Polyethylene glycol hydrogel for orthotopic injection and preparation method thereof
A polyethylene glycol type, in situ injection technology, applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as expensive, difficult to industrialize, and harsh conditions for star-shaped polyethylene glycol synthesis, and achieve Effects of reduced reaction energy consumption, simple operation, good biocompatibility and biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-26
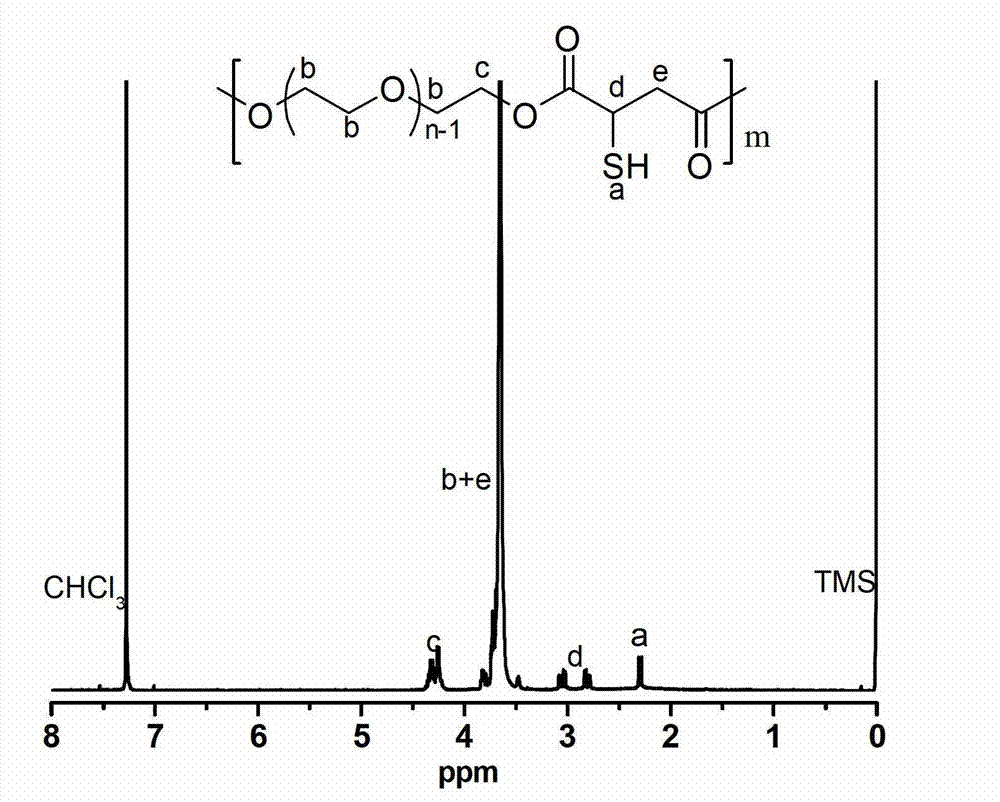
[0039] Embodiment 1-26, different rare earth triflate Ln(OTf) 3 Catalyze the synthesis of polymercapto or polyether esters with multiple double bonds (the number average molecular weight of polyethylene glycol used is 1000g / mol).
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1, scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate Sc (OTf) 3 Synthesis of Catalyzed Polymercapto Polyether Ester
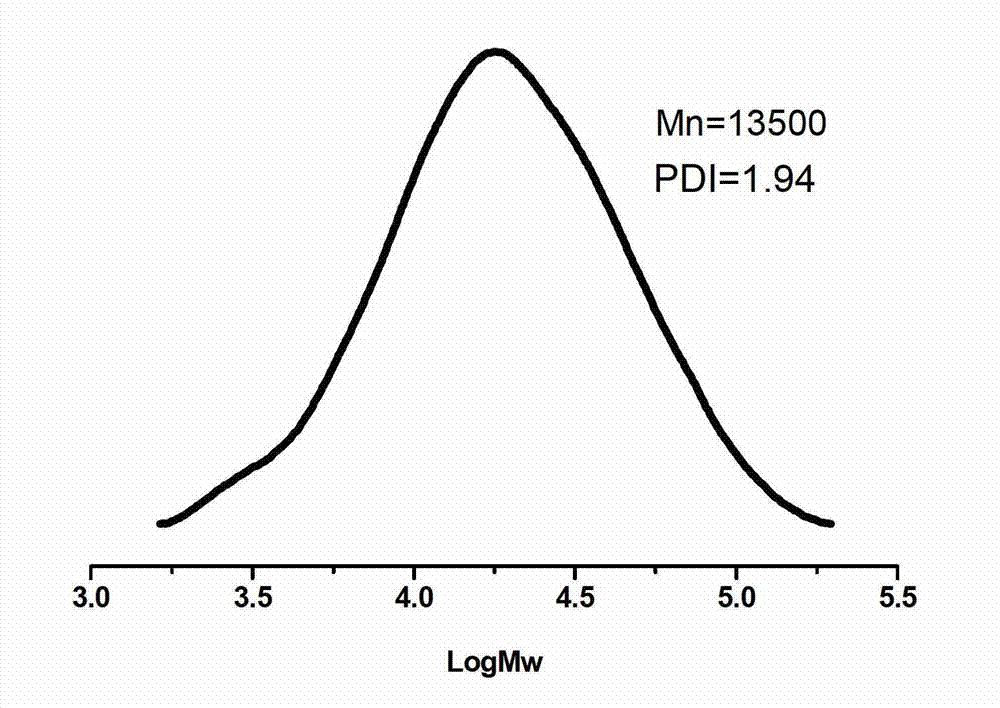
[0041] Add 45g (0.045mol) of polyethylene glycol 1000 to a 250mL three-neck flask, add 100mL of anhydrous toluene to azeotropically remove water at 140°C; then add 6.62g (0.045mol) of thiomalic acid, 0.33g (0.67 mmol) scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate catalyst. Under the action of mechanical stirring, react at 80°C for 3 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, then connect the circulating water pump to depressurize the reaction for 4 hours, keep the temperature at 80°C, and the pressure of the decompression reaction