Method for preparing resistant starch employing microwave technology
A technology of resistant starch and starch, which is applied in the field of starch processing, can solve the problems of low content of resistant starch, long aging process, low production efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, product safety and stable structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Preparation of resistant starch by microwave post-treatment
[0025] Weigh 0.75 kg of high-amylose corn starch (amylose content is 70%), add 4.25 kg of tap water to make the starch slurry concentration 15%, shake at room temperature for 5 minutes, and mix the starch and water evenly to obtain a starch slurry sample. The obtained starch slurry sample was pregelatinized at 100° C. for 30 min. Put the pregelatinized starch in an autoclave at a temperature of 121 °C and a pressure of 0.1 MPa for 30 minutes, and then adjust the pH to 6.0 after cooling to 85 °C, and add 20 U / g of starch high temperature resistant α - Amylase (Shanghai Jingchun Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Aladdin Reagent), at a temperature of 85° C., enzymolysis for 15 minutes. Adjust the pH to 5.2, add 30 U / g of starch pullulanase (Genencor, USA), and enzymolyze for 4 hours at a temperature of 50°C, so that the length of the starch chain segment is 20-110DP. The material after enzymatic hydr...
Embodiment 2
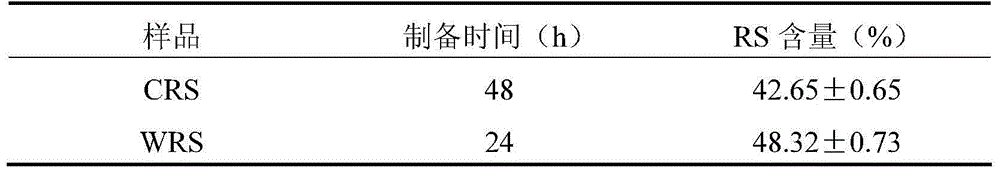
[0028] Embodiment 2: the impact of enzymatic hydrolysis on the preparation of resistant starch
[0029]The basic preparation method of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1. The difference of this embodiment is that after the autoclave treatment, the material is divided into two parts: enzymatic hydrolysis and non-enzymatic hydrolysis. Among them, the enzymatic