Visualized microscopic model of real core and manufacturing method of visualized microscopic model of real core
A technology of real cores and microscopic models, applied in teaching models, educational appliances, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of easily damaged core pores physical and chemical properties, epoxy resin sealing core pores and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
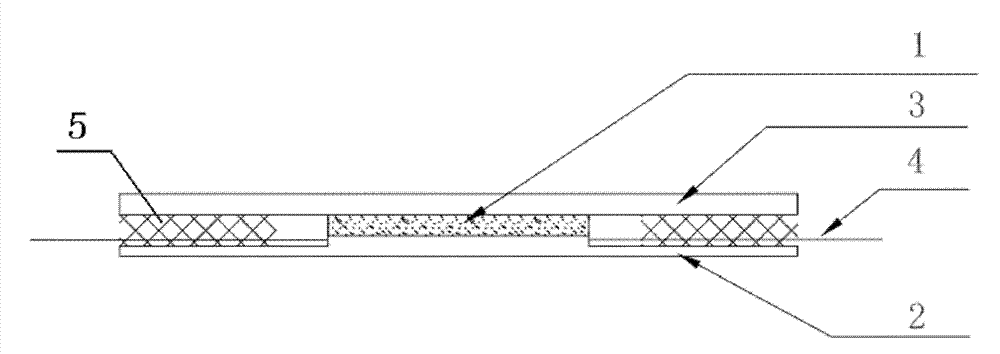
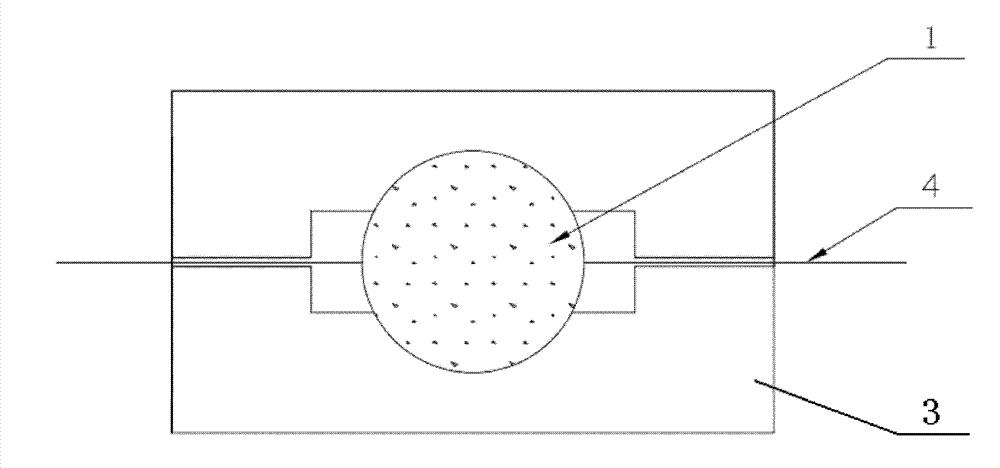
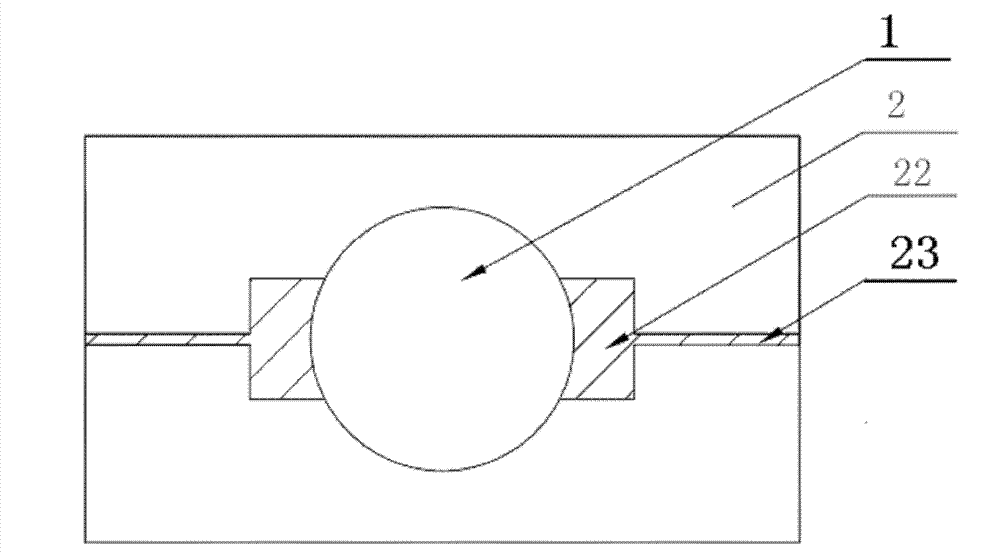
[0035] Figure 1(a)(b) and figure 2 As shown, the present embodiment provides a real rock core visual microscopic model, which is a high-temperature pressure-formed model including a real rock core slice 1, a plexiglass slide 2, a plexiglass cover 3 and a needle 4, wherein the real rock core The sheet 1 is sandwiched between the plexiglass cover sheet 3 and the plexiglass slide 2, and the plexiglass slide 2 is provided with connected guide grooves 22 and needle grooves 23 on both sides of the real rock core slice 1, and the guide groove 22 It is connected with the real rock core piece 1; the pinhole at one end of the needle head 4 is in the guiding groove 22, and is in contact with the side wall of the guiding groove 22 at the end of the real rock core piece.
[0036] When preparing the real rock core visual microscopic model, the following steps are adopted:
[0037] (1) Processing of real rock core slices: After the real rock core slices 1 are washed with oil and dried, one fa...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0045] When preparing the real rock core visual microscopic model, the following steps are adopted:
[0046] (1) Processing of real rock core slices: after the real rock core slices 1 are washed with oil and dried, one face of the real rock core slices 1 is ground on the grinding machine, and a section of 4 mm long is cut, and the ground surface is ground Bond it to a clean ground glass piece with optical resin glue, and then grind the core piece to about 0.2 mm in a grinder.
[0047] (2) Pretreatment of the rock core sheet: soak the processed real rock core sheet 1 in acetone solvent overnight, the optical resin glue on the real rock core sheet 1 and the ground glass sheet has been completely dissolved, and dry the real rock core sheet 1;
[0048] (3) Processing of plexiglass slides and plexiglass cover slips: two plexiglass sheets with a length of 65 mm and a width of 37 mm are cut out from a 2 mm thick pl...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0053] When preparing the real rock core visual microscopic model, the following steps are adopted:
[0054] (1) Processing of real rock core slices: After the real rock core slices 1 are washed with oil and dried, one face of the real rock core slices 1 is ground on the grinding machine, and a section of 3 mm long is cut, and the ground surface is ground Bond it to a clean ground glass piece with optical resin glue, and then grind the real core piece 1 to about 0.2 mm in a grinder;
[0055] (2) Pretreatment of rock core slices: soak the processed real rock core slices 1 in a mixed solvent of ethanol and acetone for more than 2 days until it is observed that there is no viscous soluble glue on the real rock core slices 1 and ground glass slices, that is, optical resin glue Completely dissolved, dry the real core piece 1;
[0056] (3) Processing of plexiglass slides and plexiglass cover slips: two plexiglass...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com