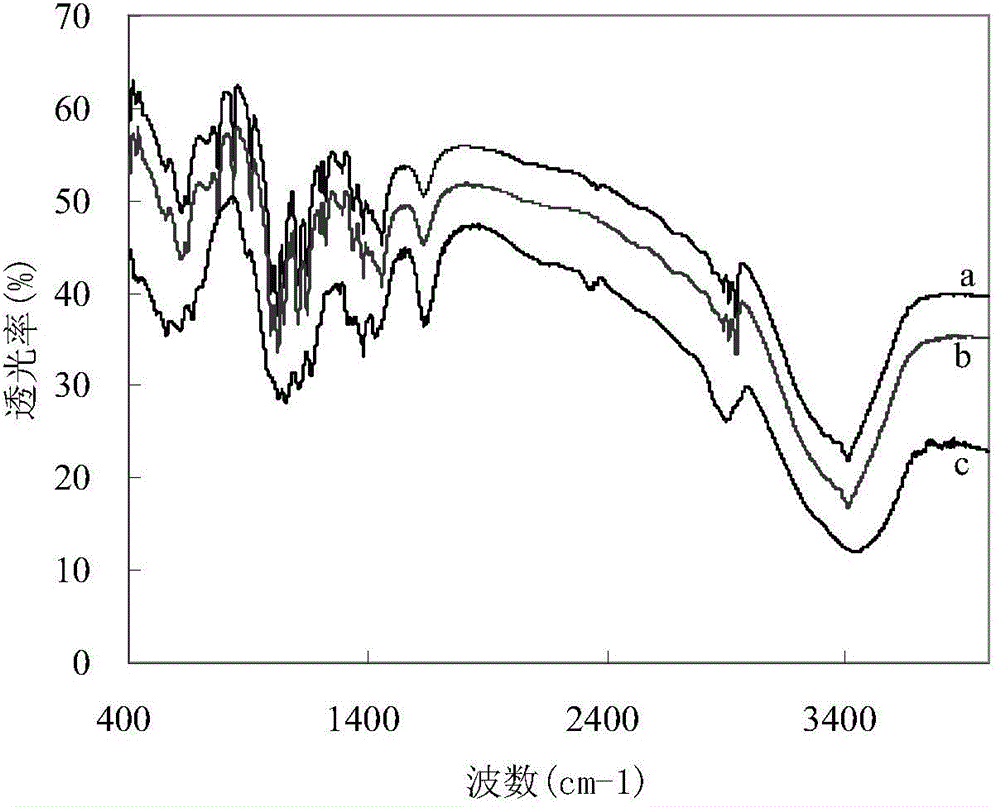
A kind of weak polar acid two-liquid phase catalyzed method for preparing glucose by hydrolysis of cellulose
A weak polarity and cellulose technology, applied in the field of glucose, can solve the problems of long hydrolysis time, low reaction efficiency, and difficult separation of catalyst and residue, and achieve high hydrolysis efficiency, low content of by-products, and shorten the hydrolysis time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Add 2% microcrystalline cellulose and 1% weakly polar catalyst into water, solvent ratio (non-polar: water) = 1:2, and hydrolyze at 190°C for 1 hour. Glucose was detected, and the comparison of the hydrolysis effect of the weak polar acid catalyst on microcrystalline cellulose is shown in Table 1.
[0020] Table 1
[0021]
[0022] It can be seen from Table 1 that the type of acid catalyst has a significant impact on the yield of glucose, and phthalic acid can obtain better results.
Embodiment 2
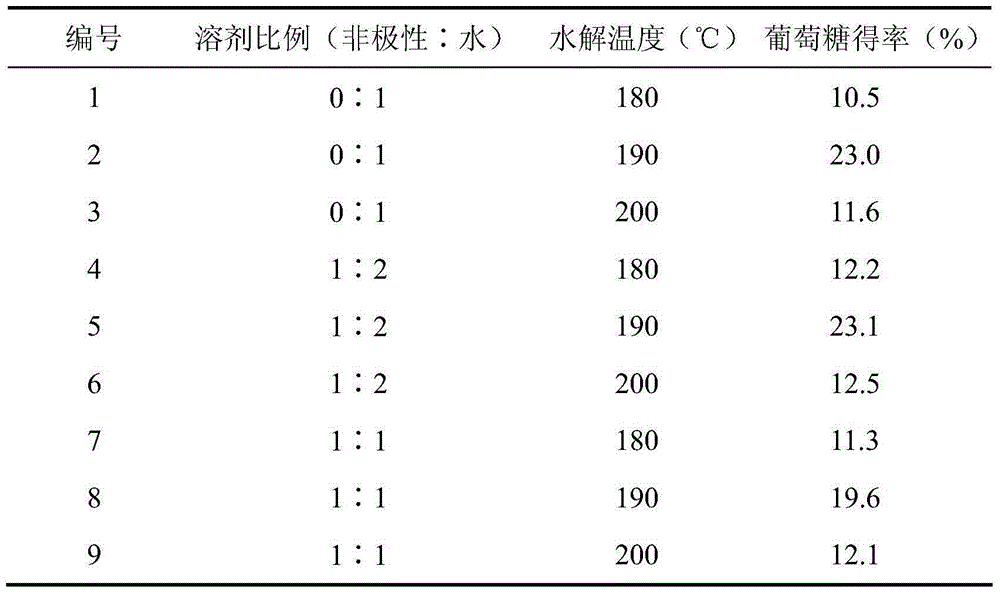
[0024] Add 2% microcrystalline cellulose and 1% phthalic acid into water, solvent ratio (non-polar: water) = 1:2, and hydrolyze at different temperatures for 2 hours. Glucose was detected, and the comparison of hydrolysis effects of phthalic acid on microcrystalline cellulose at different temperatures is shown in Table 2.
[0025] Table 2
[0026]
[0027] It can be seen from Table 2 that the hydrolysis temperature has a significant effect on the glucose yield. When the temperature is lower than 190℃, the yield of glucose increases with the increase of hydrolysis temperature; when the temperature is higher than 190℃, the yield of glucose tends to decrease. It shows that at a higher temperature, the conversion of the product glucose into hydroxymethylfurfural and other by-products is enhanced, which makes the glucose yield decrease instead. The solvent ratio had a significant effect on the glucose yield. When the water solvent is completely used, the glucose yield is rela...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Add 2% microcrystalline cellulose and 1% phthalic acid into water, hydrolyze at 190°C for different times, solvent ratio (non-polar: water) = 1:2. Glucose was detected, and the comparison of hydrolysis effects of phthalic acid on microcrystalline cellulose under different hydrolysis times is shown in Table 3.
[0030] table 3
[0031]
[0032] It should be pointed out that it takes about 40 minutes for the reaction system to heat up from room temperature to the target temperature, and the heating process is not included in the hydrolysis reaction time. Therefore, when the hydrolysis time is 0 h, the glucose yield is greater than zero. It can be seen from Table 2 that when hydrolyzed at 190°C, the glucose yield basically reached the maximum at 1 h, and the increase in the glucose yield was limited when the reaction time was prolonged, and even the glucose degraded and the final yield decreased. At the same time, for the consideration of reducing energy consumption, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com