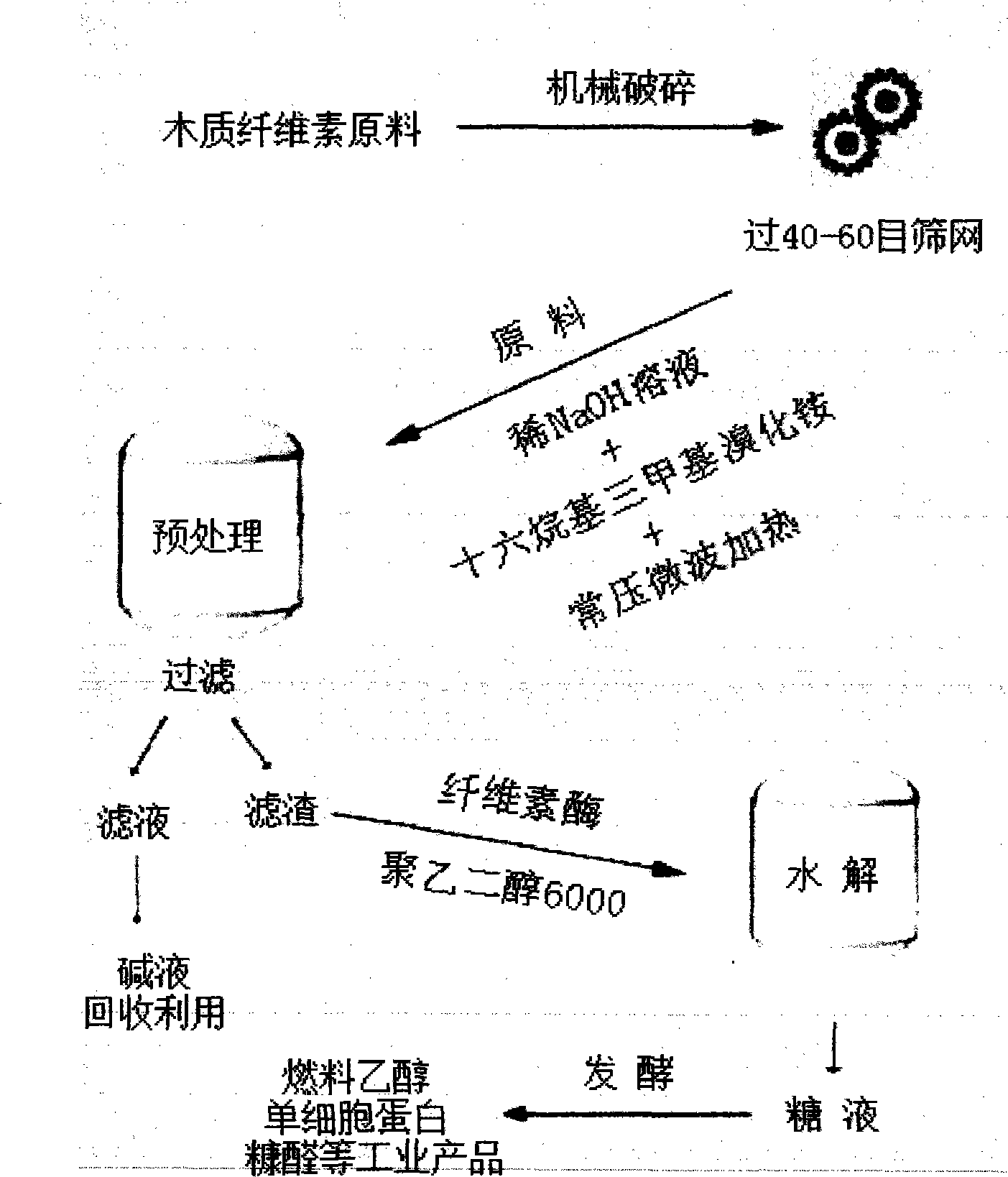
Method for efficiently degrading lignocelluloses raw material
A technology of lignocellulose and cellulase, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve the problems of reducing production cost and energy consumption, reducing the crystallinity of cellulose raw materials, and shortening the pretreatment time, so as to shorten the pretreatment time and improve the pretreatment time. Treatment effect, effect of relieving environmental stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
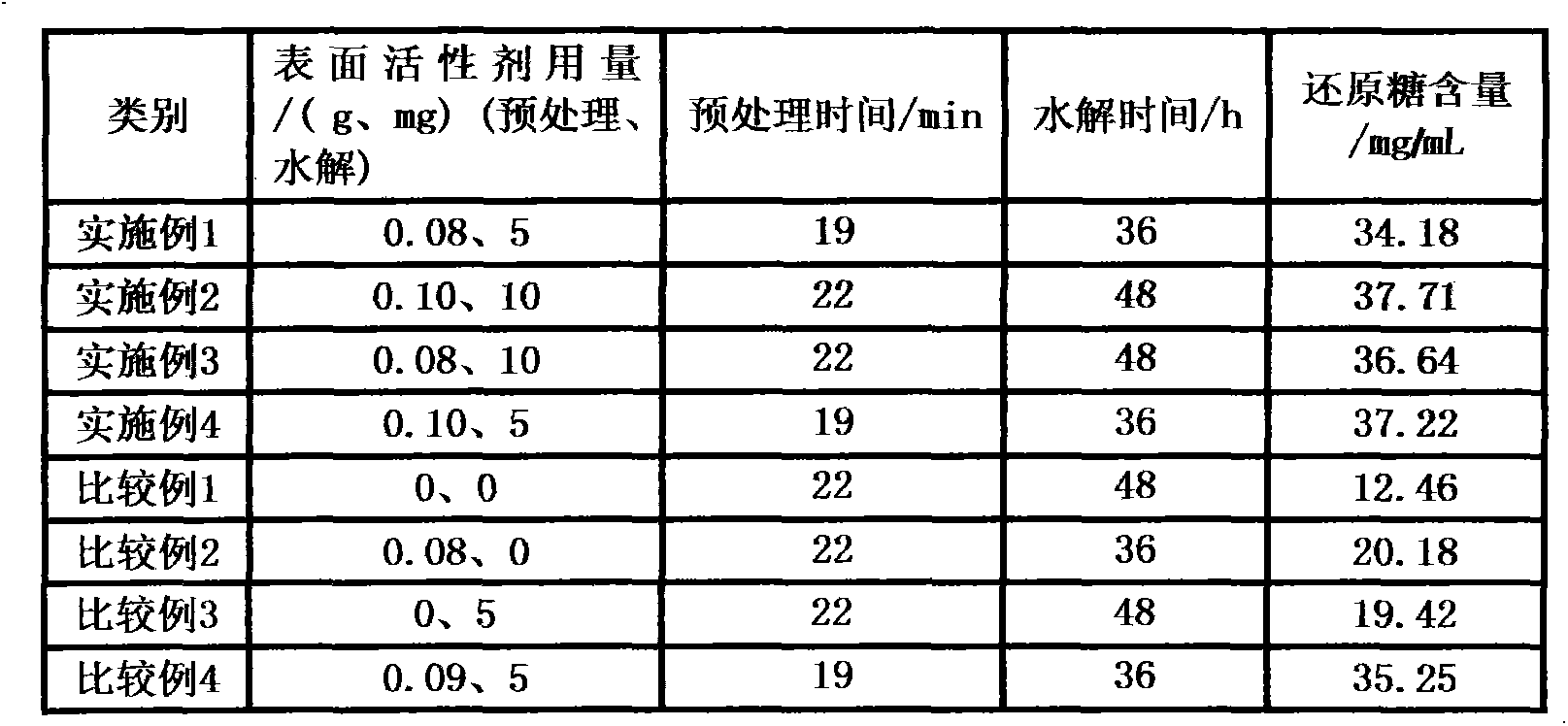
[0032] Take 0.08g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, add 25mL of NaOH solution with a mass fraction of 1.75%, stir until it is completely dissolved, add 1g of raw material of peanut shell powder, and then under normal pressure and microwave power of 640W, Heat treatment for 19 minutes, then filter and separate, wash the filter residue with tap water until the filtrate is neutral, and dry at 65°C; take 0.5g of the residue, add 10mg of cellulase and 5mg of PEG6000, and then add 0.1mol / L lemon with a pH of 4.8 Acid-sodium citrate buffer 25mL was hydrolyzed for 36h at a water bath temperature of 45°C and a speed of 160r / min, and then centrifuged at a speed of 5000r / min for 10min, using 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid method for the determination of reducing sugar content in the supernatant. The results are shown in Table 1
Embodiment 2
