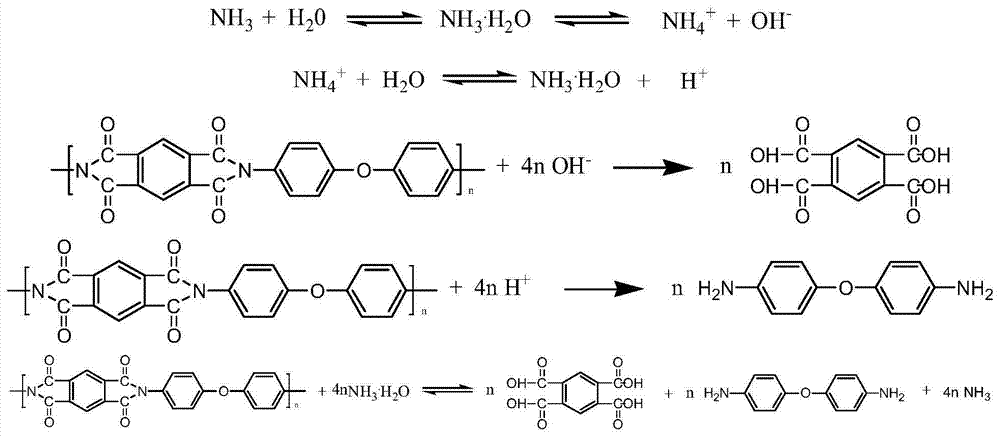
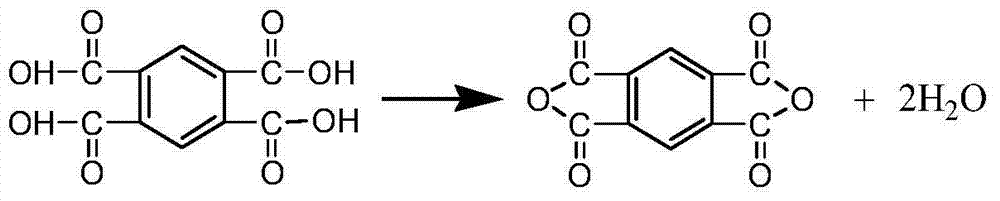
Modified polyimide film and modified polyimide precursor composite film waste material recovery processing method
A polyimide precursor and polyimide film technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of unspecified separation of inorganic nano-fillers, difficulty in recycling and processing, etc., and achieve the effects of shortening time, improving purity, and increasing reaction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Preparation of glass fiber (GF) suspension
[0032] Using 12.5g of nano-sized glass fiber (GF), add 2000ml of aprotic solvent N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), under the condition of 20kHz ultrasonic dispersion, fully stir for 60min to make a stable suspension.
[0033] (2) Preparation of modified polyamic acid composite solution
[0034] Add the suspension obtained above into the polyamic acid polymerization reactor, control the temperature at 10-60°C, add 239.3g of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether, and carry out mechanical stirring. After it is completely dissolved, the temperature Between 50 and 60°C, add 260.7 g of pyromellitic dianhydride in batches while stirring to prepare a polyamic acid composite solution with uniform viscosity and stability.
[0035] (3) Preparation of modified polyimide film and its polyimide precursor composition film
[0036] Put the polyamic acid composite solution obtained above to form a liquid film on a clean steel plate, put it in an oven,...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Replace the glass fiber (GF) in Example 1 with silica, the yield of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether is 63.7g, the product purity is 99.9%, and the melting point is 191-192°C. The yield of the pyromellitic dianhydride product was 69.0 g. The product has a purity of 99.5% and a melting point of 284-285°C. Except above changes, other operation steps and product quality are consistent with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Change glass fiber (GF) into alumina (Al 2 o 3 ), the yield of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether was 63.5g. The purity of the product is 99.9%, and the melting point is 191-192°C. The yield of the pyromellitic dianhydride product was 68.5 g. The product has a purity of 99.5% and a melting point of 284-285°C. Except above changes, other operation steps and product quality are consistent with embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com