A micro-injection mold for biodegradable vascular stent
A vascular stent and micro-injection technology, which is applied in the field of micro-injection molds for biodegradable vascular stents, can solve the problems of difficult control of solder joints, complex winding structure, and affecting the deformation performance of stents, so as to ensure the overall strength and fatigue performance and avoid production. Low efficiency, avoiding the effect of poor surface quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with technical solutions and accompanying drawings.
[0021] Injection molding biodegradable polymer vascular stent, the concrete steps of embodiment are as follows:
[0022] step 1
[0023] Use a drying oven to dry the biodegradable polymer material at a certain temperature to remove moisture.
[0024] step 2
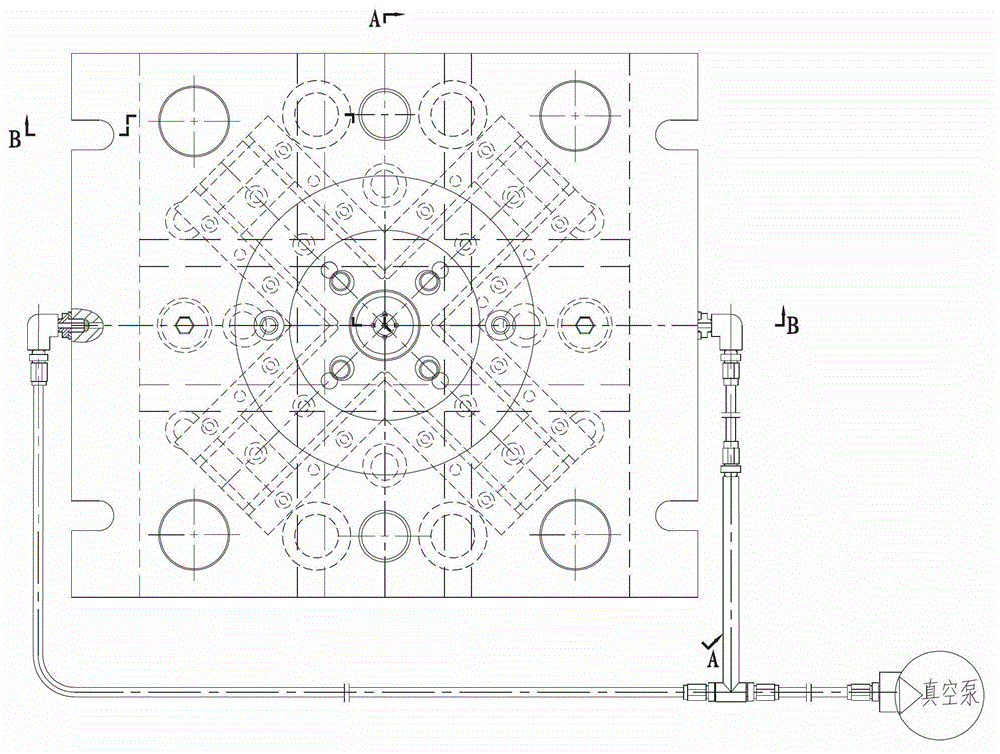
[0025] Install the biodegradable polymer stent mold on the injection molding machine and start the vacuum pump.
[0026] step 3
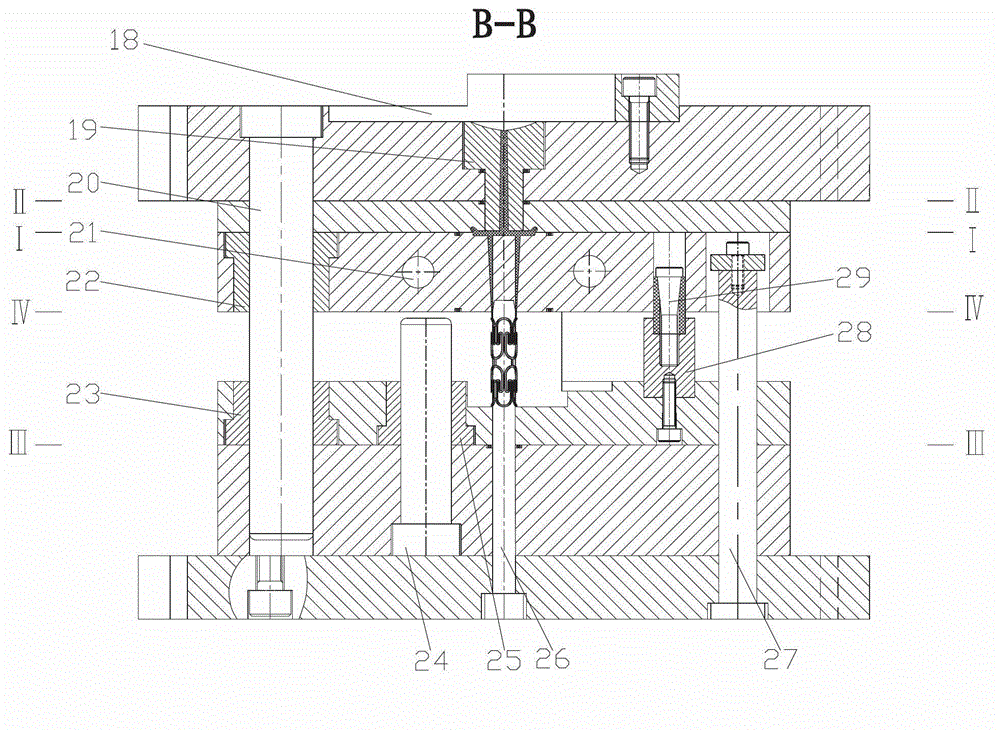
[0027] Start the mold temperature machine, and heat the mold before filling through the heating oil channel.
[0028] step 4
[0029] Add a certain amount of dried biodegradable polymer material into the hopper of the injection molding machine, and set the process parameters such as melt temperature, injection volume, injection rate and injection pressure required for the injection molding process.
[0030] step 5
[0031] The polymer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com