GaN-based light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and growing method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and growth methods, applied in the field of GaN-based light-emitting diode epitaxial wafers and their growth, can solve problems such as high difficulty, long-term stable production instability, and complex growth, and achieve the effects of reducing density and improving ESD resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
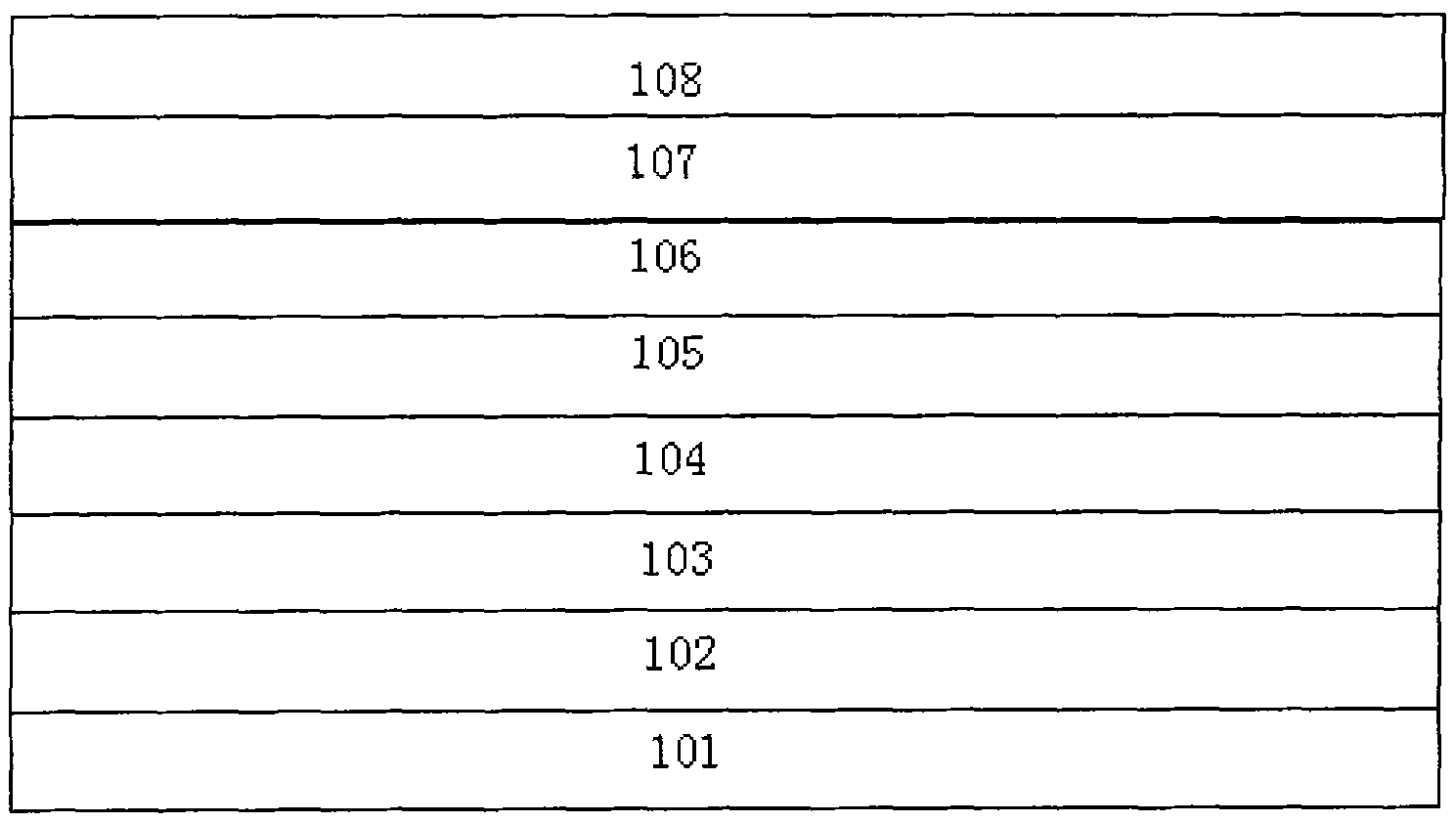
[0012] The MOCVD method is used to grow sequentially from bottom to top:
[0013] 1. Put the sapphire substrate with (0001) crystal orientation into the reaction chamber, and then 2 The temperature in the environment is raised to 1100° C., stabilized for 3 minutes, and the substrate is purified at high temperature.
[0014] 2. Lower the temperature to 530° C. and grow a low-temperature gallium nitride-based buffer layer with a thickness of 20 nm at a growth pressure of 300 mbar.
[0015] 3. The temperature is raised to 1170° C., the growth pressure is 100 mbar, and non-doped gallium nitride with a thickness of 1.3 μm is grown.
[0016] 4. At 1170° C. and a growth pressure of 100 mbar, grow n-type gallium nitride with a thickness of 1.5 μm.
[0017] 5. In N 2 The multi-quantum well layer is grown for 5 cycles in the environment, the growth pressure is 100mbar, the GaN barrier layer: the thickness is 10nm, the growth temperature is 800°C; the InGaN well layer: the thickness i...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The MOCVD method is used to grow sequentially from bottom to top:
[0025] 1. Put the sapphire substrate with (0001) crystal orientation into the reaction chamber, and then 2 The temperature in the environment is raised to 1200° C., stabilized for 5 minutes, and the substrate is purified at high temperature.
[0026] 2. Lower the temperature to 550° C. and grow a low-temperature gallium nitride-based buffer layer with a thickness of 40 nm at a growth pressure of 500 mbar.
[0027] 3. Raise the temperature to 1180° C. and grow the non-doped GaN with a thickness of 1.5 μm at a growth pressure of 300 mbar.
[0028] 4. At 1180° C. and a growth pressure of 300 mbar, grow n-type gallium nitride with a thickness of 1.7 μm.
[0029] 5. In N 2 The multi-quantum well layer is grown for 5 cycles in the environment, the growth pressure is 100mbar, the GaN barrier layer: the thickness is 10nm, the growth temperature is 800°C; the InGaN well layer: the thickness is 1nm, the growth...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The MOCVD method is used to grow sequentially from bottom to top:
[0037] 1. Put the sapphire substrate with (0001) crystal orientation into the reaction chamber, and then 2 The temperature in the environment is raised to 1200° C., stabilized for 5 minutes, and the substrate is purified at high temperature.
[0038] 2. Lower the temperature to 570° C. and grow a low-temperature gallium nitride-based buffer layer with a thickness of 50 nm at a growth pressure of 700 mbar.
[0039] 3. Raise the temperature to 1190° C. and grow the non-doped GaN with a thickness of 1.8 μm at a growth pressure of 700 mbar.
[0040] 4. At 1190° C. and a growth pressure of 700 mbar, grow n-type gallium nitride with a thickness of 2 μm.
[0041] 5. In N 2 The multi-quantum well layer is grown for 5 cycles in the environment, the growth pressure is 100mbar, the GaN barrier layer: the thickness is 10nm, the growth temperature is 800°C; the InGaN well layer: the thickness is 1nm, the growth tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com