Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal and method for producing the same
A manufacturing method and technology of copper alloys, which are applied in the plating of superimposed layers, chemical instruments and methods, and metal material coating processes, etc., can solve problems such as the reduction of the kinetic friction coefficient, the reduction of solder wettability, and the increase of contact resistance. , to achieve the effect of reducing the coefficient of kinetic friction, low contact resistance, and stable contact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
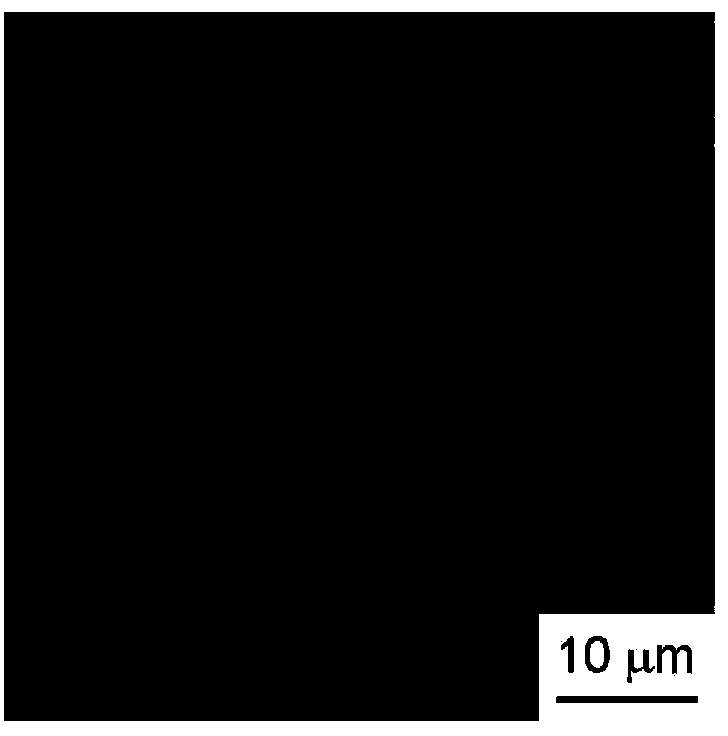
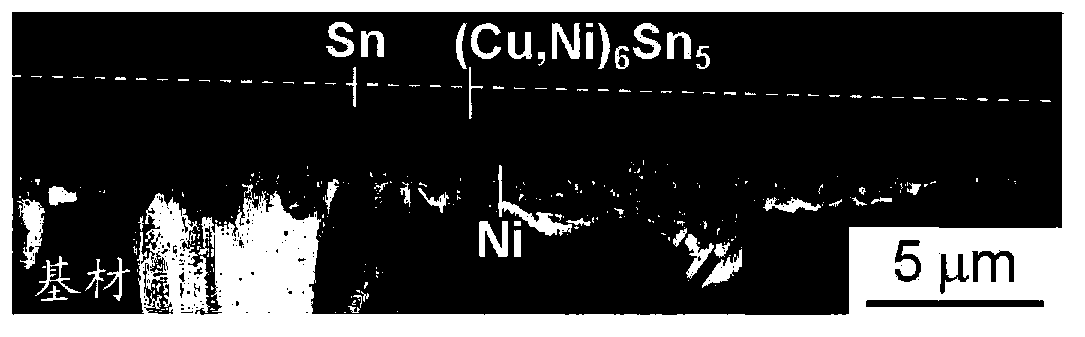
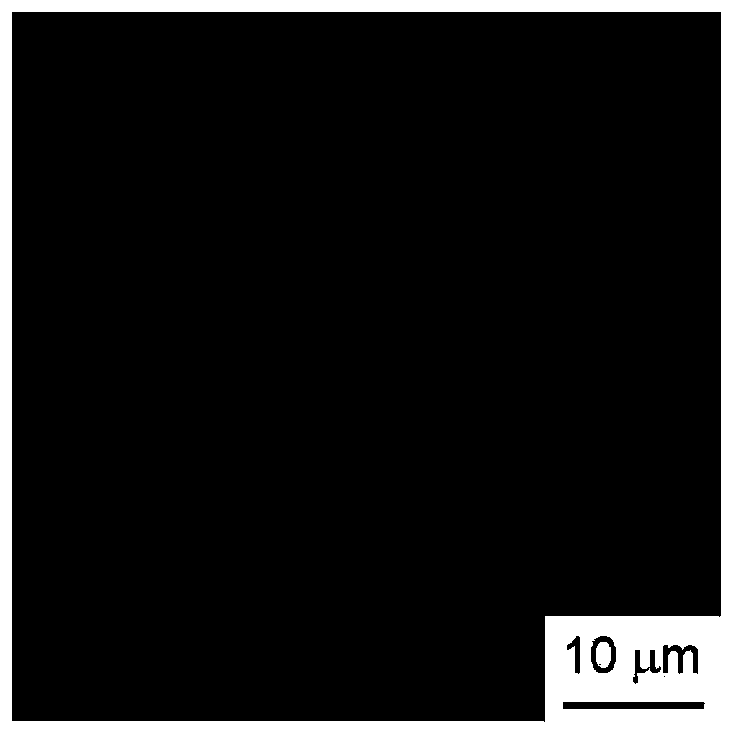
[0069] A Corson-based (Cu-Ni-Si-based) copper alloy with a plate thickness of 0.25 mm is used as the base material, and nickel plating, copper plating, and tin plating are sequentially performed. In this case, the plating conditions of nickel plating, copper plating, and tin plating are the same in Examples and Comparative Examples, and are shown in Table 1. In Table 1, Dk is the current density of the cathode, ASD is A / dm 2 The omitted representation of .
[0070] [Table 1]
[0071]
[0072] After the coating treatment with the thickness shown in Table 2, in the examples and comparative examples, as a reflow treatment, in a reducing atmosphere, the temperature was raised until the surface temperature of the substrate became 240-360 °C, and then the above-mentioned coating was heated according to the thickness of the coating. (1) After the time within the range indicated in (2), cool with water.
[0073] Table 2 shows the holding time of (1) and (2).
[0074] [Table 2] ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com