Preparation method of vanadium sodium fluophosphate cathode material of hybrid ion battery
A technology of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate and positive electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as easy sintering of lithium ions, unsuitable for high-rate current charging and discharging, production and application restrictions, and achieve large-scale production. High stability, improved electrochemical performance, easy to control and realize the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
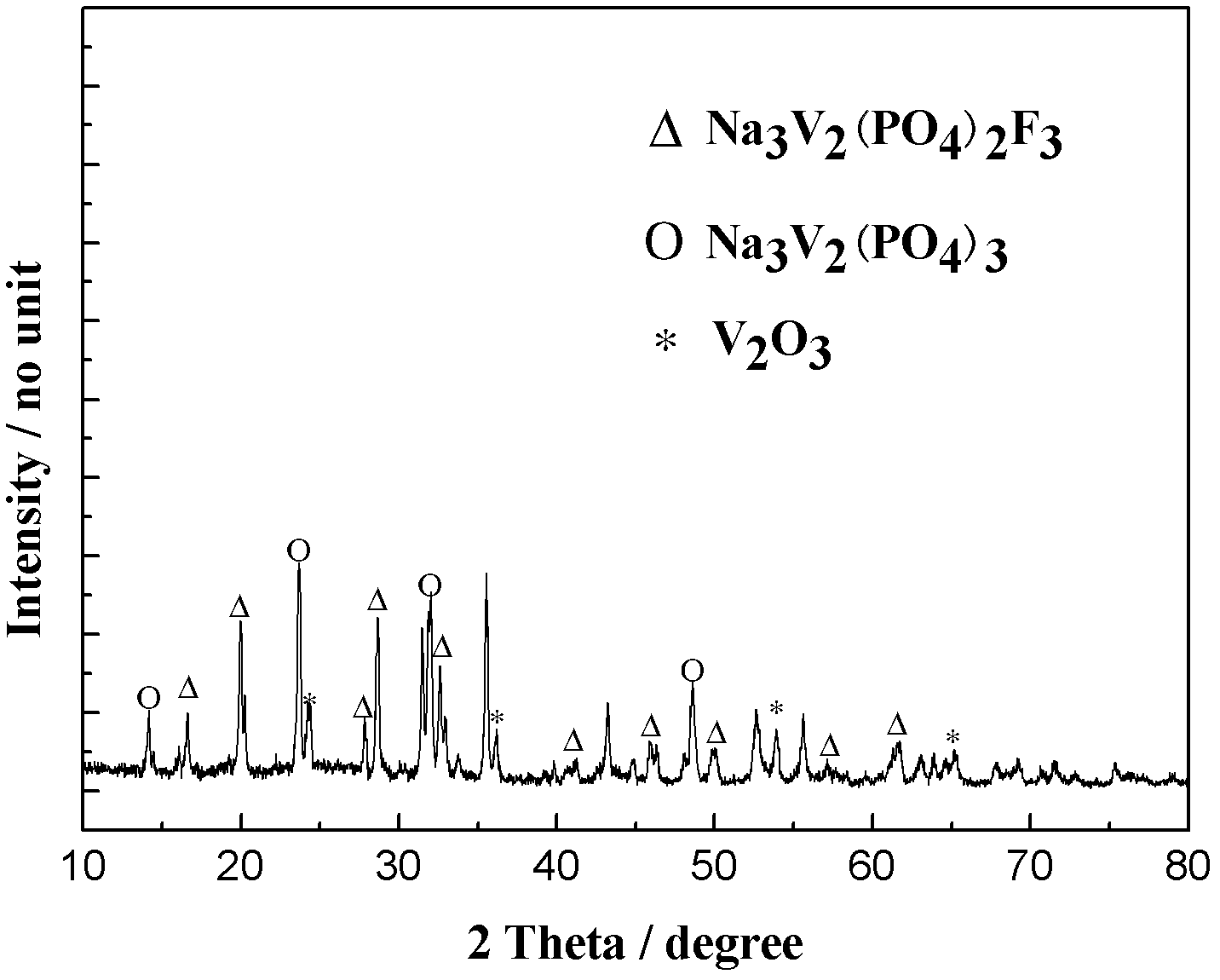
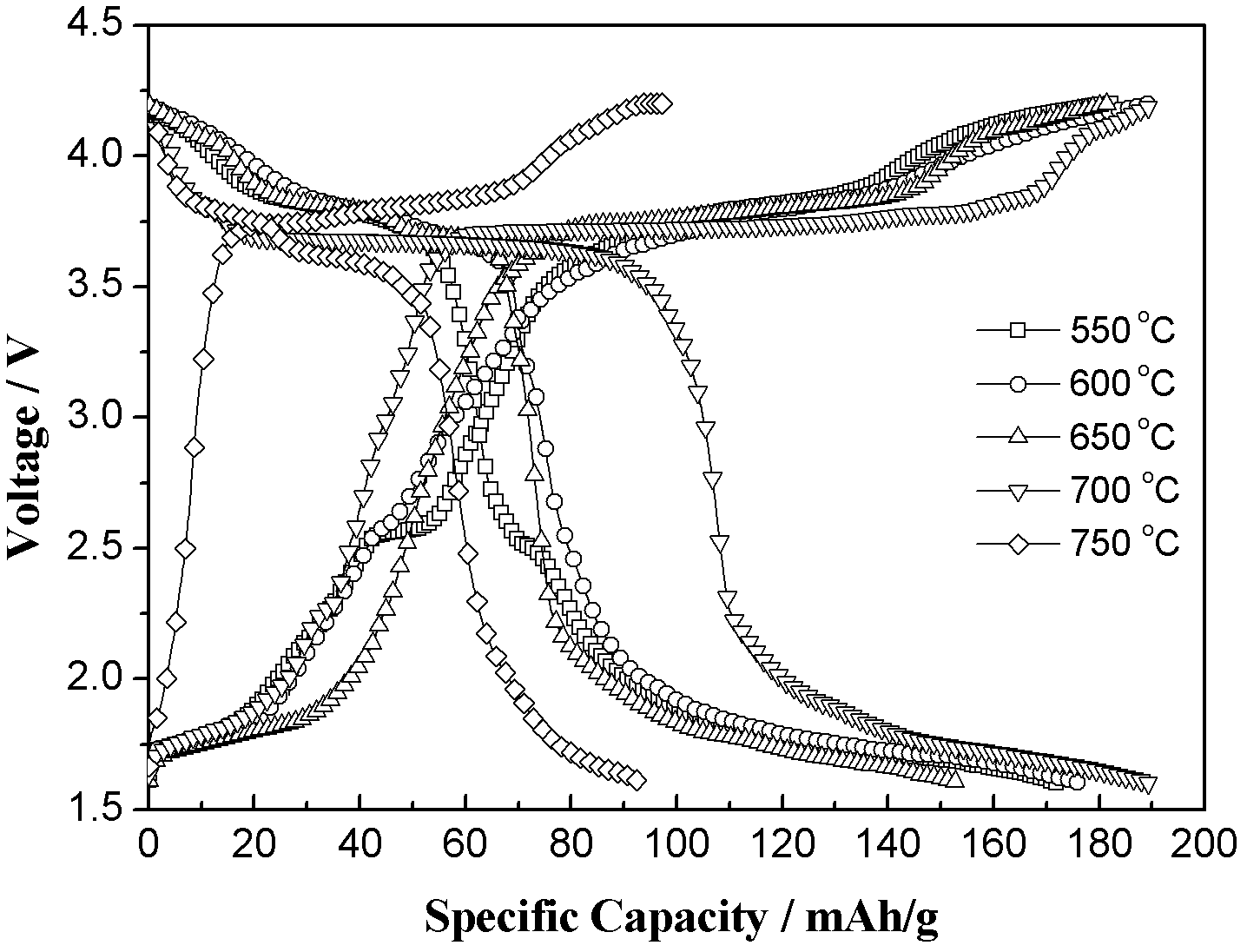
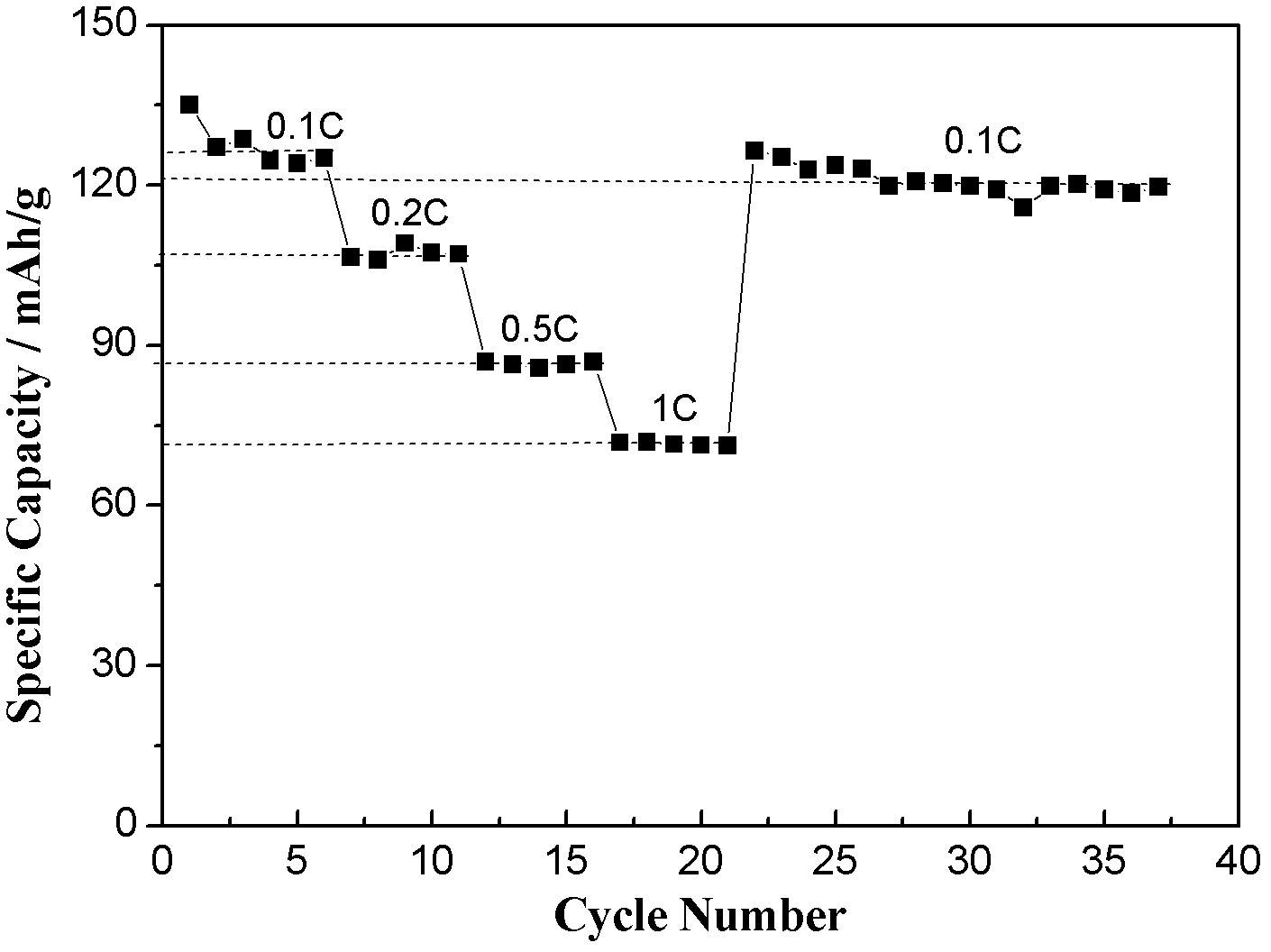
[0028] Firstly, accurately weigh 2.5g of raw materials and 0.125g of conductive agent acetylene black, the acetylene black as conductive agent is 5% of the total weight of raw materials, put them in a mortar and grind them for 2.5h to obtain a uniformly mixed precursor . The raw material part includes 0.567g NaF, 0.802g V 2 o 5 , 1.025g NH 4 h 2 PO 4 and 0.106g reducing agent acetylene black (V:P:F molar ratio is about 2:2:3). The well-ground precursor powder was placed in a tube furnace, and the temperature was gradually raised to 350°C at a rate of 3°C / min under an argon protective