hydrolysis part is to cool the pregelatinized material to 85 ° C, adjust the pH to 6.0, add 20 U / g starch of high temperature resistant α-amylase (Shanghai Crystal Pure Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Aladdin reagent), at temperature Enzymatic hydrolysis for 15 minutes at 85°C. Adjust the pH to 5.2, add 30 U / g of starch pullulanase (Genencor, USA), and enzymolyze for 4 hours at a temperature of 50°C, so that the length of the starch chain segment is 20-110DP. Spread the enzymatically hydrolyzed material and another part of the material on the flat plate separately, so that the thickness of the starch l...
Embodiment 3
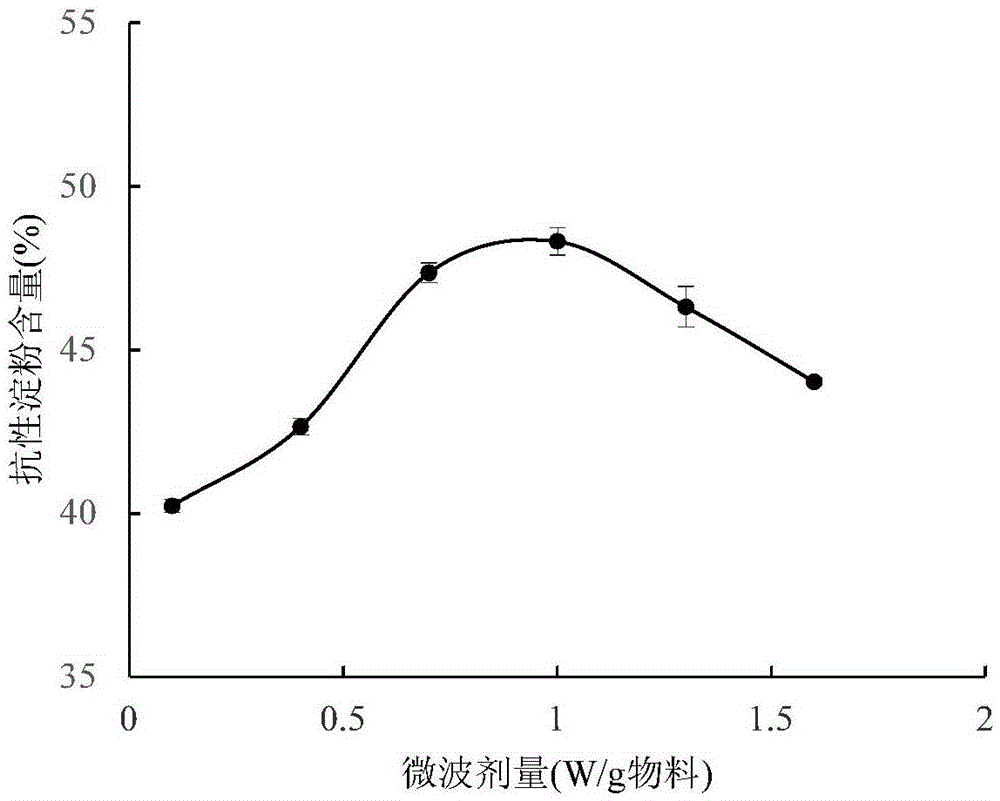
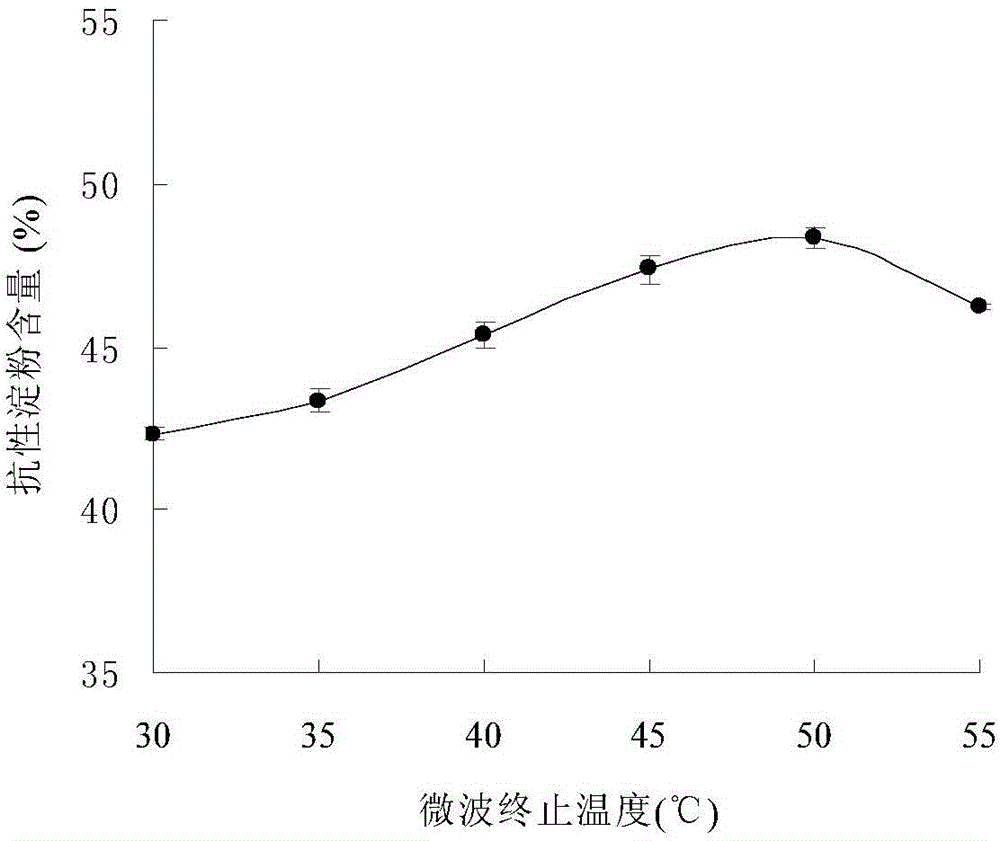
[0032] Embodiment 3: the impact of microwave dose and microwave termination temperature on the preparation of resistant starch
[0033] The basic preparation method of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1. The difference is that the sample is enzymatically hydrolyzed and spread on the plate so that the thickness of the starch layer is 0.1-2mm, and then the plate is placed at 4°C for 4 hours, the plate is taken out, and the plate is placed in a microwave oven. The power of the microwave oven is adjusted to 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 1.0, 1.3, 1.6w / g material, dry the material, when the temperature of the material reaches 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55 ℃, take out the material and cool it to room temperature, and continue to place it in 4 Under the condition of ℃ for 4 hours, the above steps were repeated 3 times, and the water content of the starch was measured to be 14%. The dried sample was placed in a pulverizer for pulverization, and passed through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com