Porous decellularized tissue engineering cartilage support and preparation method thereof
A tissue engineering and decellularization technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of low initial mechanical strength and inability to completely simulate the performance of natural cartilage, and achieve good biomechanical properties, easy operation and simple technical requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] (1) Take the cartilage of the femoral condyle of fresh adult porcine, remove the surrounding tissue, wash with a sterilized distilled water spray gun under high pressure, and remove blood components and adipose tissue as much as possible.
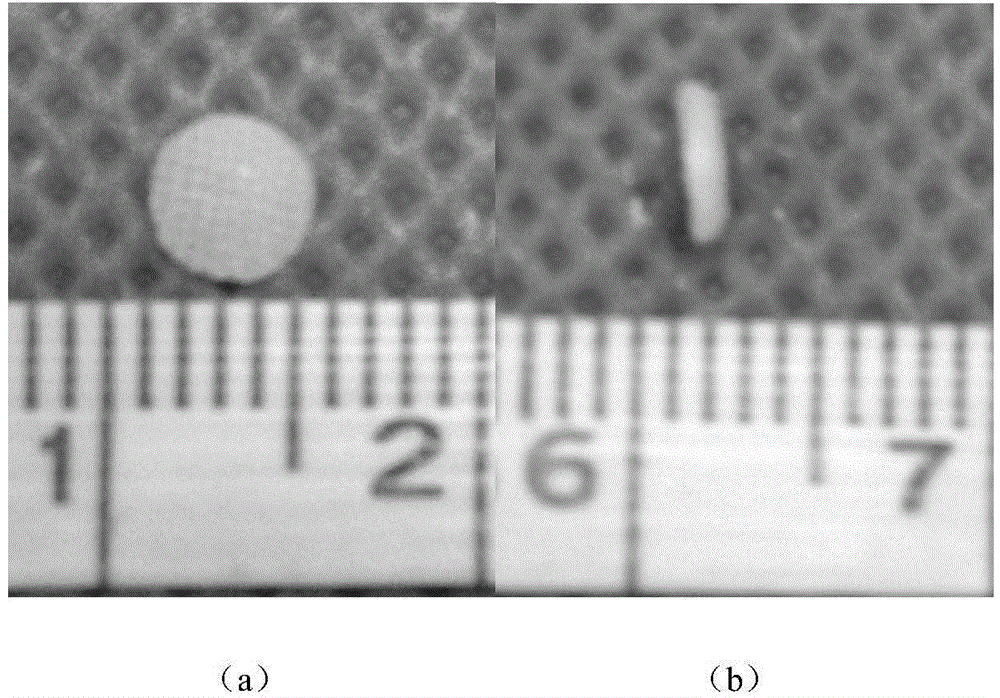
[0039] (2) The obtained cartilage was made into 5 cylindrical cartilage slices with a diameter of 4 mm and a thickness of 2 mm (see figure 1 ).
[0040] (3) After being stored at -24°C for 24 hours, it was frozen in a -80°C refrigerator for 72 hours and then taken out.
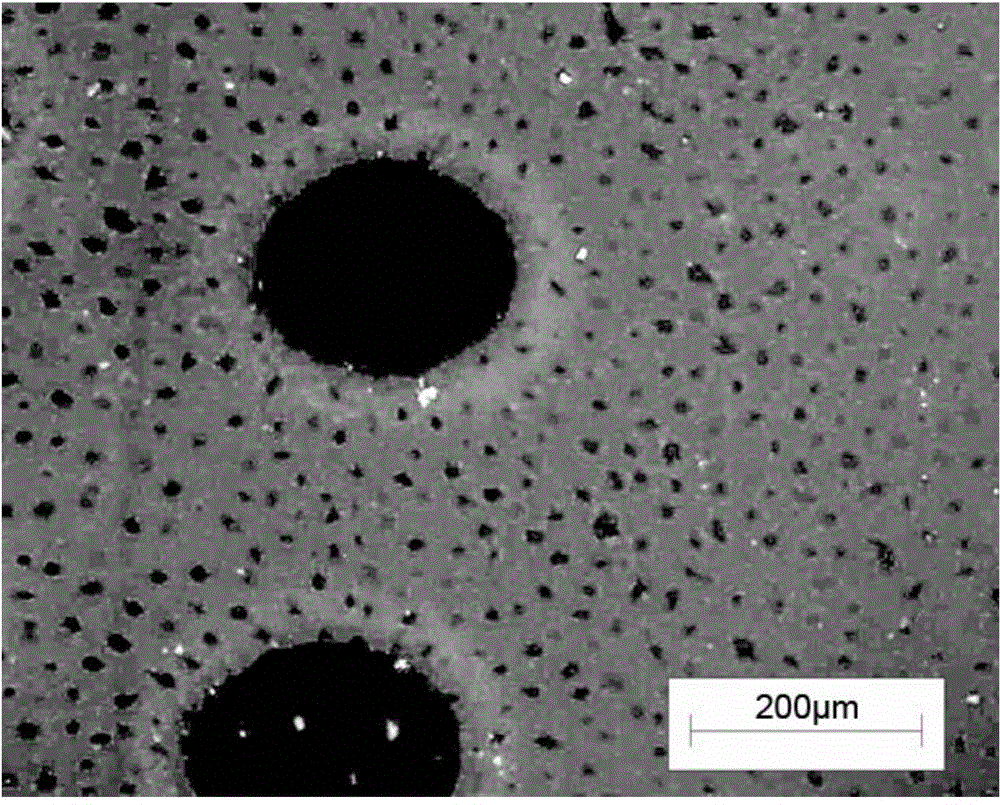
[0041] (4) Soak the prepared tissue engineered cartilage slices in 0.01MPBS buffer solution, and drill holes on the soaked cartilage slices with a carbon dioxide laser puncher. The hole diameter is 300 μm, the hole spacing is 300 μm, and the porosity is 85%.
