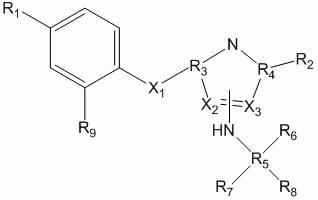
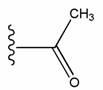
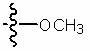
Compositions and methods relating to heat shock transcription factor activating compounds and targets thereof
A compound and composition technology, applied in the field of heat shock transcription factor activation compounds, can solve problems affecting functions, incomplete folding of proteins, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0122] This example describes the optimization of growth conditions for the DTY512 strain. Such as image 3 It was demonstrated that the growth conditions of the yhsfΔ strain (DTY512 strain) of the pRS424-GPD-hHSF1 plasmid implicating 1) the yeast HSF gene coupled to the GAL promoter, and 2) hHSF1 expression were from petri dish to 96-well microplate format to optimize. Cells were grown in synthetic complete medium lacking uracil and tryptophan in the presence of the non-inducing / non-repressing carbon source raffinose (2%) to select for plasmid maintenance. A concentration of galactose (0.01%) was empirically identified that induced sufficient levels of yeast HSF to enhance yeast cell viability while sensitizing cells after addition of 4% glucose to enhance glucose repression of yeast HSF expression. Selected cells were grown to mid log phase in selective synthetic complete medium containing 2% raffinose and 0.01% galactose. The culture was then diluted to ~5,000 cells / ml i...
Embodiment II
[0124] This example describes the identification of candidate HSF1 activating compounds. Such as image 3 As shown, suitable growth conditions were identified, applying yeast-based human HSF1 activators screened into high-throughput 96-well grid plates for galactose induction and glucose repression parameters. This screen evaluated a combinatorial chemical library of ~10,500 different compounds constructed from ~75 individual scaffolds in the PPD library (PPD Discovery Research, Research Triangle Park, NC). Although this was an appropriately sized screen, ~50 different library components were identified that would adequately enhance yeast cell growth within 48-96 hours of inoculation at a concentration of 10 micromolar. Figure 4A Small samples of 5 compounds that stimulate yeast cell growth with varying potency, a DMSO solvent control and one compound that was negative in this screen are shown. Subsequent analysis of 32 more potent compounds confirmed that the potency of al...
Embodiment III
[0128] This example describes the materials and methods used in Examples IV-VII.
[0129] cell culture. Wild-type and hsf1 - / - mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells were grown in DMEM + 10% FBS (37 o C, 5% CO 2 )middle. For MEF cells, at the time of experiment, mix 6X10 5 cells were seeded in each well of a 6-well plate. Cells were incubated under these conditions for an additional 12 hours, at which point the cells were washed twice with IX PBS before the growth medium was switched to serum-free OptiMEM medium (Invitrogen). For PC-12 cells, make 5X10 5 Cells were seeded in each well of a 6-well plate in 2 ml of serum-free OptiMEM medium and incubated under these conditions for an additional 12 hours. After 12 hours, HSF1A or DMSO was added to MEF or PC-12 cells, and at 37 o C for 15 hours.
[0130] western blotting. After 15 hr of treatment, cells were washed twice in IX PBS and collected by scraping. Cells were lysed using lysis buffer solution (25mM Tris, 150m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com