A heat-resistant titanium alloy and its processing and manufacturing method and application
A titanium alloy, hot working technology, applied in the field of titanium-based alloys, can solve the problems of affecting application, strength and toughness matching room temperature plasticity difference and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~6
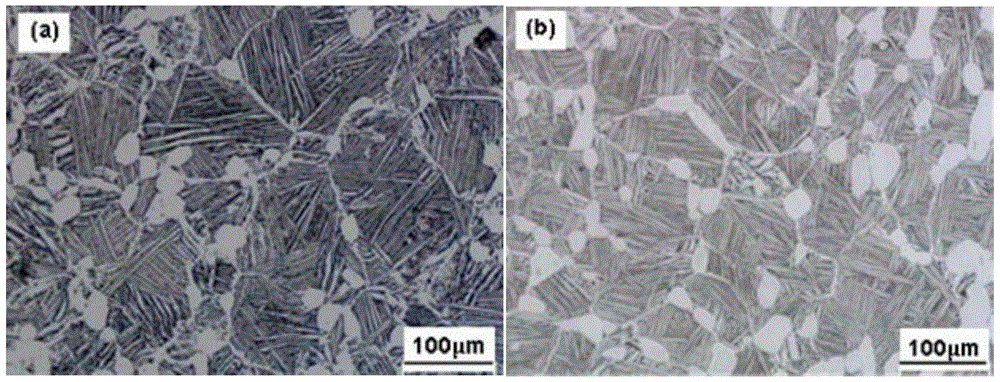
[0081] The ingredients of Examples 1-6 are listed in Table 2. Alloy smelting to make Φ220mm ingot, 1 # ~5 # The measured phase transition points of the component alloys are all 1045±5°C, so the same temperature is used for thermal processing and heat treatment. 6 # The transformation point of the alloy is 1037°C. After cutting off the cap of the ingot and peeling off the surface scale, the following thermal processing processes are used to obtain Φ27mm rods: the first fire, 1180°C, hydraulic press forging, Φ220mm→Φ170mm; the second fire, 1080°C, hydraulic press forging, Φ170mm→ Φ120mm; the third fire, 1025℃, precision forging machine forging, Φ120mm→Φ80mm; the fourth fire, 1015℃, precision forging machine forging, Φ80mm→Φ50mm; the fifth fire, 1000℃, precision forging machine forging, Φ50mm→Φ27mm. After the grinding wheel is blanked, heat treatment is carried out, and then the samples are processed and mechanical properties are tested. The results are shown in Table 3 and T...
Embodiment 7~11
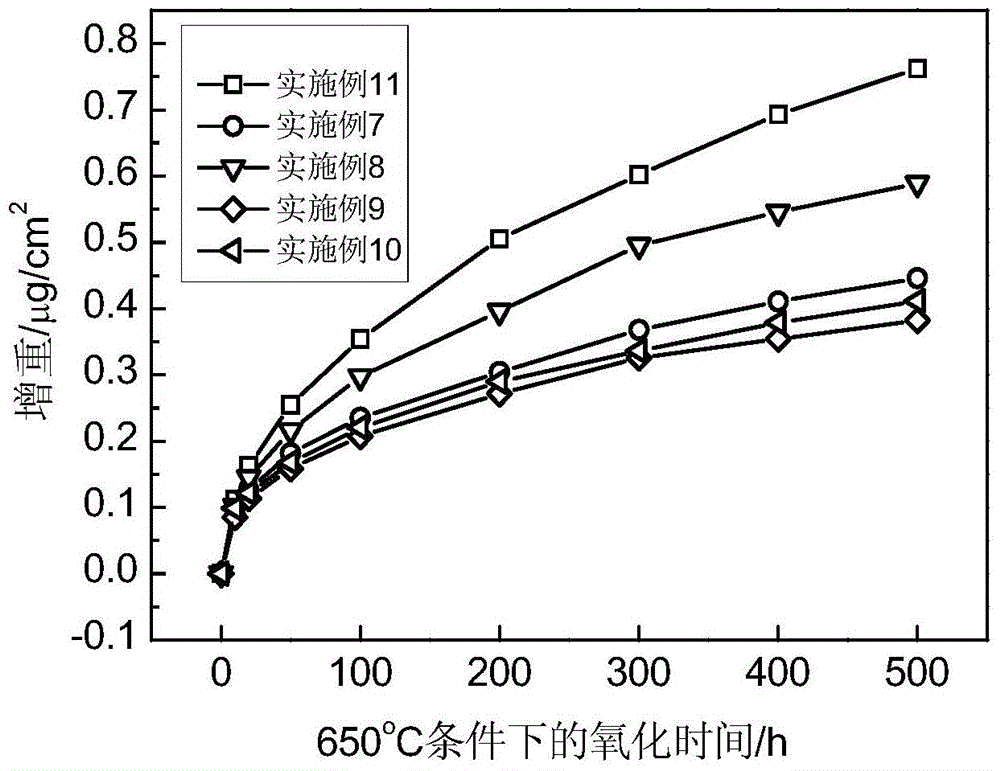
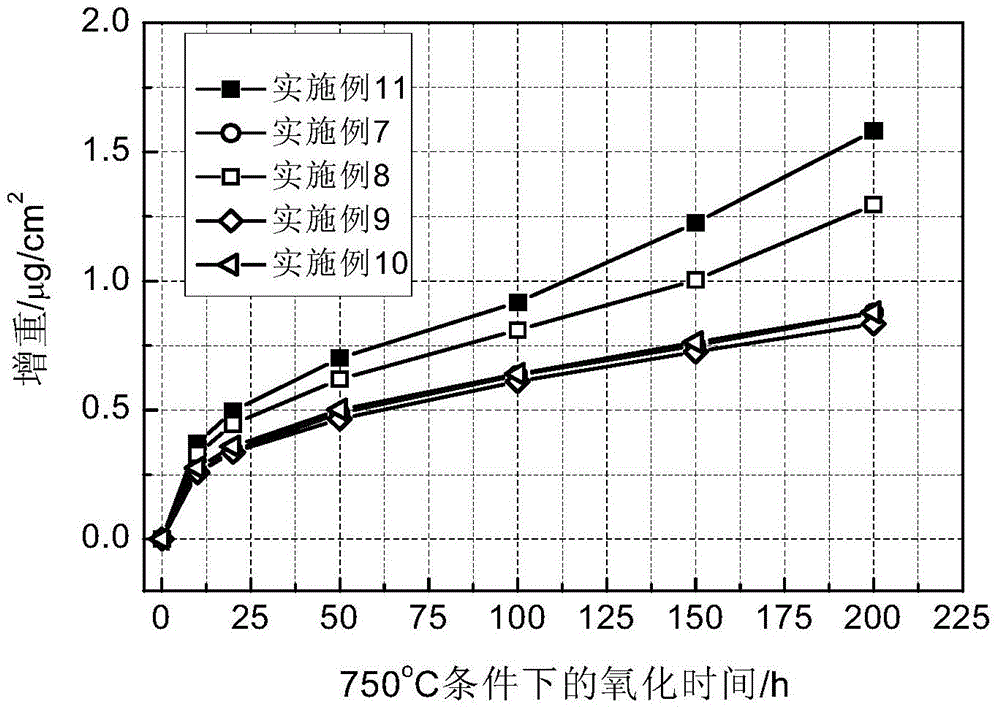
[0091] The measured components of Examples 7-11 are listed in Table 5. The alloy was smelted to produce a Φ220mm ingot, and the test results of the phase transition point are shown in Table 6. After cutting off the cap of the ingot and peeling off the surface scale, the Φ27mm bar is