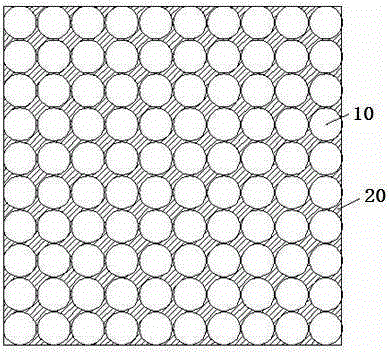
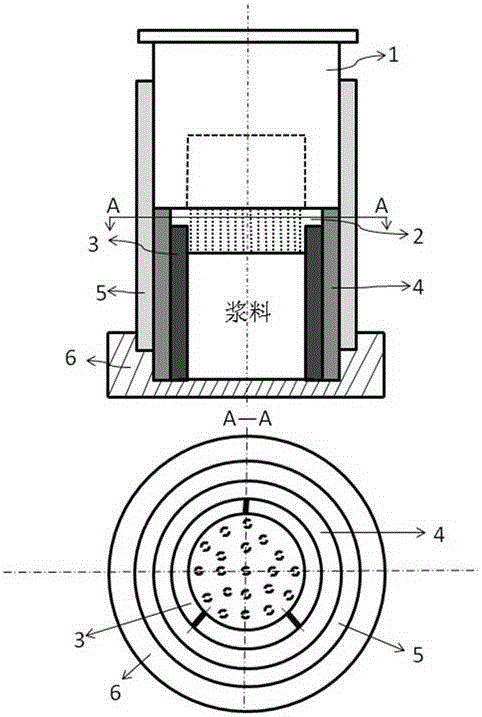
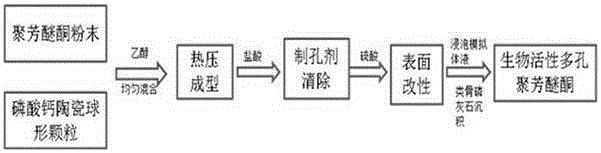
Porous polyaryletherketone material with bioactivity, and preparation method and application thereof
A polyaryletherketone, bioactive technology, applied in the field of porous polyaryletherketone materials and their preparation, can solve problems such as limited mechanical bonding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] The specific preparation steps of the porous PEKK material in this embodiment are as follows:
[0079] 1) Weigh 0.20g of PEKK powder (powder particle size is 50 mesh), mix it with an appropriate amount of ethanol, and put it into the mold, apply a pressure of 42Mpa to compact;
[0080] 2) Weigh out 0.08g of PEKK powder and 0.40g of HA spherical particles and mix them evenly, then add an appropriate amount of ethanol and then perform wet mixing;
[0081] 3) Then add the uniformly mixed material in step 2) to the mold to spread it on top of the compacted material in step 1), and heat to 380°C;
[0082] 4) While applying pressure (40MPa) to the mold, heat and keep the pressure for 1 hour, after natural cooling, demold and take out the sample to obtain the mixed material body;
[0083] 5) Put the green sample obtained in (4) into hydrochloric acid and stir for 3 hours to remove the HA spherical particles to obtain porous PEKK, put it in deionized water for ultrasonic cleaning for 15 ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Comparative experiment before and after chemical modification
[0087] The specific preparation process of the chemically modified porous PEKK-P (sulfonated porous PEKK-SP) material in this example is as follows: The porous PEKK-P sample prepared in Example 1 is put into 60wt% sulfuric acid for modification. After treatment for 1 hour, put it into deionized water and ultrasonic treatment for 15 minutes, repeat washing 4 times and then dry for 5 hours to obtain sulfonated porous PEKK-SP, which is recorded as sample 2.
[0088] Using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) to analyze the sulfonated porous PEKK ( Image 6 b) Sample and porous PEKK ( Image 6 a) The surface morphology and physical and chemical properties of the sample are compared and characterized, such as Image 6 with Figure 8 As shown, after chemical modification, on the one hand, the surface of the material can have a three-dimensional interconnected microporous structure, and on t...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Comparative test before and after bone-like apatite deposition
[0091] The specific preparation steps of the biologically active porous PEKK-P material in this example are as follows: soak the sulfonated porous PEKK-SP in simulated body fluid (SBF) to deposit bone-like apatite, take it out after 7 days and clean it with deionized water. Dry for 3 hours to obtain a bioactive porous PEKK-BSP material, which is recorded as sample 3. As a comparison, the porous PEKK without sulfonation treatment prepared in Example 1 was subjected to the operation of depositing bone-like apatite under the same conditions, and the obtained product was recorded as sample 4.
[0092] In this embodiment, the simulated body fluid (SBF) can be a commercially available simulated body fluid, or it can be configured according to the following components: Na + (140-150mM), K + (4-6mM), Mg 2+ (1-3mM),Ca 2+ (2-4mM),Cl - (140-150mM), HCO 3 - (3-10mM), HPO 4 - (0.5-1.0mM), SO 4 2- (0.5-1.0mM), pH (7.0-7.5). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com