[0042] (5) After drilling, rinse and soak the porous tissue engineered cartilage sheet prepared in step (4) with sterile three-distilled water, freeze at -20°C for 24 hours, then transfer to -80°C for 72 hours...
Embodiment 2
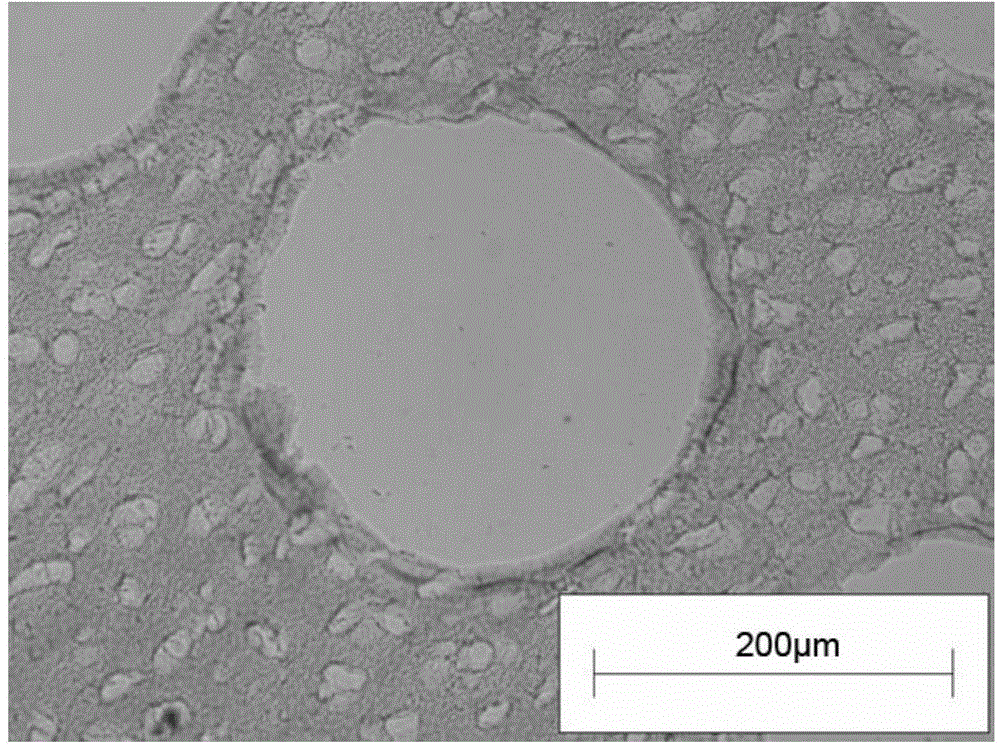
[0046] Frozen sections of the prepared scaffolds were stained with Hoechst 33258 (see figure 2 ), without nuclear staining, indicating that the cartilage slices were successfully decellularized; HE staining (see image 3 ), toluidine blue staining (see Figure 4 ), showing the microstructure of the tissue engineered cartilage scaffold; scanning electron microscopy shows the internal structure of the tissue engineered cartilage scaffold (see Figure 5 ).
[0047] The prepared tissue engineered cartilage scaffold and the cartilage tissue of the same size were subjected to biomechanical tests, and the compression elastic modulus of the prepared cartilage scaffold was 0.5734 ± 0.021Mpa, which was statistically different from normal articular cartilage (0.6875 ± 0.013Mpa) ( *P Image 6 ).
[0048] Inoculate mouse fibroblast L929 in a 96-well plate, and set up three groups, namely negative control group, test group, positive control group, normal culture medium was added to the n...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com