Recombinant saccharymyces cerevisiae for producing ginsengenins as well as construction method and application of same
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied to recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing ginsenosides and its construction and application fields, can solve the problem that the output of ginsenoside compounds cannot meet the needs of society, and affects the clinical application of ginsenosides as pharmaceutical raw materials for ginsenosides. Development and application of intermediates, limitations of quality growth environment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
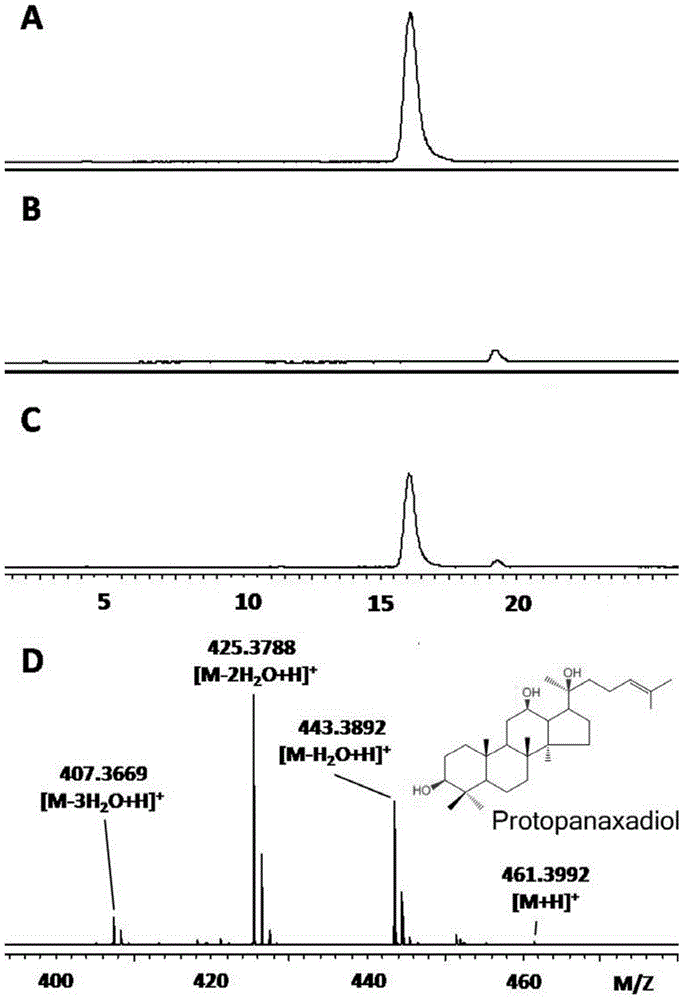
[0069] Example 1: Plasmid Construction
[0070] 1. The cloning of genetic elements is divided into the following three steps:
[0071] (1) Yeast genomic DNA extraction
[0072] Genomic DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742, described in Carrie baker brachmann et al., 1998, YEAST, 14:115-132, available to the public from Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.) was extracted.
[0073] (2) Acquisition of Arabidopsis cDNA
[0074] Total RNA was extracted from Arabidopsis thaliana (col-0 ecotype, recorded in Athanasios Theologis et al., 2000, Nature 408: 816-820, and the public can obtain it from Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), and was reverse-transcribed to obtain pseudo A. thaliana cDNA.
[0075] (3) PCR amplification and cloning of gene elements
[0076] Using the genomic DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742, recorded in Carri...
Embodiment 2
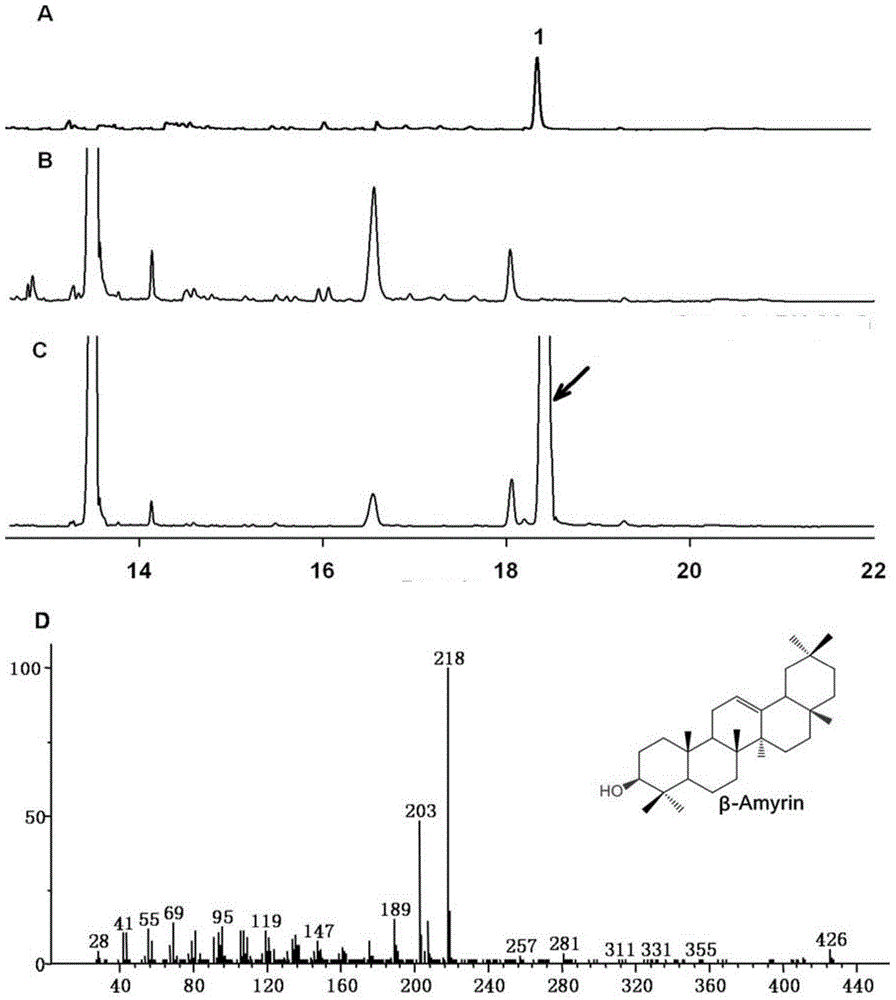
[0153] Embodiment 2, construction of engineering bacteria Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) BY-βA
[0154] 1. Construction of BY4742-TRP engineering bacteria
[0155] Using the p-ΔTrp1 plasmid in Example 1 as a template and using the primers in Table 11, amplify about 2056 bp of Trp-Loxp-HIS3.