obtained by the following thermal processing process: the first fire, 1180°C, hydraulic press forging, Φ220mm→Φ170mm; the second fire, 1090°C, hydraulic press forging, Φ170mm→ Φ120mm; the third fire, 20℃ below the phase transition point in Table 6, precision forging machine forging, Φ120mm→Φ80mm; the fourth fire, 30℃ below the phase transition point in Table 6, precision forging machine forging, Φ80mm→Φ50mm; fifth Fire, 40°C at the phase transition point in Table 6, forged on a precision forging machine, Φ50mm→Φ27mm. After the grinding wheel is blanked, heat treatment is carried out, and then the samples are processed and the mechanical properties are tested. The results are shown in Tables 7-13. ...
Embodiment 12~15
[0114] The ingredients of Examples 12-15 are listed in Table 14. The alloy was smelted to produce a Φ220mm ingot, and the results of the phase transition point test are shown in Table 15. After cutting off the cap of the ingot and peeling off the surface scale, the following thermal processing processes are used to obtain Φ27mm rods: the first fire, 1180°C, hydraulic press forging, Φ220mm→Φ170mm; the second fire, 1080°C, hydraulic press forging, Φ170mm→ Φ120mm; the third fire, 10℃ below the phase transition point in Table 15, precision forging machine forging, Φ120mm→Φ80mm; the fourth fire, 20℃ below the phase transition point in Table 15, precision forging machine forging, Φ80mm→Φ50mm; fifth Fire, 35°C at the phase transition point in Table 15, forged with precision forging machine, Φ50mm→Φ27mm. After the grinding wheel is blanked, heat treatment is carried out, and then the sample is processed for mechanical performance testing. The results are shown in Tables 16-18.
[01...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com