GaN-based high-electron-mobility transistor and manufacturing method thereof
A high electron mobility, gallium nitride-based technology, applied in the field of gallium nitride-based high electron mobility transistors and their fabrication, can solve problems such as insufficiently meeting the requirements of high electron mobility transistors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
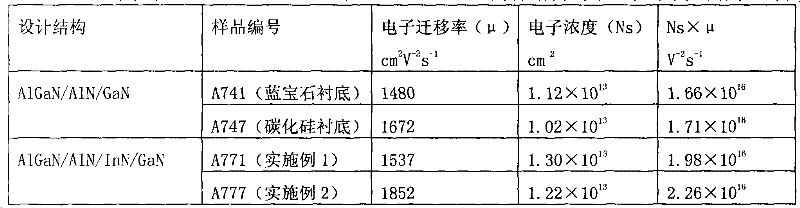
[0034] Embodiment 1: sapphire substrate
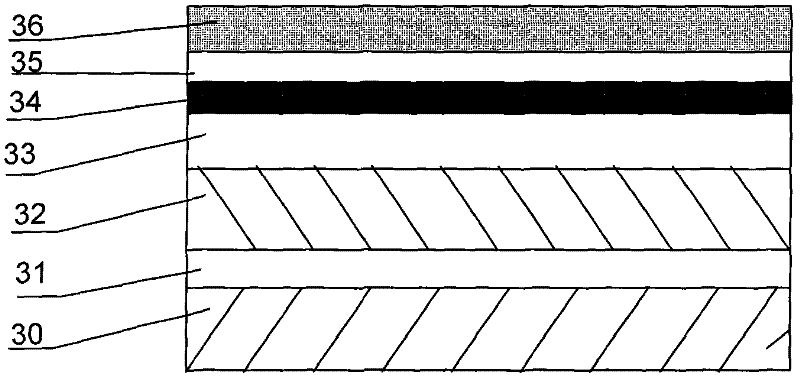
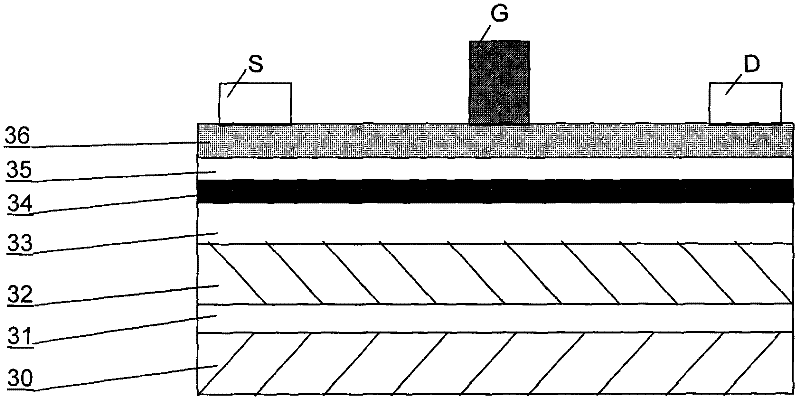
[0035] First, the sapphire substrate is cleaned at high temperature for 10 minutes. Then grow an aluminum nitrogen buffer layer 31 on the sapphire (0001) surface at a growth temperature of 1100° C. and a growth thickness of 30 nm.
[0036] A layer of high-resistance gallium nitride layer 32 is grown on the aluminum nitrogen buffer layer 31 with a thickness of 3 μm and a growth temperature of 1120° C.
[0037] A gallium nitride channel layer 33 is grown on the high-resistance gallium nitride layer 32 with a thickness of 30 nm and a growth temperature of 1080° C.
[0038] An indium nitrogen insertion layer 34 is grown on the gallium nitride channel layer 33 with a thickness of 10 nm and a growth temperature of 650° C. This layer contains indium nitrogen, which has the smallest electron effective mass among all group III nitride semiconductors, has high mobility and high saturation velocity. Thereby improving the mobility of the device...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Silicon carbide substrate
[0042] First, the silicon carbide substrate is cleaned at high temperature for 10 minutes; the aluminum nitrogen buffer layer 31 is grown again at a growth temperature of 1100° C. and a growth thickness of 30 nm.
[0043] A layer of high-resistance gallium nitride layer 32 is grown on the aluminum nitrogen buffer layer 31 with a thickness of 3 μm and a growth temperature of 1120° C.
[0044] A gallium nitride channel layer 33 is grown on the high-resistance gallium nitride layer 32 with a thickness of 30 nm and a growth temperature of 1080° C.
[0045] An indium nitrogen insertion layer 34 is grown on the gallium nitride channel layer 33 with a thickness of 10 nm and a growth temperature of 650° C.
[0046] An AlN insertion layer 35 is grown on the InN insertion layer 34 with a thickness of 8nm and a growth temperature of 1100°C.
[0047] An AlGaN barrier layer 36 is grown on the AlN insertion layer 35 with a thickness of 30nm, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com