Preparation method of chitosan-grafted beta-cyclodextrin bonded silica gel absorbent
A technology of bonding silica gel and cyclodextrin, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve large enrichment multiples, good reproducibility, and good reproducibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Preparation of chitosan grafted β-cyclodextrin bonded silica gel adsorbent
[0020] (1) Activation of silica gel: soak the silica gel with concentrated nitric acid and deionized water (volume ratio 1:1) for 12 hours, then use deionized water to filter until neutral, and then use concentrated hydrochloric acid and deionized water (volume ratio 1:1 ) magnetically stirred for 12 h, washed with deionized water and filtered until neutral. Dry at 60 °C for 24 h and cool in a drying oven;
[0021] (2) γ-aminopropyl bonded silica gel: Take 10 g of the activated silica gel in step (1) in a 250 mL three-neck flask, then measure 50 mL of toluene and 20 mL of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane ( YDH-550), in an oil bath at 110 °C, stirred and refluxed for 16 h, after cooling, the product was washed with toluene, ethanol, and acetone in turn and suction filtered until no gel was present. Dry at 60 °C for 24 h and cool in a drying oven;
[0022] (3) Silica gel aldehyde group modificatio...
Embodiment 2
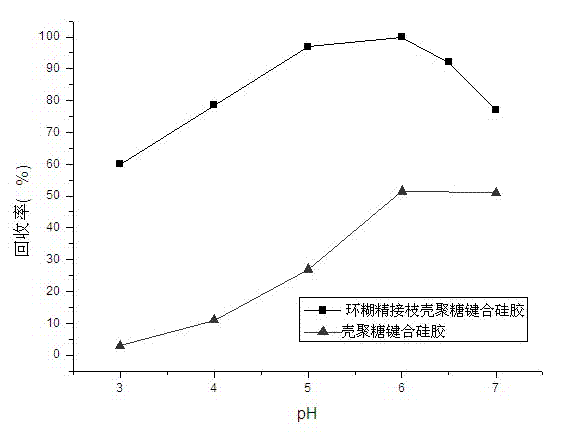
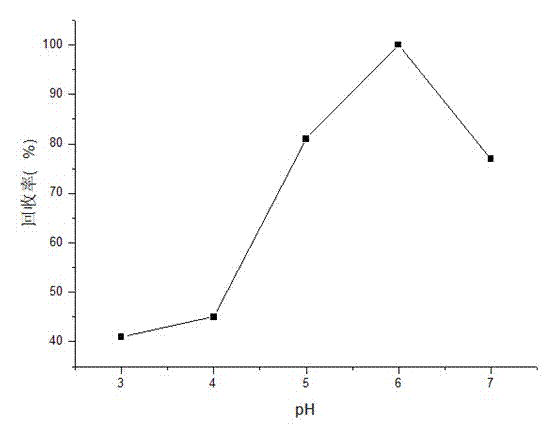
[0026] Effect of pH on Adsorption Properties of Chitosan Grafted β-Cyclodextrin Bonded Silica Gel Adsorbent
[0027] The absorption rate was measured by flame atomic absorption method (FAAS) through the static test of solutions with different pH values. figure 1 For the effect of pH on the adsorption performance of chitosan-grafted β-cyclodextrin-bonded silica gel and chitosan-bonded silica gel for Cd(II), figure 2 The effect of pH on the adsorption of Cd(II) on chitosan-grafted β-cyclodextrin-bonded silica gel. The initial Cu(II) ion concentration: 2.0 mg / L; adsorbent dosage: 0.15g; shaking time: 30 min; sample volume: 50 mL; 25°C. Initial Cd(II) ion concentration: 1.0 μg / ml; adsorbent dosage: 0.15g; shaking time: 30 min; temperature: 25°C; sample volume: 50ml.
Embodiment 3
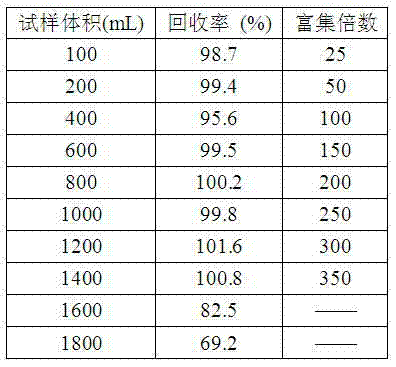
[0029] Determination of maximum enrichment fold
[0030] The enrichment performance of adsorbent for Cu(II) under different sample volume conditions was investigated by dynamic experiment method. In the experiment, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600 and 1800 mL sample solutions containing 10 μg Cu(II) were enriched by column extraction under optimal extraction and elution conditions, and then The maximum enrichment factor was studied by measuring the recovery rate of Cu(II). The results are shown in Table 1. When the sample volume increased to 1600 mL, the recovery rate of Cu(II) dropped to 82.5%, and when the sample volume increased to 1800 mL, the recovery rate of Cu(II) decreased even more. to 69.2%. This shows that the adsorbent has a good extraction and enrichment ability for Cu(II). Since 4 mL of hydrochloric acid solution can achieve quantitative recovery of Cu(II), the maximum enrichment factor is 350, which is expected to achieve ppb level Cu in the sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com