Semiconductor structure with low resistance substrate and low power loss
A semiconductor and conductive structure technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc., can solve problems such as micro-cracking, product service life reduction, cost increase, etc., to achieve continuous production capacity and reduce Effect of power loss and resistance reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
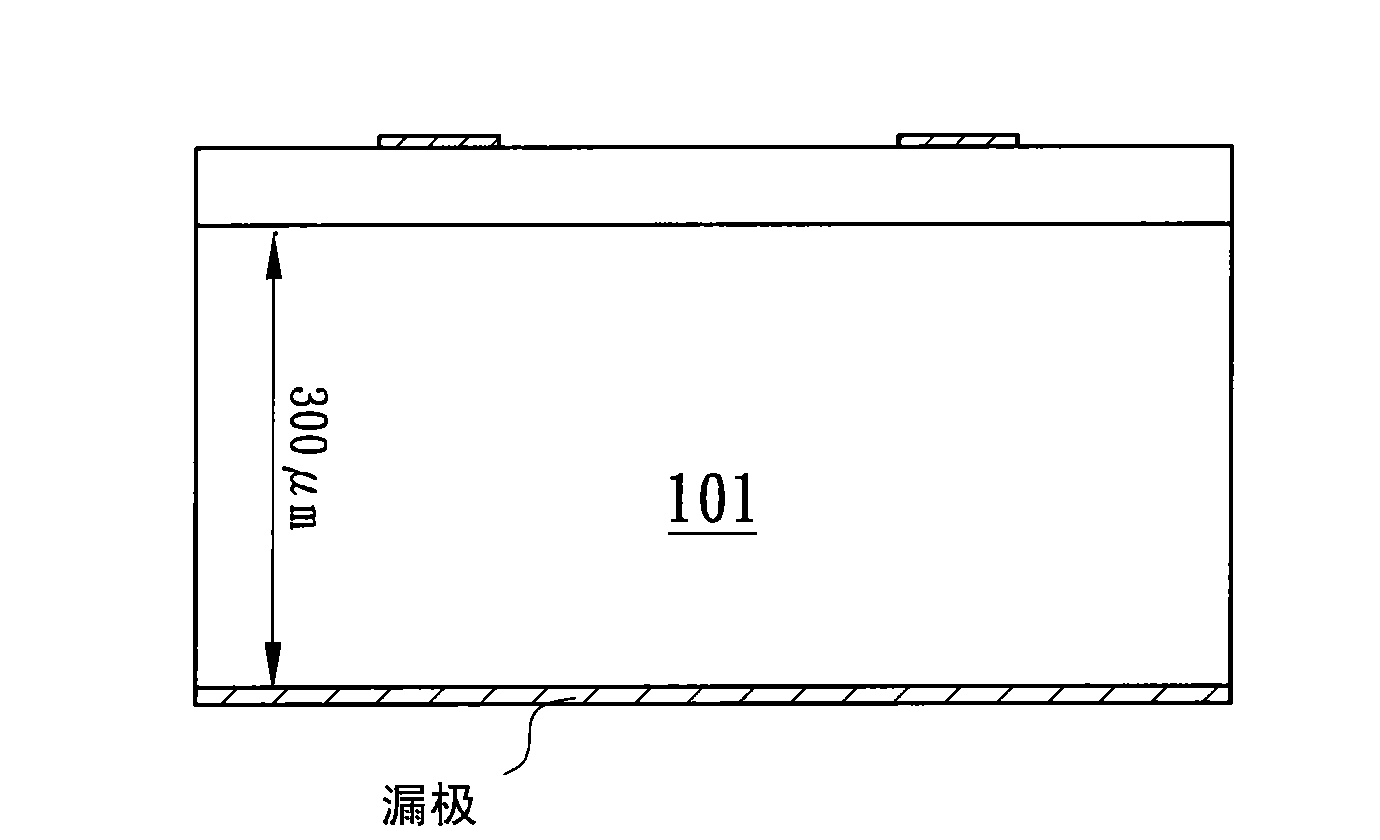
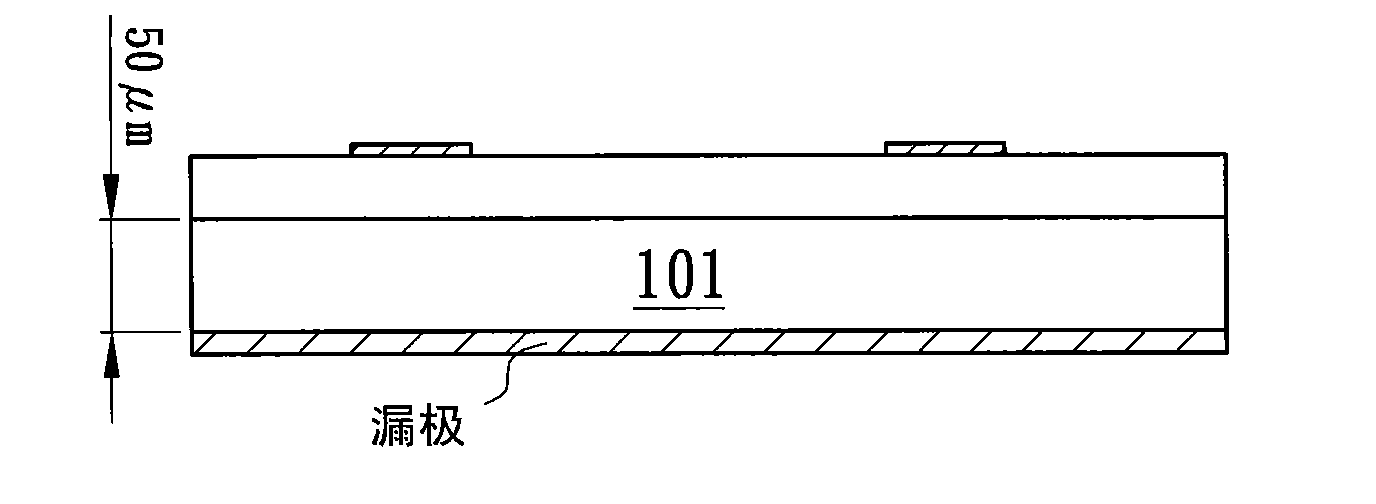
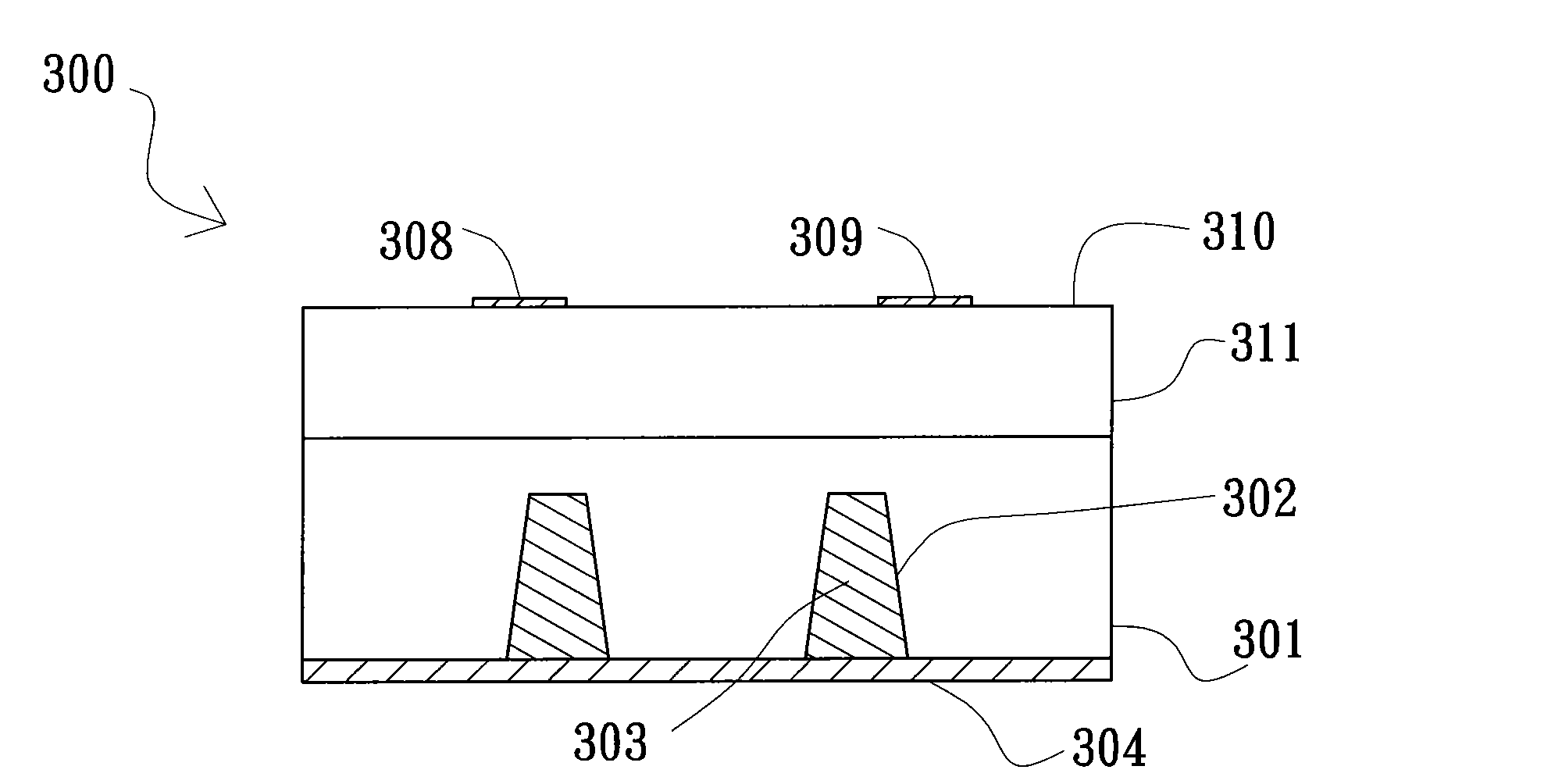
[0038] Figure 3A A first embodiment of the low power loss semiconductor structure of the present invention is shown. Such as Figure 3A As shown, a semiconductor unit 300 has a substrate 301, and at least one hole 302 is formed in the substrate 301, wherein the hole 302 can be implemented in a through silicon via (TSV) manner. A conductive substance 303 is located in the hole 302 , and a conductive structure 304 is located on the surface of the substrate 301 and the conductive substance 303 . The conductive structure 304 serves as a drain electrode of the power semiconductor. A source electrode 308 and a gate electrode 309 are located on a surface 310 of the semiconductor unit 300 . The advantage of reducing the resistance of the semiconductor unit 300 can be achieved by using the conductive structure 304 in the hole 302 to partially or completely replace the substrate 301 with a relatively high resistance value.
[0039] Figure 3B to Figure 3C It is the manufacturing m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com