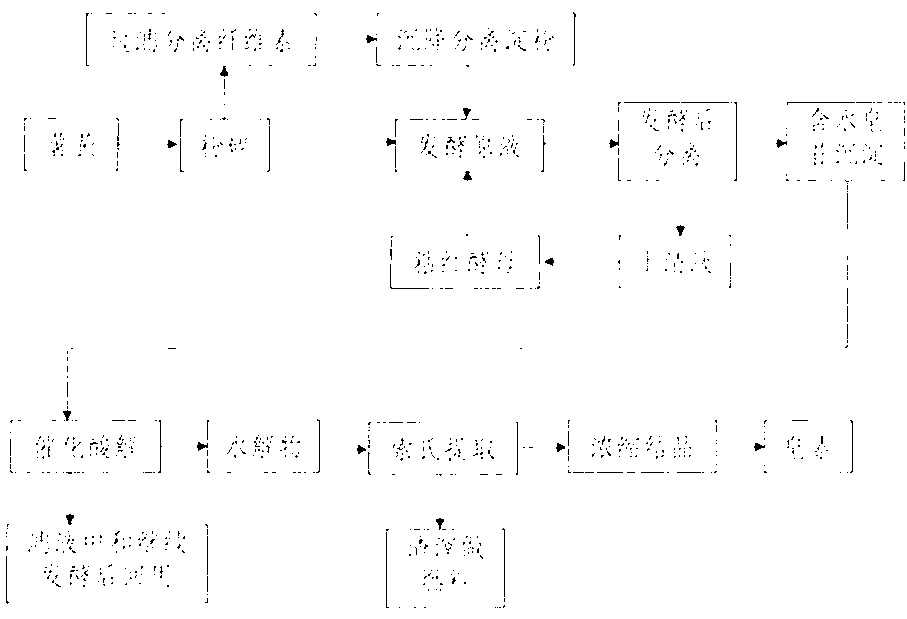Novel process for extracting diosgenin
A technology of diosgenin and a new process, which is applied in the field of extraction process of diosgenin, can solve the problems of complicated equipment, shortened reaction time, and large water consumption, so as to reduce the amount of acid used, increase the yield of saponin, reduce the The effect of water consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Take by weighing 100 grams of fresh Dioscorea scutellaria rhizome samples that have been washed and removed;
[0034] (2) The sample is crushed, and 200 grams of water is added to make a slurry;
[0035] (3) Filter the solid-liquid mixture with double-layer gauze, add 100 grams of water to the filter residue, continue to crush it once with a Joyoung cooking machine, collect the filtrate, and collect the filter residue separately for processing;
[0036] (4) Pour the filtrate into a separatory funnel and let it stand for layers. The upper layer is a clear liquid layer, the middle is a suspension layer, and the lower white layer is a starch layer. Pour out a total of 350ml of the upper layer and the middle layer into a beaker, and collect the lower layer. Starch to be processed.
[0037] (5) Add 0.2 g of Rhodotorula viscoscens strain to the suspension, let it stand for fermentation for 24 hours, separate 250ml of the supernatant (Rhododovis viscoscens strain A), and ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) Take by weighing 100 grams of fresh Dioscorea scutellaria rhizome samples that have been washed and removed;
[0045] (2) The sample is pulverized, and the Rhodotorula viscosus bacterium liquid A added in embodiment 1 is transferred into slurry;
[0046] (3) Leave to ferment for 48 hours, separate 200ml of the supernatant (Rhodotorula viscosum liquid A), and transfer 100ml of the remaining concentrated saponin mixture into the autoclave;
[0047] (4) Slowly add concentrated sulfuric acid into the suspension to adjust the concentration of sulfuric acid to 0.5N, add 1.5 g of ferric sulfate, adjust the temperature to 125°C, and hydrolyze in an autoclave for 3 hours.
[0048] (5) Filter the hydrolyzate to separate the filter residue, wash it with a small amount of lime solution and water successively until the pH value is neutral, and combine the filtrate and lotion to about 120ml.
[0049] (6) The filter residue, namely the hydrolyzate, was oven-dried at 60°C to obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) Take by weighing 100 grams of fresh Dioscorea scutellaria rhizome samples that have been washed and removed;
[0054] (2) Pulverize the sample, add 1.2 grams of Rhodotorula viscosum and 250 milliliters of water to make a slurry;
[0055] (3) Leave to ferment for 48 hours, separate 250ml of the supernatant (Rhodotorula viscosum liquid A), and transfer 100ml of the remaining concentrated saponin mixture into the autoclave;
[0056] (4) Slowly add concentrated hydrochloric acid into the suspension to adjust the concentration of hydrochloric acid to 1.0N, add 1.5 g of ferric chloride salt, adjust the temperature to 125°C, and hydrolyze in an autoclave for 3 hours.
[0057] (5) Filter the hydrolyzate to separate the filter residue, wash it with a small amount of lime solution and water successively until the pH value is neutral, and combine the filtrate and lotion to about 120ml.
[0058] (6) The filter residue, namely the hydrolyzate, was oven-dried at 60°C to obtain 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com