Method for directly obtaining martensite die steel through laser 3D printing technology
A 3D printing and martensite technology, which is applied in the field of laser 3D printing rapid manufacturing of directly obtained martensitic die steel, can solve the problems of high scrap rate, complex process and high cost, reduce brittleness, avoid traditional processes, mechanical Excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
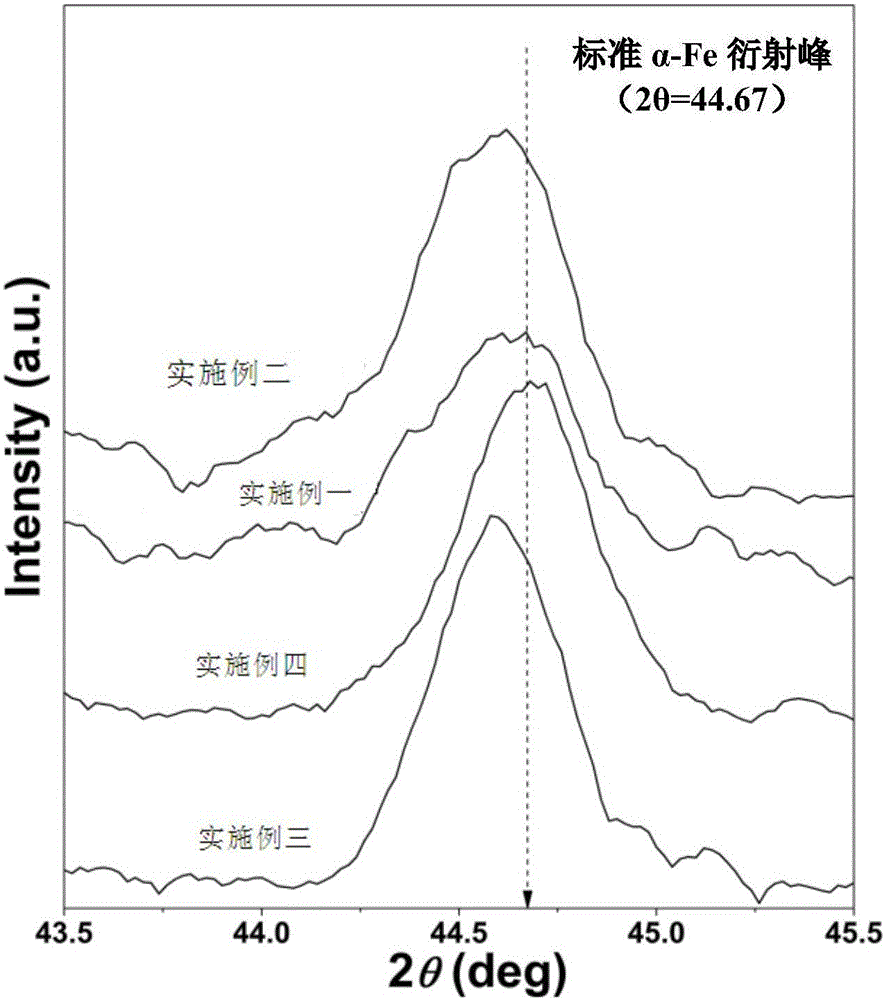
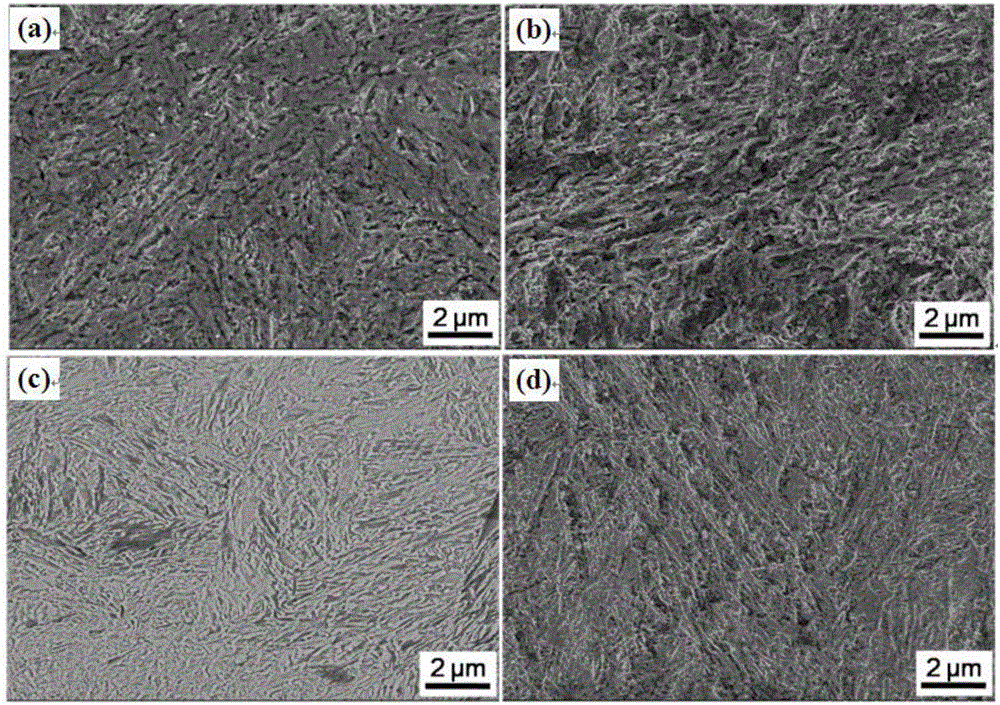
Embodiment 1
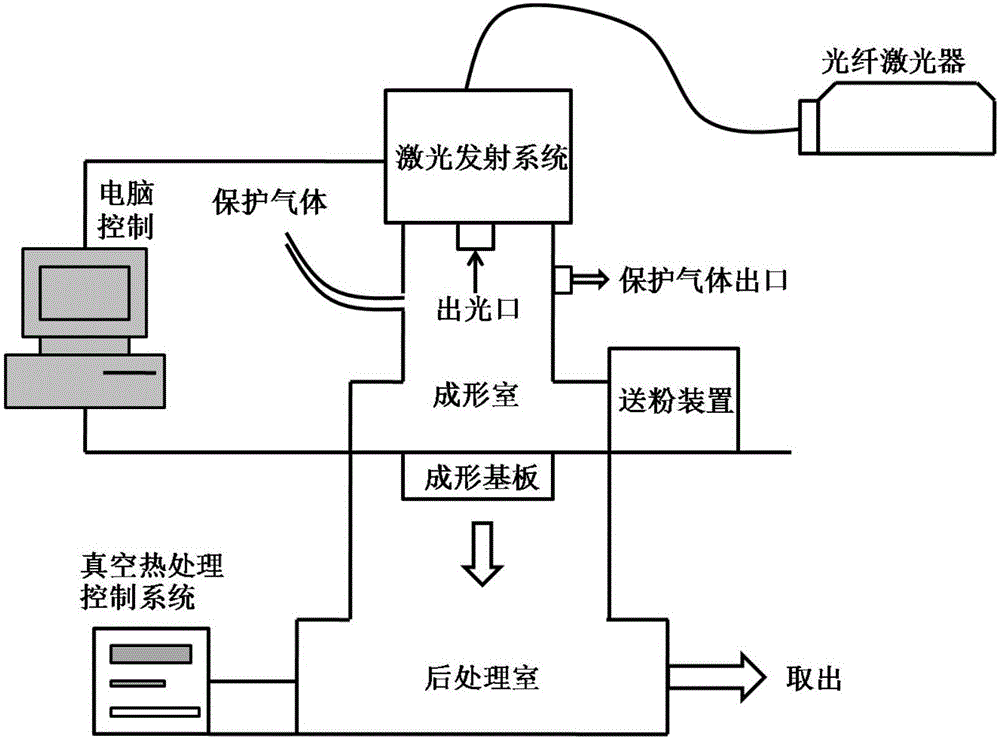
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for directly obtaining martensitic die steel using laser 3D printing technology described in the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0035] (1) Establish the geometric model of the mold on the computer, use the slicing software to carry out layered discretization of the geometric model, and generate a scanning model from the two-dimensional geometric contour.
[0036] (2) Add Mn, Ni, and Cr powders of the same particle size and shape to the iron powder, the average particle diameter of the iron powder is 60 μm, and the mass percentages of Mn, Ni, and Cr powders added are 2.0%, 4.0%, and 1.2% respectively ; After mixing the metal powder evenly, put it into a drying oven for drying treatment for 8 hours.
[0037] (3) Fix the substrate horizontally on the forming cylinder, adjust the height of the horizontal substrate and the scraper to a suitable position, and ensure that the scraper can smoothly send the metal powder ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment one is that the distribution ratio of each component in the metal powder and the laser process parameters in step (6) are changed, specifically:
[0047] The mass percentages of Mn, Ni, Cr powder added are 2.2%, 3.6%, 1.4% respectively
[0048] The laser power is set to 60W, the scanning speed is set to 400mm / s, and the laser line energy density η is 150J / m at this time. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the distribution ratio of each component in the metal powder and the laser process parameters in step (6) are changed,
[0051] The mass percentages of Mn, Ni, Cr powder added are 2.1%, 4%, 1.3% respectively
[0052] The laser power is set to 80W, the scanning speed is set to 200mm / s, and the laser line energy density η is 400J / m at this time.
[0053] Others are the same as the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Coefficient of friction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wear rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com