol for 3-5 min, then rinse with sterile water for 3-4 times, rinse with 2.5% NaClO 2 Rinse for 2-5 minutes, and finally wash 5 times with sterile water;
[0033] (2) Isolation and screening of bacterial strains: Grind the roots, stems and leaves of Chinese chives respectively, absorb the juice and spread it evenly on the enriched medium plate, and culture at 30° C. in the dark for 2-7 days.
[0034] (3) Strain enrichment culture: After the colony grows, pick a single colony and streak it on ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Preparation of HJY bacterial agent
[0043] 1. Strain activation: Pick the Sphingomonas HJY obtained in Example 1 to the strain preservation medium, streak and pick a single colony for two times at 30°C (24 h each time), and then pick Take a single colony and put it in the strain activation medium, shake it at 30°C, 150-200 rpm for 12-24 h;
[0044] 2. Preparation of liquid seeds: inoculate the activated strain in step 1 according to the inoculum volume of 1% of the volume of the seed medium in a fermenter equipped with seed medium, and cultivate in air at 25-38°C for 16-24 h, get liquid seeds;
[0045] 3. Liquid fermentation: Inoculate liquid seeds into a fermenter with seed medium, the inoculation amount is 1% of the volume of the medium, and culture at 30-35°C and 150 rpm in the dark for 4-6 hours to obtain live bacteria Somatic culture;
[0046] 4. Bacterial agent preparation: Take 50 ml of live bacterial culture and centrifuge at 4 °C and 5000 rpm for ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Degradation of chlorpyrifos under in vitro conditions by HJY bacterial agent
[0048] 1. Inoculate 2ml of the HJY bacterial agent obtained in Example 2 into 100ml of MSM medium, add chlorpyrifos to a final concentration of 20 mg / L, and measure the initial OD of the medium 600 and the content of chlorpyrifos; at the same time, the culture medium not inoculated with HJY bacterial agent (adding the same volume of sterile saline as the bacterial agent) was used as the control group, and each treatment was repeated 3 times;
[0049] Both the control group and the experimental group were cultured at 30°C and 200 rpm in the dark, and samples were taken at different times to determine the OD 600 value and chlorpyrifos residue; after 12 days, sampling and extraction were carried out, and the content of chlorpyrifos o-phenyl was measured by HPLC, and the measurement results were as follows: Figure 4 As shown, in the MSM medium with 20 mg / L chlorpyrifos as the single c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com