Genetic engineering pseudomonas putida and construction method and application thereof
A kind of Pseudomonas putida, genetic engineering technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria and other directions, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of reaction control and production cost, and achieve simple operation, high transformation efficiency, Stable effect of strain passage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Construction of the hspB gene knockout plasmid pK18mob-hspB:
[0043] The bacterial strain used in this example is Pseudomonas putida XPSN (CCTCC No. M205038).
[0044] The composition of medium used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0045] LB liquid medium: yeast extract 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, tryptone 10g / L, pH 7.0. Sterilize with high temperature and high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes before use.
[0046] LB solid medium: add 1.5% (w / v) agar powder to LB liquid medium. Sterilize with high temperature and high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes before use.
[0047] (1) Amplify the 6-hydroxyl-3-succinylpyridine 3-hydroxylase gene (hspB) fragment:
[0048] Using the Pseudomonas putida XPSN genome as a template, PCR amplification was performed according to the method described in "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition)".
[0049] PCR amplification primer: upstream primer PH-F: 5′-ccg GAATTC ggggacaaatgtggtggtg-3', downstream primer PH-...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The hspB gene in the strain Pseudomonas putida XPSN was knocked out, and the genetic engineering strain Pseudomonas putida (Pseudomonas putida) P-HSP was constructed.
[0064] The knockout plasmid pK18mob-hspB was introduced into P. Inserted into the hspB gene, thereby inactivating the hspB gene.
