Method for measuring surface adhesive capacity and elastic modulus of soft material
A technology of elastic modulus and measurement method, applied in the direction of measurement device, analysis material, surface/boundary effect, etc. Large volume and other problems, to achieve the effect of a wide range of test materials, good stability and repeatability, and small sample volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The measurement of the force-displacement curve of embodiment 1 gel
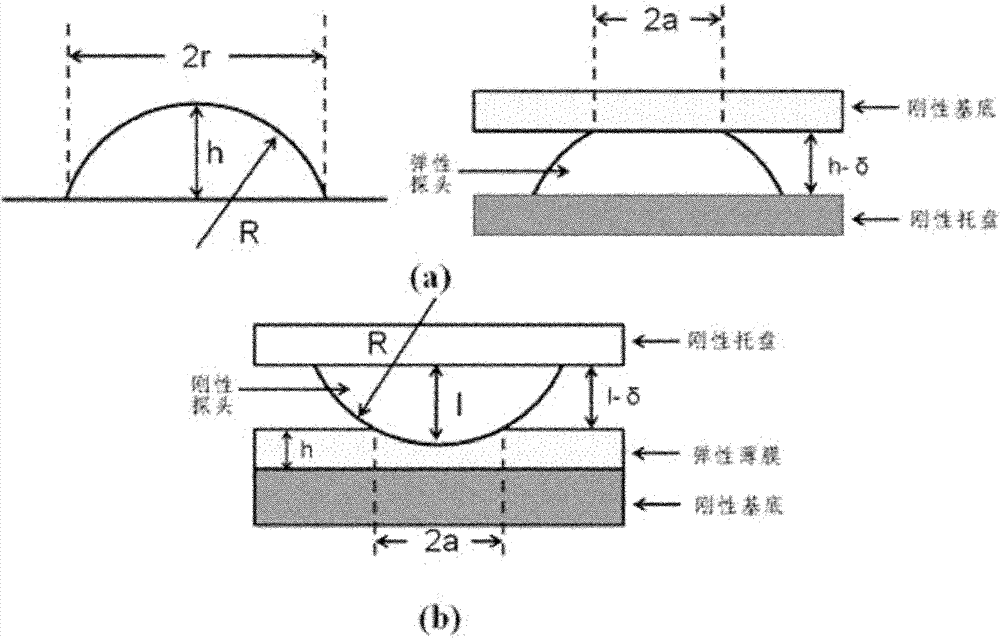
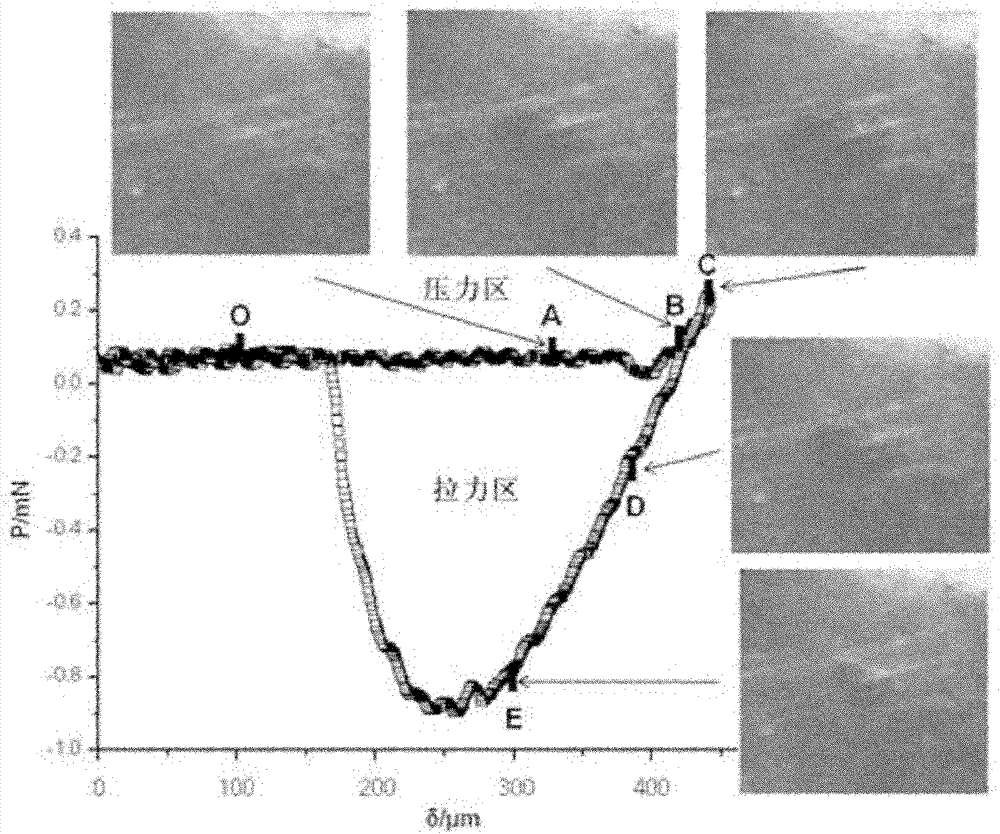
[0038] figure 1 (a) is a schematic diagram of the geometric dimensions of the elastic probe. The radius of the spherical surface is R, the radius of the bottom surface is r, and the height is h. The elastic probe fixed on the rigid tray is in contact with the rigid substrate. The radius of the contact surface is a, and it is perpendicular to the substrate direction produces deformation δ; (b) is a schematic diagram of a medium-rigid probe, in which the rigid probe presses down on the elastic film attached to the rigid substrate, and the amount of pressure perpendicular to the substrate is δ. like figure 1 As shown in (b), a round self-made gel with a thickness h of 4 mm and a radius of 10 mm is glued to the glass slide with 502 glue. 