Method for preparing poly sulfoacid inner salt anticoagulant biomaterial via atom transfer radical polymerization
A biological material, atom transfer technology, applied in anticoagulant treatment, packaging item types, special packaging items, etc., to achieve the effects of controllable relative molecular mass, wide range of applicable monomers, and good anticoagulant properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
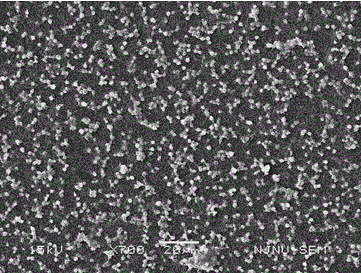
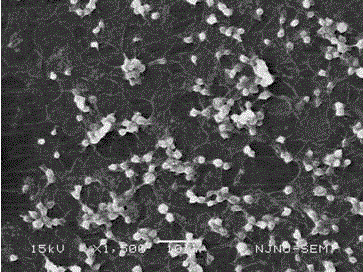
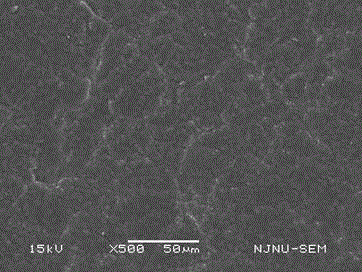
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A kind of preparation method of the anticoagulant polyurethane film of surface graft polyammonium sulfonate inner salt, concrete steps are as follows:
[0026] (1) Membrane activation
[0027] Add 0.010g of dibutyltin dilaurate as a catalyst to the toluene solution of 0.6mol / L hexamethylene diisocyanate, put a polyurethane (PU) diaphragm when heated to 50°C, take it out after 2.5h, and use toluene and ethanol respectively , washed with distilled water several times, and dried under vacuum at 40°C.
[0028] (2) Immobilization of initiator (containing bromine group)
[0029] Under nitrogen protection, 0.075 g of triethylamine was added as a catalyst to 1.4 mol / L 2-bromoethanol in methanol solution, and the activated membrane in step (1) was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. After the reaction, the membrane was washed several times with methanol and distilled water to remove unreacted 2-bromoethanol, and dried under vacuum at 40° C. for 5 h. Accurately weigh the drie...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A kind of preparation method of the anticoagulant polyurethane film of surface graft polyammonium sulfonate inner salt, concrete steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) Membrane activation
[0038] Add 0.010g of dibutyltin dilaurate as a catalyst to the toluene solution of 0.6mol / L hexamethylene diisocyanate, put the diaphragm in when heated to 50°C, take it out after 2.5h, and wash it with toluene, ethanol, and distilled water respectively. times, dried under vacuum at 40°C.
[0039] (2) Immobilization of initiator (containing bromine group)
[0040] Under nitrogen protection, 0.075 g of triethylamine was added as a catalyst to 1.4 mol / L 2-bromoethanol in methanol solution, and the activated membrane in step (1) was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. After the reaction, the membrane was washed several times with methanol and distilled water to remove unreacted 2-bromoethanol, and dried under vacuum at 40° C. for 5 h. Accurately weigh the dried membrane.
[0041] (3) A...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A kind of preparation method of the anticoagulant polyurethane film of surface graft polyammonium sulfonate inner salt, concrete steps are as follows:
[0046] (1) Membrane activation
[0047] Add 0.010g of dibutyltin dilaurate as a catalyst to the toluene solution of 0.6mol / L hexamethylene diisocyanate, put the diaphragm in when heated to 50°C, take it out after 2.5h, and wash it with toluene, ethanol, and distilled water respectively. times, dried under vacuum at 40°C.
[0048] (2) Immobilization of initiator (containing bromine group)
[0049] Under nitrogen protection, 0.075 g of triethylamine was added as a catalyst to 1.4 mol / L 2-bromoethanol in methanol solution, and the activated membrane in step (1) was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. After the reaction, the membrane was washed several times with methanol and distilled water to remove unreacted 2-bromoethanol, and dried under vacuum at 40° C. for 5 h. Accurately weigh the dried membrane.
[0050] (3) A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com