atmosphere, and kept at this temperature for 8 hours, and a solid mixture was obtained after natural cooling. After the solid powder is completely transferred to the mortar and fully ground again, the set temperature is reached at a heating rate of 3°C / min. Carry out calcination in the range of 550-750°C, keep warm in argon atmosphere for 8 hours, and cool naturally to obtain sodium vanadium...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Accurately weigh 2.5g of raw materials and 0.125g of conductive agent acetylene black. The acetylene black used as conductive agent is 5% of the total weight of the raw materials. They are placed in a mortar and ground for 2.5 hours to obtain a uniformly mixed precursor. The raw material part includes 0.567g NaF, 0.802g V 2 o 5 , 1.128g NH 4 h 2 PO 4 and 0.106g reducing agent acetylene black (V:P:F molar ratio is about 2:2.2:3). The well-ground precursor powder was placed in a tube furnace, and the temperature was gradually raised to 350°C at a rate of 3°C / min under an argon protective atmosphere, and kept at this temperature for 8 hours, and a solid mixture was obtained after natural cooling. Completely transfer the solid powder to a mortar and fully grind it again, then calcinate at 550-750°C with a heating rate of 3°C / min, keep it in an argon atmosphere for 8 hours, and cool naturally with the furnace to obtain sodium vanadium phosphate. Other steps are the same...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Accurately weigh 2.5g of raw materials and 0.075g of conductive agent acetylene black. The acetylene black used as conductive agent is 3% of the total weight of raw materials. They are placed in a mortar and thoroughly ground for 2.5 hours to obtain a uniformly mixed precursor. The raw material part includes 0.567g NaF, 0.802g V 2 o 5 , 1.025g NH 4 h 2 PO 4 and 0.106g reducing agent acetylene black (V:P:F molar ratio is about 2:2:3). The well-ground precursor powder was placed in a tube furnace, and the temperature was gradually raised to 350°C at a rate of 3°C / min under an argon protective atmosphere, and kept at this temperature for 8 hours, and a solid mixture was obtained after natural cooling. Completely transfer the solid powder to a mortar and fully grind it again, then calcinate at 550-750°C with a heating rate of 3°C / min, keep it in an argon atmosphere for 8 hours, and cool naturally with the furnace to obtain sodium vanadium phosphate. Other steps are the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com