[0156] Culture Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 overnight in YPD, take 1ml (OD about 0.6-1.0) and put it into 1.5ml EP tube, centrifuge at 10000g for 1min at 4°C, discard the supernatant, wash the precipitate with sterile water (4°C), do the same Centrifuge under conditions and discard the supernatant. Add 1ml of treatment solution (10mM LiAc; 10mM DTT; 0.6M sorbitol; 10mM Tris-HCl (pH7.5), add DTT only when the treatment solution is used) to the bacteria, and place it at 25°C for 20min. Centrifuge, discard the supernatant, add 1ml of 1M sorbitol (0.22um aqueous membrane membrane sterilization) to resuspend the bacteria, centrifuge, discard the supernatant (resuspend...
Embodiment 3
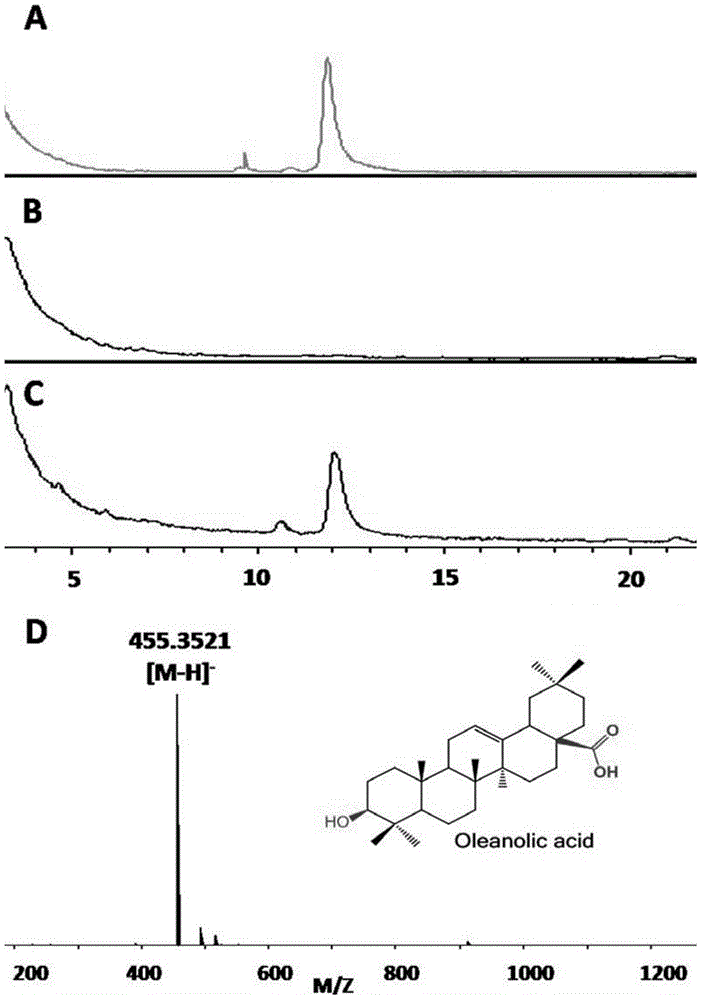
[0182] Embodiment 3, the construction of engineering bacteria recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY-OA
[0183] 1) Trp-HIS3-up, P PGK1 -GgbAS-T ADH1 , P TDH3 -AtCPR1-T TPI1 , P TEF1 -MtOAS-T CYC1 and Trp-down preparation
[0184] A 1861bp DNA fragment M1 (Trp-HIS3-up) shown in SEQ ID No. 7 was prepared, and M1 contained a homologous fragment upstream of the Trp1 site shown in positions 1429-1861 of SEQ ID No. 7. A 648bp DNA fragment M5 (Trp-down) shown in SEQ ID No. 12 was prepared, and M5 contained a homologous fragment downstream of the Trp1 site shown in positions 1-455 of SEQ ID No. 12. Use the PCR templates and primers described in Table 15 to perform PCR to obtain functional modules (DNA fragments M2-M4): about 3206bp of M2 (P PGK1 -GgbAS-T ADH1 ), about 3281bp of M3 (P TDH3 -AtCPR1-T TPI1 ) and about 2177bp of M4 (P TEF1 -MtOAS-T CYC1 ). M2 (P PGK1 -GgbAS-T ADH1 ) containing the expression cassette P of the GgbAS gene PGK1 -GgbAS-T ADH1 , the expressi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com