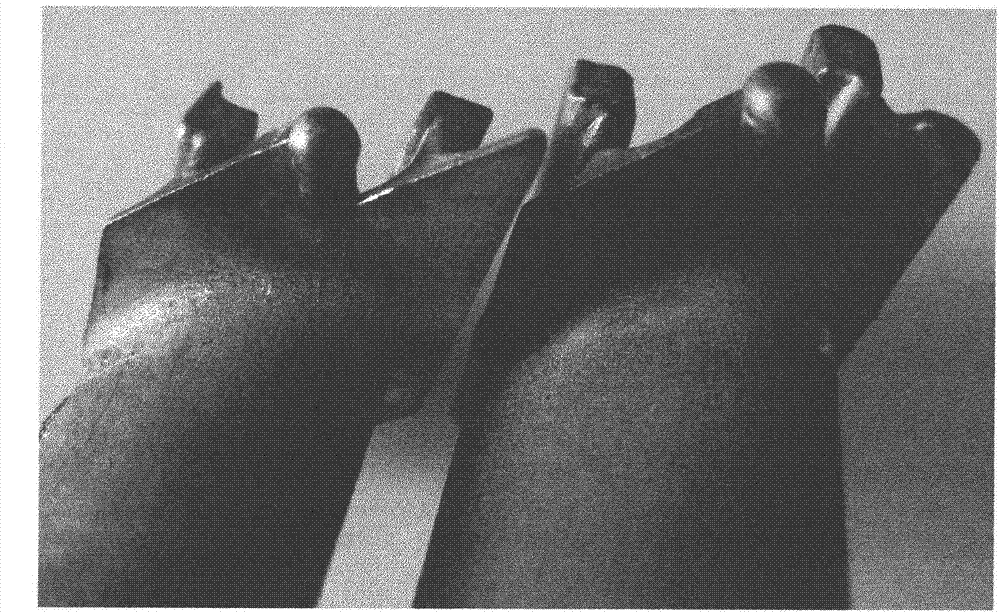
Method for overlaying wear-resistant layer of blade shroud of turbine working blade
A wear-resistant layer and blade technology, which is applied in the field of argon tungsten arc welding technology, can solve the problems of aging cracks in the substrate and increase the difficulty of surfacing welding operations, etc., so as to improve the working life, wide application prospects and high technology maturity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1 A method for surfacing wear-resistant layer of blade shroud of turbine working blade
[0028] The T800 cobalt-based wear-resistant alloy welding wire developed by American GE company B50TF193 standard is used to surfacing the wear-resistant layer of the low-pressure turbine working blade crown (small inclination angle, small damping surface "Z-shaped tooth" structure). The content of this embodiment is mainly as follows:
[0029] 1. Preparation before welding
[0030] 1.1 Solution heat treatment: The solution heat treatment system is to raise the temperature to 1220 ° C ± 10 ° C, keep it warm for 4.0h ~ 4.5h, and then cool it with argon in vacuum.
[0031] 1.2 Cleaning before welding: use mechanical grinding to clean the surfacing welding surface and its surrounding 15mm area, including the surface where the edge is connected to the surfacing welding surface, clean the welding wire, the surfacing welding surface and its surrounding area with acetone or alc...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 A method for surfacing wear-resistant layer of blade shroud of turbine working blade
[0045] The S-6 cobalt-based wear-resistant alloy welding wire developed by the American Metal Society AMS5788 standard is used to surfacing the wear-resistant layer of the blade crown ("Z-shaped tooth" structure) of the low-pressure turbine blade.
[0046] In this example, S-6 cobalt-based alloy welding wire is used, and its main component is Co-Cr-W alloy. Compared with Example 1, the inclination angle of the "Z-shaped tooth" of the working blade crown of this low-pressure turbine exceeds 90 degrees, which is relatively easy in welding operation, and does not need to be separately surfacing at the root of the transfer R, which is only applied to Example 1 Parameter 2 can complete the surfacing. The surface of the surfacing layer should be silver-gray metallic luster (depending on the alloy composition of the welding wire) after visual inspection after welding, and other...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3 A method for surfacing wear-resistant layer of turbine working blade crown
[0048] A method for overlaying a wear-resistant layer on a blade crown of a working turbine blade uses manual argon tungsten arc welding, and its specific process parameters meet the following requirements:
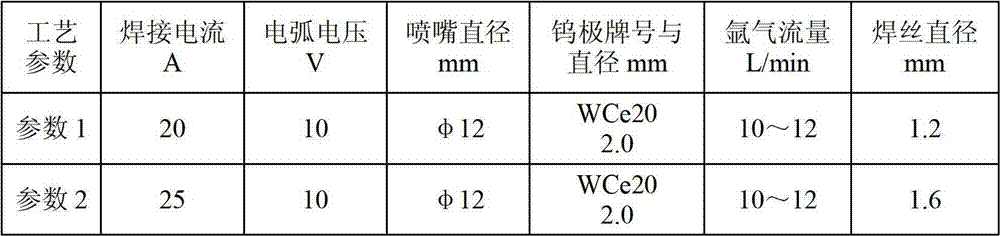
[0049] Welding wire selection: T800 cobalt-based wear-resistant alloy welding wire developed according to the standard B50TF193 of GE Company of the United States and S-6 cobalt-based wear-resistant alloy welding wire developed according to the standard AMS5788 of the American Institute of Metals; diameters are: φ1.6mm and φ1.2mm; tungsten Pole grade and diameter: WCe20φ2.0mm; nozzle diameter: φ12mm, welding current: 20A~25A, shielding gas flow: 10L / min~12L / min.
[0050] Specifically, in the method for overlaying the wear-resistant layer of the blade crown of the turbine working blade, when performing the operation of overlaying the "Z-shaped tooth" of the blade crown and tran...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com