[0065] The amphipathic hybrid recipient strain used in this example is Pseudomonas putida XPSN (CCTCC No. M205038).
[0066] The composition of medium used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0067] LB liquid medium: yeast extract 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, tryptone 10g / L, pH 7.0. Sterilize with high temperature and high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes before use.
[0068] LB solid medium: add 1.5% (w / v) agar powder to LB liquid medium. Sterilize with high temperature and high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes before use.
[0069] M9 citrate liquid medium: Liquid A: Dissolve 5 g of trisodium citrate in an appropriate amount of distilled water and set the volume...
Embodiment 3
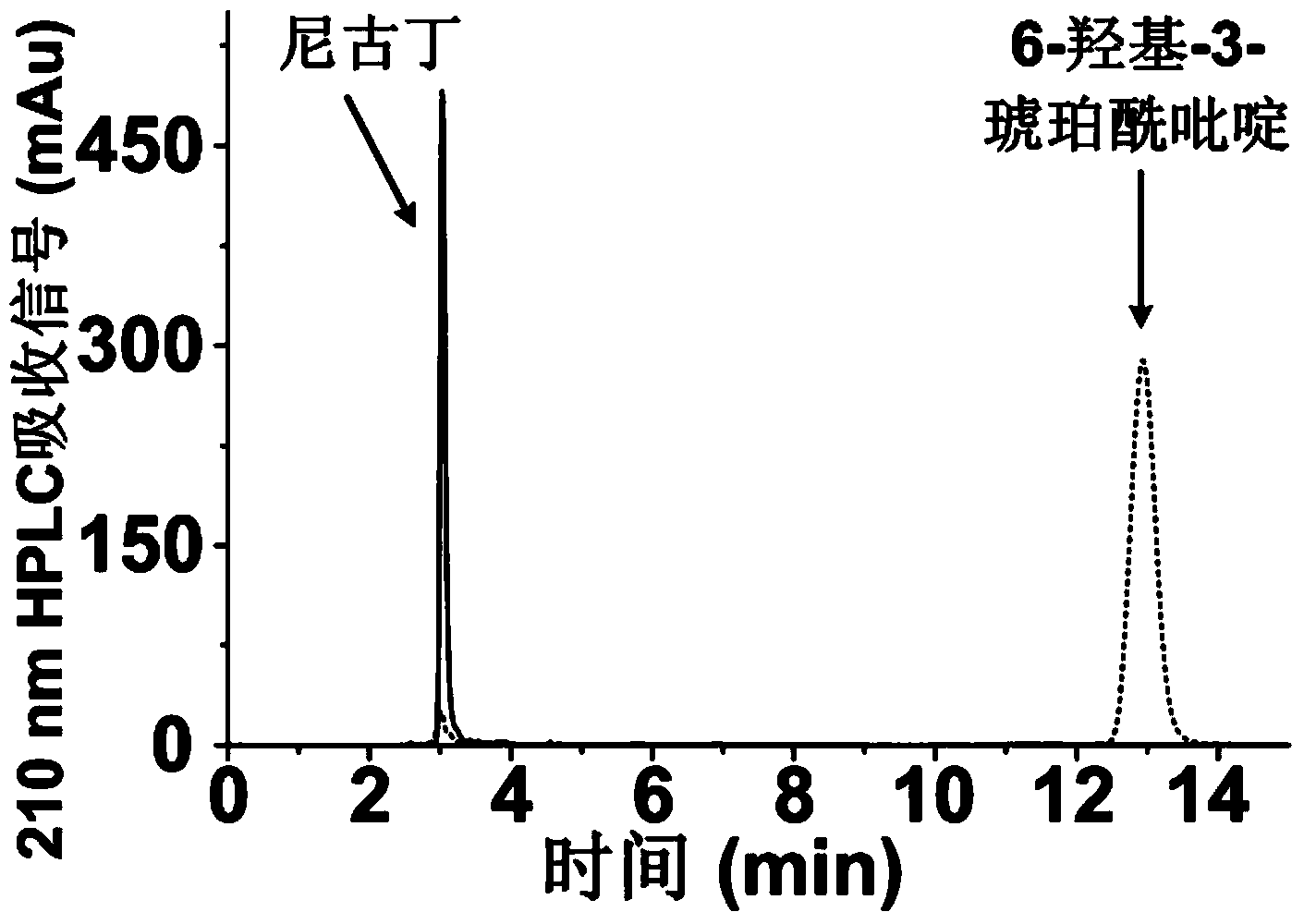
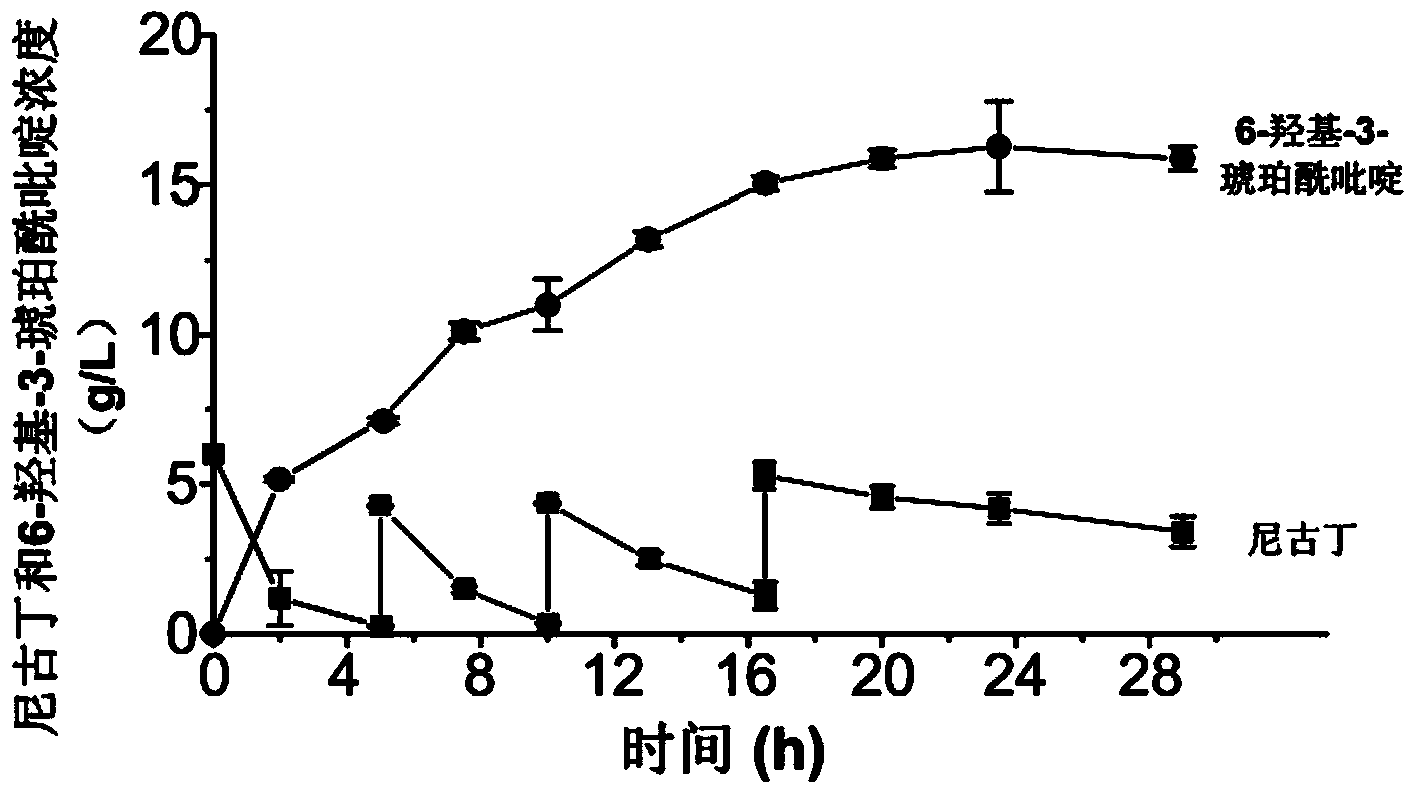
[0086] Production of 6-hydroxy-3-succinylpyridine by a method catalyzed by resting cells of Pseudomonas putida P-HSP
[0087] The strain used in this example is a genetically engineered strain of Pseudomonas putida P-HSP (the deposit number is CCTCC M2014135).
[0088] The composition of medium used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0089] LB liquid medium: yeast extract 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, tryptone 10g / L, pH 7.0. Sterilize with high temperature and high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes before use.
[0090] LB solid medium: add 1.5% (w / v) agar powder to LB liquid medium. Sterilize with high temperature and high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes before use.
[0091] In this embodiment, the steps for producing 6-hydroxyl-3-succinylpyridine using resting cell catalytic method are as follows:
[0092] (1) Slant culture: Pseudomonas putida P-HSP was inoculated on LB solid slant medium, and cultured at 30°C for 12 hours;
[0093] (2) Seed culture: Inoculate th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com