Method for preparing (methyl) acrylate polymer
An acrylate and polymer technology, applied in the field of acrylate polymers, can solve the problems of only 90% light transmittance of materials, complicated preparation process, etc., and achieves improved processing flow properties, increased initial thermal decomposition temperature, widened Effects in the processing range and field of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
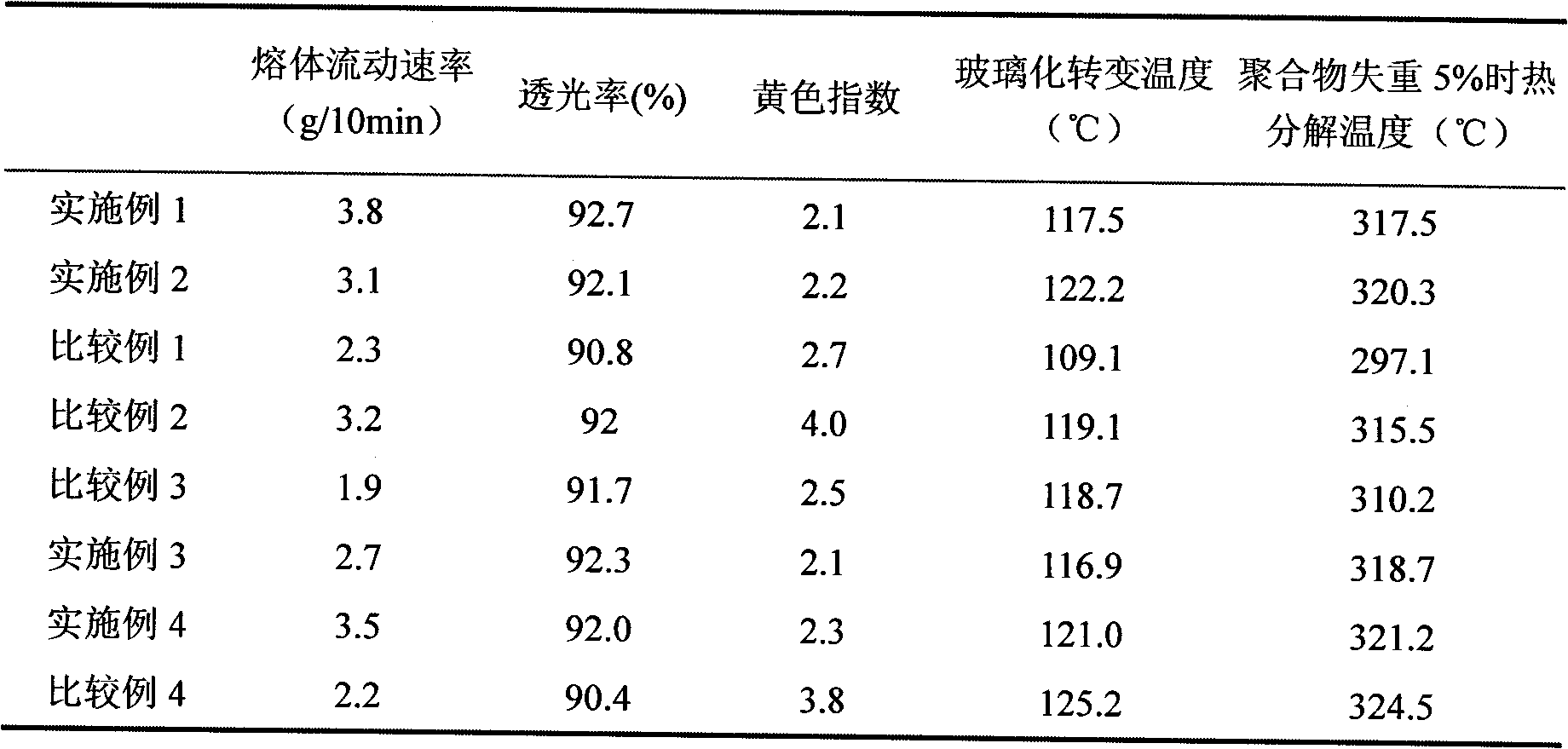
[0019] In the batching tank with a jacket, the raw materials such as methyl methacrylate, N-isopropylmaleimide, styrene, etc. are mixed, and then sent to the intermediate tank for temporary storage to ensure a constant feed amount. The feed composition of the monomer mixture: based on 100 parts by weight of methyl methacrylate, 3 parts by weight of N-cyclohexylmaleimide, 2 parts by weight of ethyl acrylate, 2 parts by weight of styrene, 0.15 parts by weight of di-tert- Butyl peroxide and 0.2 parts by weight of tert-dodecylmercaptan. Fill the batching tank and intermediate tank with nitrogen, remove the oxygen mixed in the monomer mixed solution, and control the oxygen content therein at 2ppm. The mixed solution of the above raw materials was continuously added to the 20L circulating tubular reactor replaced by nitrogen with a pump. The temperature in the circulating tubular reactor was maintained at 135°C. Until the polymerization conversion rate reaches 43.8%, the polymeriz...
Embodiment 2
[0021] The same equipment and operating method as in Example 1 were used. Adjusted the ratio of N-cyclohexylmaleimide in the copolymerization system, the raw material mixed solution consists of: taking 100 parts by weight of methyl methacrylate as the base, 5 parts by weight of N-cyclohexylmaleimide, 1 Parts by weight of ethyl acrylate, 4 parts by weight of styrene, 5 parts by weight of toluene, 0.15 parts by weight of di-tert-butyl peroxide and 0.2 parts by weight of tert-dodecyl mercaptan. The glass transition temperature and thermal decomposition temperature of the polymer increase with the increase of N-cyclohexylmaleimide content, the glass transition temperature reaches 122.2 ° C, and the thermal decomposition temperature reaches 320.3 ° C when the thermal weight loss is 5%. The product has excellent light transmission and apparent gloss. The polymer test results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0029] The same equipment and operating method as in Example 1 were used. The monomer composition of the polymerization system was adjusted: taking 100 parts by weight of methyl methacrylate as the base, 3 parts by weight of N-isopropylmaleimide, 2 parts by weight of ethyl acrylate, 2 parts by weight of styrene, 0.15 parts by weight of Di-tert-butyl peroxide and 0.2 parts by weight of tert-dodecylmercaptan. The glass transition temperature and thermal decomposition temperature of the polymer increased with the addition of N-isopropylmaleimide, the glass transition temperature reached 116.9°C, and the thermal decomposition temperature reached 318.7°C when the thermal weight loss was 5%. Polymer products have excellent light transmission and apparent gloss. The polymer test results are listed in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com