Preparation of barley grass powder and domestic fungus powder compounded chewing tablet, and medium short wave infrared drying method
A short-wave infrared, edible fungus technology, applied in food preparation, application, food science and other directions, to achieve the effect of short drying time, high thermal efficiency and stable quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Preparation of chewable tablets compounded with barley grass powder and shiitake mushroom powder and drying in medium and short wave infrared
[0023]The barley grass powder was ultrafinely pulverized at 600 rpm for 10 min with a PM100 planetary ball mill, and passed through a 200-mesh sieve. After the shiitake mushrooms are cleaned and trimmed, they are cut into 10mm slices with a moisture content of 88%, dried, pulverized, and passed through a 120-mesh sieve to obtain shiitake mushroom fine powder, with a moisture content of 6.2%. Mix wheatgrass fine powder and shiitake mushroom fine powder according to the mass ratio of 3:2, add 10%-20% dextrin and starch (1:1), 30%-50% compound sweetener (lactose: mannitol: wood Sugar alcohol=4:1:4), 10%-20% microcrystalline cellulose and 0.4%-1% citric acid and L-malic acid (2:5) mix well, add 1% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution , stirred, wet granulation, demoulding, medium and short wave infrared drying...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Preparation of chewable tablets compounded with barley grass powder and white mushroom powder and drying in medium and short wave infrared
[0026] The barley grass powder was ultrafinely pulverized at 600 rpm for 10 min with a PM100 planetary ball mill, and passed through a 200-mesh sieve. White mushrooms are cleaned, trimmed, and cut into 10mm slices, with a water content of 85%, dried, pulverized, and passed through a 120-mesh sieve to obtain white mushroom fine powder, with a water content of 6%. Mix wheatgrass fine powder and white mushroom fine powder according to the mass ratio of 3:2, add 10%-20% dextrin and starch (1:1), 30%-50% compound sweetener (lactose: mannitol: Xylitol=4:1:4), 10%-20% microcrystalline cellulose and 0.4%-1% citric acid and L-malic acid (2:5) mix well, add 1% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose Aqueous solution, stirring, wet granulation, demoulding, medium and short wave infrared drying at 60°C for 90 minutes, coating, and medium an...
Embodiment 3
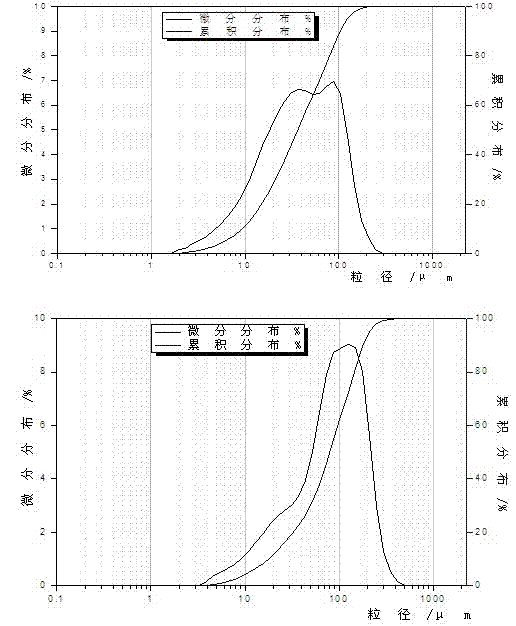
[0028] Embodiment 3: the superfine pulverization of barley grass powder and its particle size distribution figure
[0029] The ultrafine pulverization particle size distribution of barley grass powder is as follows figure 1 shown. from figure 1 It can be seen that the D of the two crushing methods 50 36.34 μm and 80.41 μm, respectively, D 90 They are 103.6 μm and 178.7 μm respectively. Among them, the characteristics of PM100 powder are that one type of micropowder tends to be smaller than 50 μm, reaching the range of broken walls, and the other part of micropowder is larger than 100 μm. The analysis shows that choosing PM100 has the best effect on superfine grinding of wheat grass powder. The particle size distribution of ultrafine powder and wheatgrass fine powder is very different. The particle size distribution of ultrafine powder is narrow, with high uniformity and easy quality control; the particle size distribution of wheatgrass fine powder is wide, with poor unifor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com