3 ± 0.001mm stainless steel ball, the pressing distance δ is 50 microns, and then leave the steel ball at the same speed until it is completely detached. figure 2 is ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 The measurement of the three cyclic force-displacement curves of the gel
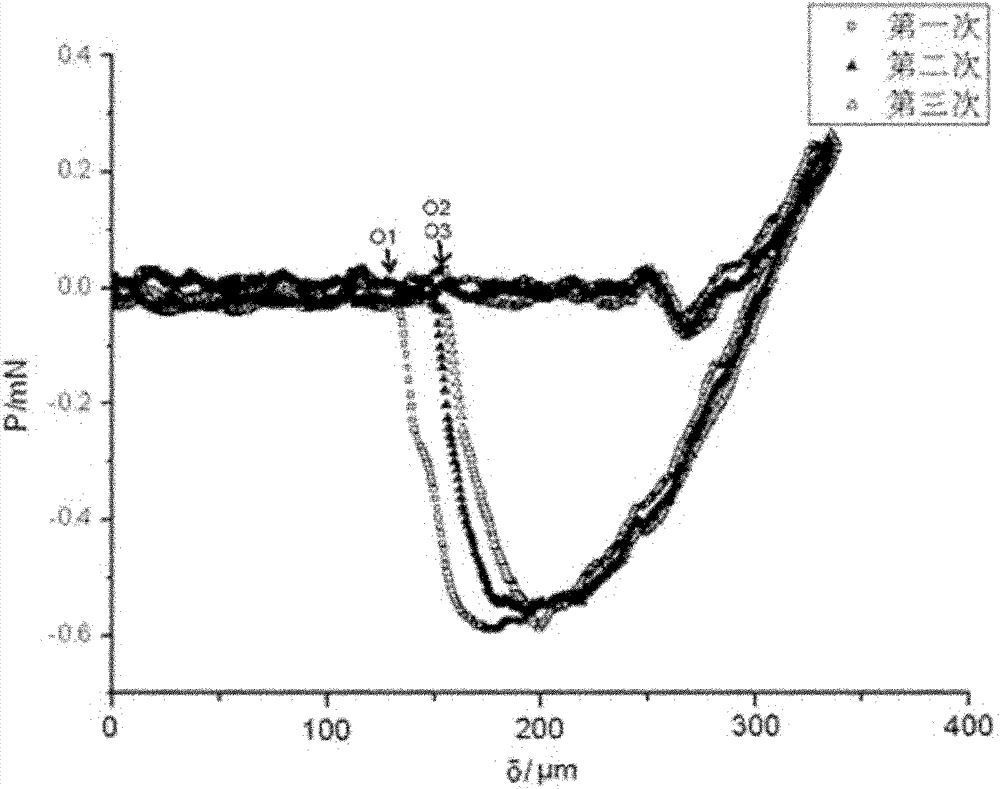
[0040] same as figure 1 As shown in (b), a round self-made gel with a thickness h of 4mm and a radius of 10mm is glued to the glass slide with 502 glue, and the radius R is 3±0.001 under the control of the stepper motor at a speed of 10 microns / second mm stainless steel ball, the pressing distance δ is 50 microns, and then leave the steel ball at the same speed until it is completely separated, and repeat the above process to obtain the results of three cycle measurements. image 3 is the cyclic force-displacement curve of the gel. As shown in the figure, O1, O2, and O3 are the tension points 0 in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd tests respectively. The viscous deformation of the material can be analyzed from the positions of the three points. There is a large distance between O2 and O1. In the second test, the material experienced obvious viscous deformation, and the positions of O3 and O2 were...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com