is 3mmHg, after slowly raising the temperature to 100°C, change the rotary vane type The vacuum oil pump continued the decompression reaction at 100° C. for 8 hours, and the reaction pressure was 0.3 mmHg. After the polycondensation reaction, the obtained polymer was dissolved in dichloromethane, extracted twice with saturated brine to remove the cata...
Embodiment 2
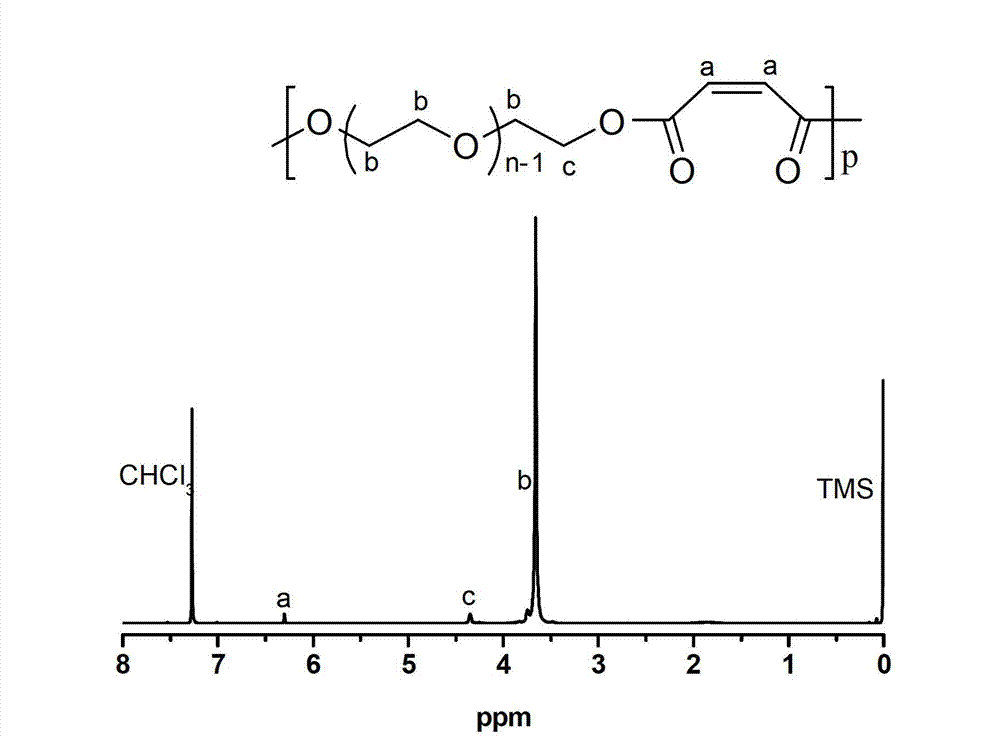
[0045] Embodiment 2, scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate Sc (OTf) 3 Catalyzed synthesis of polyether esters with multiple double bonds
[0046] Add 45g (0.045mol) polyethylene glycol 1000 to a 250mL three-necked flask, add 100mL anhydrous toluene to remove water azeotropically at 140°C; then add 4.34g (0.045mol) maleic anhydride, 0.33g (0.67mmol) ) scandium triflate catalyst. Under the action of mechanical stirring, after reacting at 100°C for 3 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, connect the circulating water pump and maintain it at 100°C for 4 hours under reduced pressure. The oil pump continued the decompression reaction at 120° C. for 8 hours, and the reaction pressure was 0.3 mmHg. After the polycondensation reaction, the obtained polymer was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran, and the catalyst was removed through a separation column filled with neutral alumina, the solution was retained, concentrated by rotary evaporation, and finally a large amount of cold ether was added under ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com