Extracting agent, extraction system and application
An extraction agent and extraction technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of poor separation ability of heavy rare earth elements, poor extraction and stripping performance, easy emulsification cost, etc., to help protect the environment and save the amount of acid and alkali , the effect of reducing pollutant emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] The water phase refers to the water phase containing rare earth ions, wherein, the preparation method of the water phase containing rare earth ions includes the following steps: mixing the rare earth oxide with concentrated hydrochloric acid, and adding a salting-out agent (generally sodium chloride) , and then diluted to the desired concentration. Among them, the rare earth ions are all +3 valence. The pH of the aqueous phase is between 1.0-3.0. Wherein, the molar concentration of the salting-out agent in the water phase is generally 0.5mol / L-2.0mol / L.
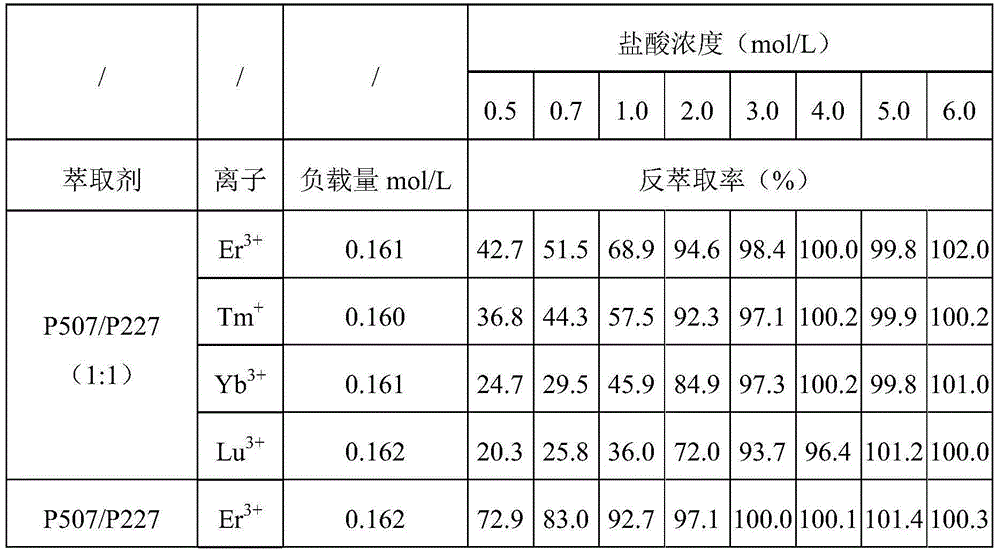
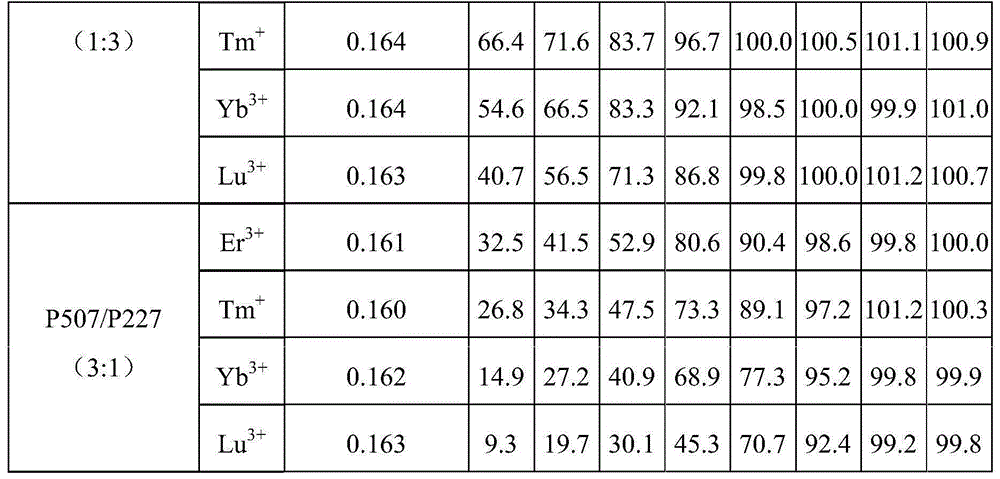
[0044] The extraction system including organic phase and aqueous phase is referred to as P507-P227 extraction system. The distribution ratio D is the rare earth content in the equilibrium organic phase and the rare earth content in the equilibrium water phase after an extraction is completed (the rare earth content in the water phase is measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), a...
Embodiment 1
[0053] Extraction and Separation of Rare Earth Elements by P507-P227 Extraction System
[0054] Organic phase: 0.50mol / LP507 and P227(n P507 :n P227 =1:1) n-dodecane solution
[0055] Water phase: 1.0M NaCl solution containing 0.01mol / L single rare earth ion, pH=3.0, that is, the water phase contains rare earth ion and salting-out agent NaCl, wherein the molar concentration of rare-earth ion is 0.01mol / L, salting-out agent NaCl The molar concentration is 1.0mol / L, and the pH value of the aqueous phase is 3.0.
[0056] Compared to (O:A)=1:1(5mL:5mL)
[0057] The organic phase was mixed with the aqueous phase, and shaken and equilibrated at 25°C for 30min. The extraction data of rare earth elements by the P507-P227 extraction system is shown in Table 1 below. It can be seen from the data in Table 1 that the average separation coefficient of the P507-P227 extraction system for rare earth elements is 2.55, which can effectively separate adjacent rare earth elements; heavy rar...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Extraction and Separation of Rare Earth Elements by P507-P227 Extraction System
[0062] Organic phase: 0.50mol / LP507 and P227(n P507 :n P227 =1:1) kerosene solution
[0063] Water phase: 1.0M NaCl solution containing 0.01mol / L single rare earth ion, pH=3.0
[0064] Compared to (O:A)=1:1(5mL:5mL)
[0065] The organic phase was mixed with the aqueous phase, and shaken and equilibrated at 25°C for 30min. The extraction data of the rare earth elements by the P507-P227 extraction system is equivalent to that of Example 1. Among them, the average separation coefficient of P507-P227 extraction system for rare earth elements is 2.45, which can effectively separate adjacent rare earth elements; the average separation between heavy rare earth elements Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and Y The coefficient is 2.43.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com