[0034]Take 0.10g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, add 25mL of NaOH solution with a mass fraction of 1.75%, stir until it is completely dissolved, add 1g of raw material of peanut shell powder, and then under normal pressure and microwave power of 640W, Heat treatment for 22 minutes, then filter and separate, wash the filter residue with tap water until the filtrate is neutral, and dry at 65°C; take 0.5g of the residue, add 10mg of cellulase and 10mg of PEG6000, add 0.1mol / L citric acid with a pH of 4.8 - Sodium citrate buffer solution 25mL, under the condition of water bath temperature 45℃, rotation speed 160r / min, hydrolyze for 48h, then centrifuge 10min under the condition of rotation speed 5000r / min, use 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid method The reducing sugar content in the supernatant was determined. The results are shown in Table 1
Embodiment 3
[0036] Take 0.08g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, add 25mL of NaOH solution with a mass fraction of 1.75%, stir until it is completely dissolved, add 1g of raw material of peanut shell powder, and then under normal pressure and microwave power of 640W, Heat treatment for 22 minutes, then filter and separate, wash the filter residue with tap water until the filtrate is neutral, and dry at 65°C; take 0.5g of the residue, add 10mg of cellulase and 10mg of PEG6000, add 0.1mol / L citric acid with a pH of 4.8 - Sodium citrate buffer solution 25mL, under the condition of water bath temperature 45℃, rotation speed 160r / min, hydrolyze for 48h, then centrifuge 10min under the condition of rotation speed 5000r / min, use 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid method The reducing sugar content in the supernatant was determined. The results are shown in Table 1
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com