Method for treating smelting wastewater containing heavy metals
A treatment method and heavy metal technology, applied in the field of environmental science, to achieve the effects of reducing the amount of sediment, ensuring the quality of effluent water, and improving the comprehensive utilization of resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
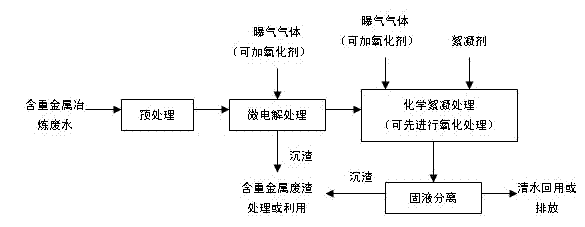
[0038] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the micro-electrolysis-chemical flocculation process for treating smelting wastewater containing heavy metals. The production workshop of a large-scale copper sulfide smelter contains heavy metal wastewater. The wastewater is mainly the ground flushing water of the smelter production workshop. The wastewater volume is 1000t / d, the pH of the wastewater is 5-6, and the heavy metal content (mg / L) is: Cu: 20.66 , Zn: 4.53, Pb: 1.80, Cd: 5.60, As: 3.71. In the treatment test, the waste water was collected and settled in the sedimentation tank to remove particulate matter, then adjusted to pH=3.0-3.5 with sulfuric acid, and the pretreated waste water was transferred to the fixed-bed micro-electrolysis equipment for iron-carbon micro-electrolysis treatment, and aeration was carried out during the treatment process; the fixed bed It is composed of iron and carbon granular fillers and iron-carbon structured fillers (structured fillers account for...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The acid washing workshop of a copper sulfide smelter contains heavy metal pickling wastewater, the wastewater volume is 200t / d, the wastewater contains 6-8% sulfuric acid, and the heavy metal components (mg / L) are: Cu: 181.70, Zn: 28.27, Pb: 167.05, Cd: 15.60, As: 176.71, F: 319.23. In the treatment test, the wastewater was adjusted to pH=2.5 with lime, and the supernatant was transferred to rolling micro-electrolysis equipment (rolling bed) for iron-carbon micro-electrolysis treatment after static precipitation. The total mass of iron and carbon particles accounted for the total mass of fillers. 100%, the ratio of iron to carbon mass is 5:1, using continuous flow iron-carbon micro-electrolysis secondary treatment, each stage of hydraulic retention is 25min, after the end of micro-electrolysis, the wastewater enters the aeration flocculation tank, adopts continuous aeration, aeration 3m 3 / m 3 Water, aeration time 40min, adjust pH=11.0 with milk of lime during aera...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Production wastewater in the indium zinc production workshop of an indium zinc smelter, the wastewater volume is 50t / d, the wastewater pH is 2.5-3.0, and the heavy metal content (mg / L) is: Cu: 4.32, Zn: 543.56, Pb: 2.77, Cd: 5.58 , As: 5.992, F: 19.06. In the treatment test, there is no particulate matter in the wastewater, and the pH of the wastewater is 2.5-3.0, which meets the requirements of iron-carbon micro-electrolysis treatment. Therefore, the wastewater directly enters the bottom aeration fluidized electrolytic cell (aeration fluidized bed) for iron-carbon micro-electrolysis treatment. The sum of the total mass of iron and carbon particles accounts for 100% of the total mass of the filler, and the ratio of iron to carbon mass is 1:1-2:1. Continuous flow iron-carbon micro-electrolysis is used for primary treatment, and the hydraulic retention is 30min. Continuous micro-electrolysis Aeration, the aeration volume is 3.0m 3 / m 3 water, and most of the ferrous io...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com