Method for producing electrolytic zinc by comprehensively recycling high-chlorine high-fluorine lead and antimony smelting waste residue
A high-chloride, fluorine, lead-antimony, and electrolytic zinc technology, applied in the field of smelting, can solve the problems of easily corroded plates, increased consumption of plates, and no zinc enrichment method, etc., to achieve large processing capacity and increased plate consumption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
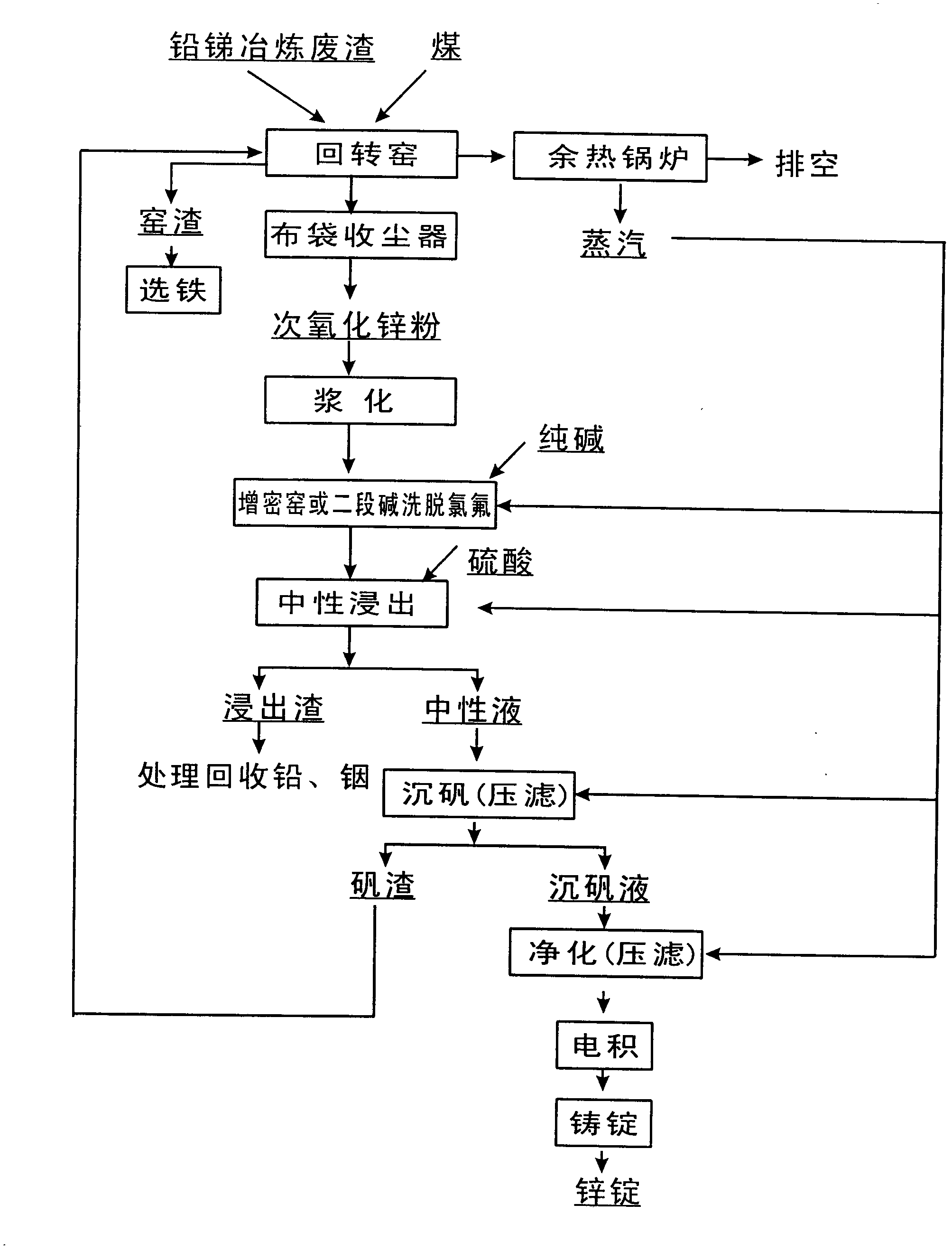
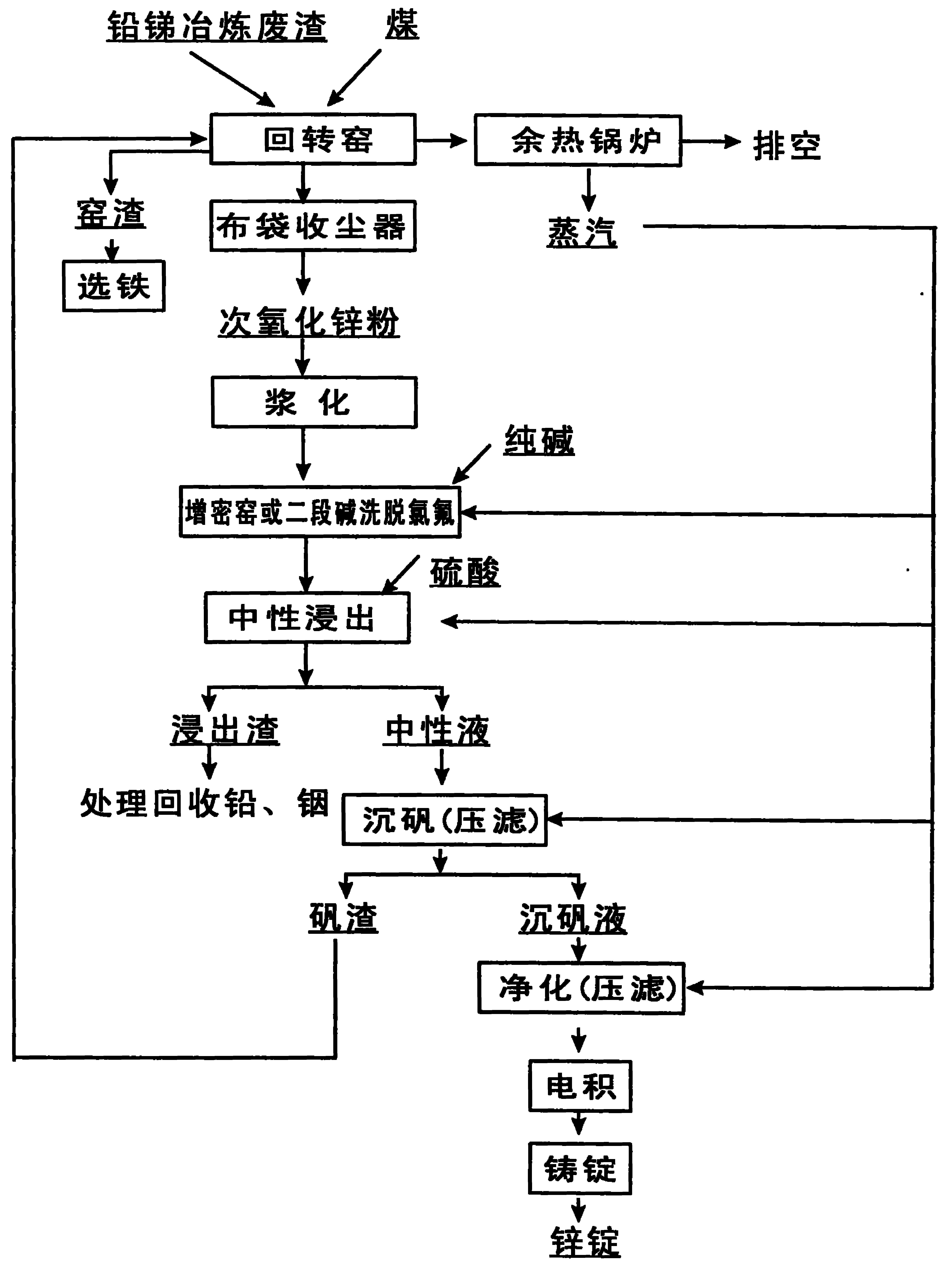
[0013] Example 1: Put the lead-antimony smelting waste slag and coal with a particle size of 1-5 mm in a rotary kiln, and carry out volatilization and roasting at a temperature of 1200 ° C for 1.5 hours, and the volatile matter enters a bag filter to collect dust and obtains Zinc oxide powder. The secondary zinc oxide powder is slurried with water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 5:1, then the pH is adjusted to 8 with soda ash, and the fluorine and chlorine are eluted with a second stage of alkali at a temperature of 70-80°C for 1 hour. Then, it is leached with hot acid as usual, treated with jarosite sinking to obtain a purified solution, and then electrolytically deposited to obtain electrolytic zinc.
Embodiment 2
[0014] Embodiment 2: Hypochlorine is put into a densification kiln through zinc powder, and the densification kiln is carried out at a temperature of 900° C. for 2 to 4 hours to dechlorinate fluorine. The rest are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com