Bilobalide B-sirolimus asymmetric compound drug eluting stent and preparation method thereof
A technology of ginkgolide and sirolimus, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of unsolved delay in endothelialization, and achieve the effects of promoting rapid endothelialization, good biological stability, and inhibiting restenosis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of ginkgolide B-sirolimus asymmetric composite drug-eluting stent
[0026] Step 1, preparation of coating drug: mix ginkgolide B and polylactic acid at a ratio of 1:1 (mass ratio) to form a "serum" for later use. Mix sirolimus and polylactic acid at a ratio of 1:1 (mass ratio) to form a "slurry" for later use.
[0027] Step 2, apply medicine to the inner and outer surfaces (blood surface) of the asymmetric stent
[0028] The mixture of ginkgolide B and polylactic acid was sprayed on the inner and outer surfaces of the stent by spraying method. According to the calculation by weighing method, each 10mm stent contained 10ug of ginkgolide B on average, and dried at low temperature for storage.
[0029] Step 3, apply medicine to the outer surface of the asymmetric stent (vessel wall)
[0030] Apply the mixture of sirolimus and polylactic acid on the outer surface of the stent (vessel wall) by roller coating method. According to the calculatio...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Observation of the physicochemical properties of ginkgolide B-sirolimus asymmetric composite drug-eluting stent
[0032] (1) Detection of coating adhesion of ginkgolide B-sirolimus asymmetric composite drug-eluting stent:
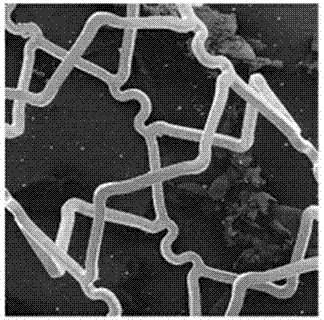
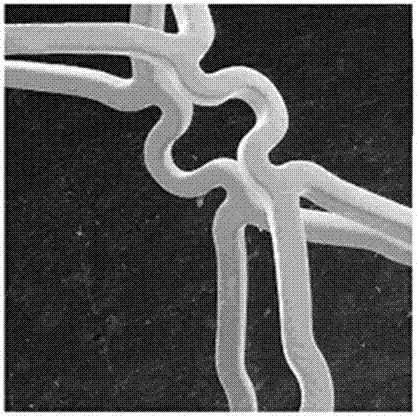
[0033] The developed stent was embedded on the surface of the balloon, and the ginkgolide B-sirolimus asymmetric composite drug-eluting stent was expanded under 12 atmospheres for 12 seconds, and the surface of the stent was uniform and smooth as observed by scanning electron microscopy ( Figure 1a ), under a 100x electronic scanning microscope ( Figure 1b ), the stent showed no significant tearing of the coating, and the coating could be stably applied to the surface of the bare metal stent.
[0034] (2) Detection of coating thickness of ginkgolide B-sirolimus asymmetric composite drug-eluting stent:
[0035] The coating thickness of the stent was measured by a scanning electron microscope, and the coating thickness of the stent was abo...
Embodiment 3
[0041]The preparation method is the same as in Example 1, except that in step 1, ginkgolide B and polylactic acid are mixed at a mass ratio of 1:0.7 to form a "serum" for later use. Mix sirolimus and polylactic acid at a mass ratio of 1:0.7 to form a "slurry" for later use.
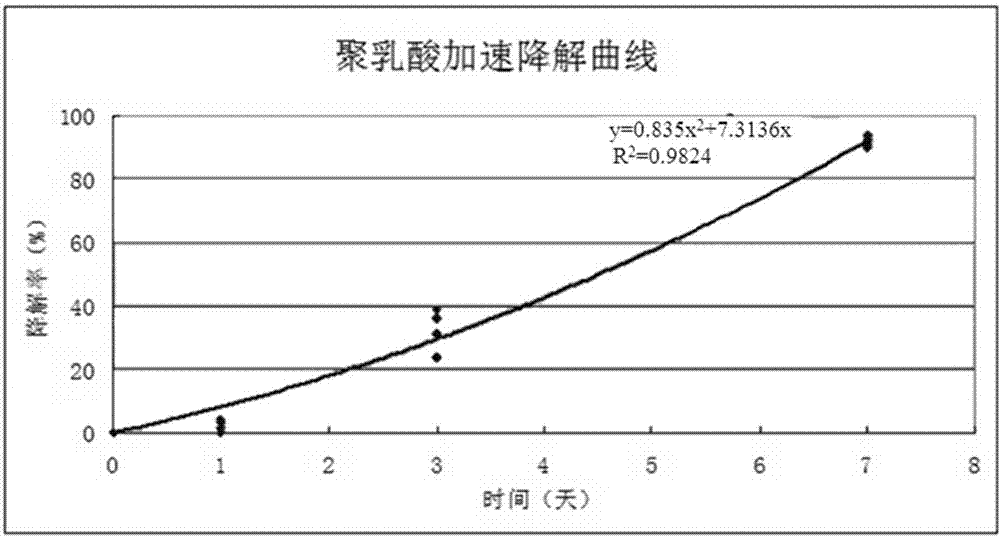
[0042] The prepared asymmetric composite drug-eluting stent was tested by the same method as in Example 2, and the results showed that the stent showed no obvious tearing of the coating, and the coating could be stably applied to the surface of the bare metal stent. The degradation rate of polylactic acid of the scaffold reached 90%, and the drug release rate reached 82%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com