Mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphate from low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite
A vanadium-titanium magnetite, low-grade technology, applied in flotation, magnetic separation, solid separation, etc., can solve the problems of limited comprehensive recovery process application, poor solubility and dispersibility, increased production costs, etc., to reduce the cost of phosphorus selection , low cost and high efficiency, and the effect of improving benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1: This ore dressing process for comprehensive recovery of iron and phosphorus from low-grade high-phosphorus vanadium-titanium magnetite adopts the following process steps.
[0019] Raw materials: select vanadium-titanium magnetite from a certain place in Chengde area. The useful minerals of this raw material are mainly magnetite, and a small amount of hematite and limonite; the non-metallic minerals are mainly plagioclase, pyroxene, hornblende and apatite. Total iron grade TFe is 9.00wt%, containing phosphorus P 2 o 5 1.73wt%, titanium content TiO 2 1.62wt%, which is low-grade high-phosphorus vanadium-titanium magnetite.
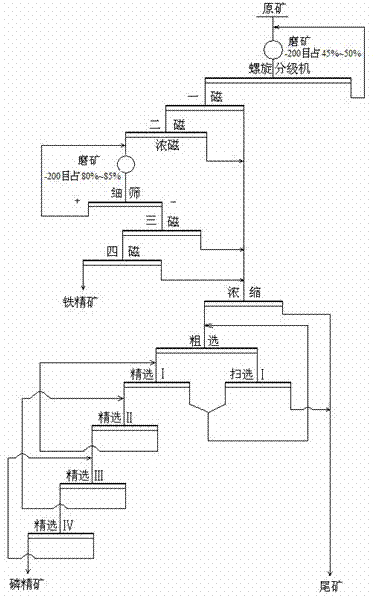
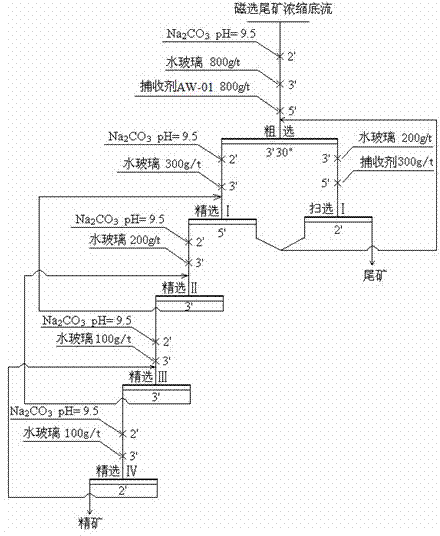
[0020] Process steps: such as figure 1 As shown, the raw ore is ground and classified in the first stage, and the grinding fineness is -200 mesh, accounting for 50%. After two magnetic separations ( figure 1 After the first magnetism and the second magnetism), the second magnetite concentrate will be graded by the second stage of gri...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: This ore dressing process for comprehensive recovery of iron and phosphorus from low-grade high-phosphorus vanadium-titanium magnetite adopts the following process steps.
[0022] Raw materials: select vanadium-titanium magnetite from a certain place in Zhangjiakou area. The useful minerals in the ore are mainly magnetite and a small amount of hematite and limonite; there is also a certain amount of metal sulfide, mainly pyrite and pyrrhotite mine. The multi-element analysis of the ore is shown in Table 1. The total iron grade TFe is 15.88%, and the phosphorus content is P 2 o 5 2.53%, titanium content TiO 2 2.62%, which is low-grade high-phosphorus vanadium-titanium magnetite.
[0023] Table 1: Results of multi-element analysis of raw ore
[0024]
[0025] Process step is basically the same as embodiment 1. Among them, the grinding fineness of the first stage is -200 mesh, accounting for 50%. After two magnetic separations, the concentrate is then...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Embodiment 3: This ore dressing process for comprehensive recovery of iron and phosphorus from low-grade high-phosphorus vanadium-titanium magnetite adopts the following process steps.
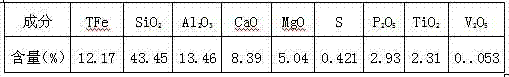
[0027] Raw materials: select vanadium-titanium magnetite from a certain place in Chengde area. The useful minerals in this ore are mainly magnetite, and there are also a small amount of hematite and limonite; the total iron grade TFe is 12.17%, and the phosphorus content is P 2 o 5 is 2.93%; vanadium and titanium content are V 2 o 5 0.053%, TiO 2 2.31%, which is low-grade high-phosphorus vanadium-titanium magnetite. The multi-element analysis of the raw ore is shown in Table 2.
[0028] Table 2: Results of multi-element analysis of raw ore
[0029]
[0030] Process step is basically the same as embodiment 1. Among them, the grinding fineness of the first stage is -200 mesh, accounting for 45%. After two magnetic separations, the concentrate is then subjected to the second sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com