Method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)-constructed composite particles with nuclear shell interpenetrating network structure
A technology of interpenetrating network structure and polyvinylidene fluoride, which is applied in the field of preparation of core-shell interpenetrating network structure composite particles, can solve the problems of changing crystalline properties, high melting temperature, difficult processing, etc., and achieves excellent anti-aging and performance. Excellent effect of improving melt processability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1PV
[0026] Implementation Case 1 Preparation of PVDF / PtBA Core-Shell Structured Composite Particles
[0027]
[0028] In a 100ml beaker, 2.6480g of PVDF seed emulsion (industrial product) with a solid content of 19.45% and an average particle diameter of 235nm was added, followed by 55.0g of deionized water, and ultrasonically dispersed for 40 minutes. The ultrasonically dispersed emulsion was poured into a four-necked reaction flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, a condenser tube, and a nitrogen inlet tube, the stirring was started and nitrogen gas was introduced, and the stirring rate was set at 300 rpm. After 15 minutes, the temperature of the reaction system was started, and 2.4870 g of tert-butyl acrylate was added to the reaction flask at the same time, and the cooling water of the reflux condenser was opened. When the temperature of the system was raised to 65°C, 5ml of an aqueous solution containing 0.0152g of potassium persulfate was added at one time, and the react...
Embodiment example 2~3
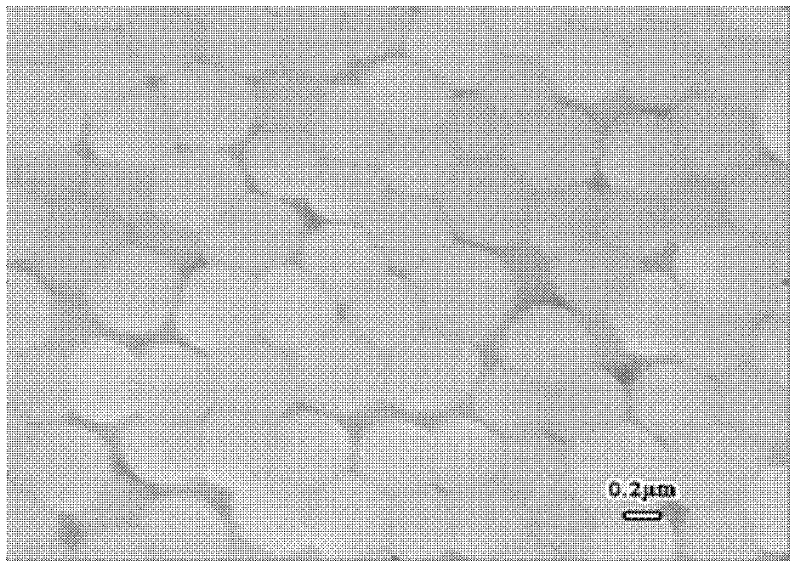
[0032]The polymerization reaction time of the implementation cases 2 to 3 is 30 minutes and 45 minutes respectively, and the rest of the implementation process is the same as that of the implementation case 1. The morphological SEM photographs of the composite particles prepared by implementation cases 2 to 3 are shown in the appendix respectively. image 3 , Figure 5 , the particle size distribution diagrams of the composite particles prepared in implementation cases 2 to 3 are shown in the attached Figure 4 and Image 6 . from image 3 It can be seen from the SEM photos that the composite latex particles in this system are not regular spherical, but special-shaped particles with an asymmetric structure. At this time, the average size of the composite latex particles is 308nm, which is higher than that of PVDF seeds with an average particle size of 235nm. , an increase of 73nm.
[0033] from Figure 5 We can clearly see that as the aggregation time increases, in ima...
Embodiment example 4~5
[0035] In embodiment case 4~5, polymerization temperature is 65 ℃, and the add-on of tBA monomer is respectively 1.5461g ( Figure 7 .b), 2.0649g( Figure 7 .c), and the rest of the operation steps are the same as the implementation case 1. The DSC curve of the composite particles prepared by implementation cases 4-5 is shown in Figure 7 . from Figure 7 It can be clearly seen that the crystallization temperature of PVDF decreases gradually from 142.5°C with the increase of the coating amount of PtBA polymer. When the feed ratio of seed to monomer is 1:4, the crystallization temperature of PVDF drops to 71.4°C. Therefore, the preparation method of the composite particles obviously changes the crystallization behavior of PVDF, so as to improve the melting processability of PVDF and the compatibility with other polymers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com