A method and device for treating organic solid waste
A technology for organic solids and waste, applied in the field of waste treatment, can solve the problems of reducing the output of organic fertilizer, unable to raise the temperature quickly, and incomplete treatment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
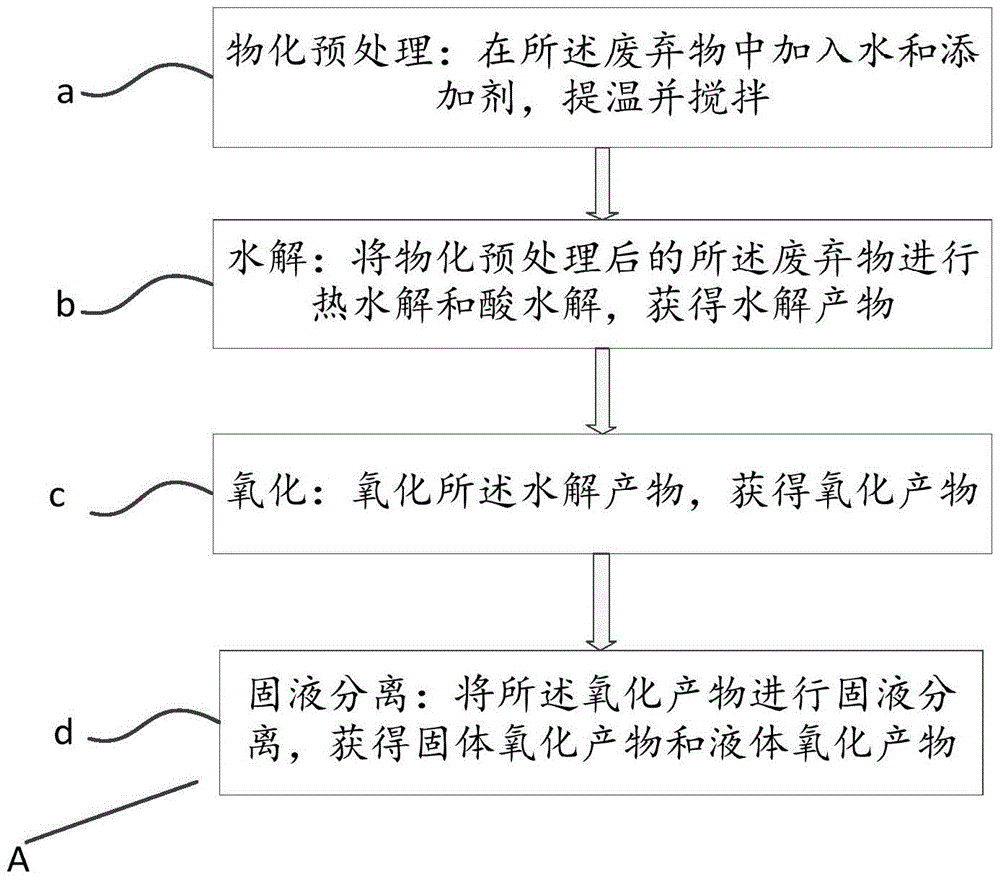
[0098] The following first introduces the method for processing organic solid waste, specifically including: a physical and chemical pretreatment: add water and additives to the waste, raise the temperature, and stir; b hydrolysis: carry out the physical and chemical pretreatment of the waste Thermal hydrolysis and acid hydrolysis to obtain a hydrolyzate; c oxidation: oxidize the hydrolyzate to obtain an oxidized product; d solid-liquid separation: perform solid-liquid separation on the oxidized product to obtain a solid oxidized product and a liquid oxidized product.
[0099] figure 1 A flow chart of method A for treating organic solid waste according to an embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0100] The method for treating organic solid wastes of the present invention can be applied to the recycling operations of most organic solid wastes. In order to achieve high-efficiency treatment and be applicable to different organic solid wastes, the unit operation and tre...
Embodiment 2
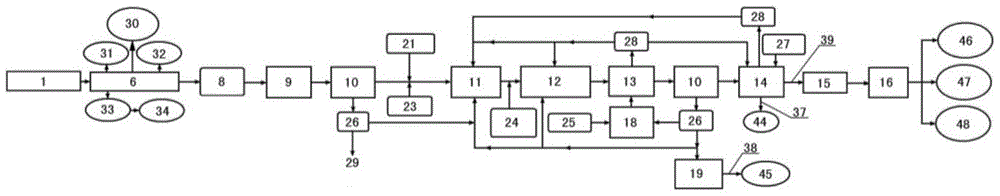
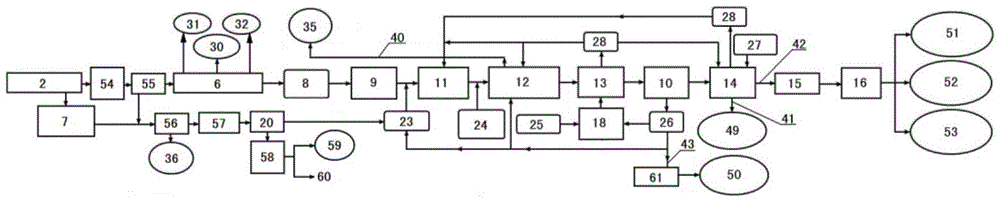
[0174] The apparatus for treating organic solid waste of the present invention is described below.
[0175] The device for treating organic solid waste of the present invention can be used for the treatment of any organic solid waste, and can be used for recycling the waste into various high-quality organic fertilizer products. Organic solid waste that can be treated includes: municipal waste, agricultural waste, green waste, sewage treatment plant sludge, animal waste, organic waste from some factories, such as waste from food, papermaking, oil refining, pharmaceutical and other factories, Sludge, some organically polluted lake or river silt, and old landfill waste / sludge, etc.
[0176] The device for treating organic solid waste of the present invention includes: a physical and chemical pretreatment tank 100 for containing and mixing the waste and water, the physical and chemical pretreatment tank includes a feed port and a discharge port; a hydrolysis tank 200, It is used ...
Embodiment 3
[0228]The domestic waste in a county-level city in China is currently treated with sanitary landfill and incineration power generation. However, during the treatment of domestic waste, it was found that the percolation water of the sanitary landfill method still seriously polluted the groundwater source, and the odor produced also caused pollution around the landfill. Moreover, the existing landfill area only allows a service life of about two to three years, and it is difficult to find other landfill sites at present. The current waste incineration plant is operated by a company, and after several years of operation, it is also found that it is losing money every month and may cause air pollution. In order to solve these problems, the city will use the active fertilizer method to deal with some of the domestic waste generated, and plans to process 100 tons of waste a day.
[0229] When carrying out active fertilizer production, it is first necessary to collect and analyze th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com