Method for constructing virus live vector recombinant vaccine by utilizing transposon
A technology of recombinant vaccines and transposons, applied in viruses/bacteriophages, botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of easy mutation, low recombination efficiency, and scarcity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Preparation method of rabies-recombinant canine adenovirus type 2
[0030] 1. Construction of GFP and rabies glycoprotein gene expression cassettes
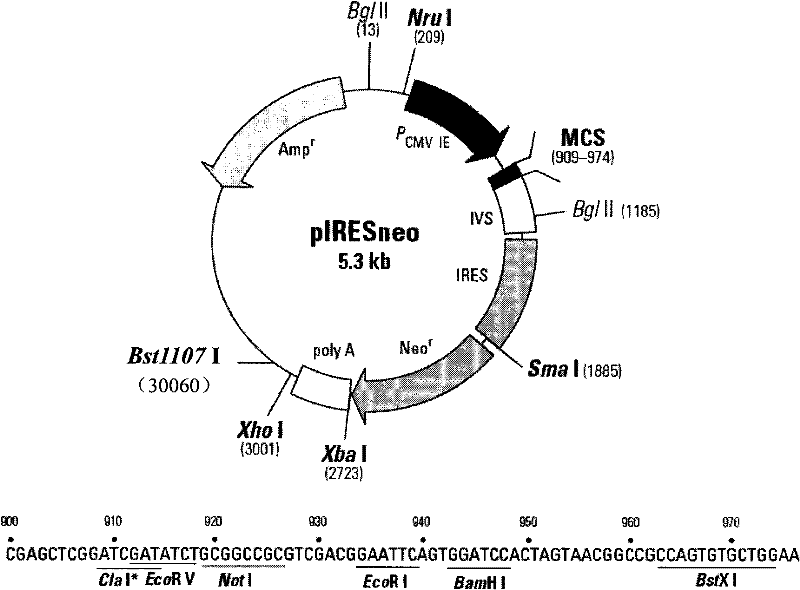
[0031] The commercially available eukaryotic expression plasmid vector pIRESneo ( figure 2 ) into the rabies virus glycoprotein gene (refer to GenBank: M31046 for the sequence) using the multiple cloning restriction sites EcoRV and BamHI, and insert the green fluorescent protein reporter gene (refer to the universal plasmid pEGPF-C1 for the sequence) using the Sma I and XbaI sites, and construct a parallel Expression cassettes expressing the glycoprotein and green fluorescent protein genes.
[0032] 2. Construction of recombinant transposons
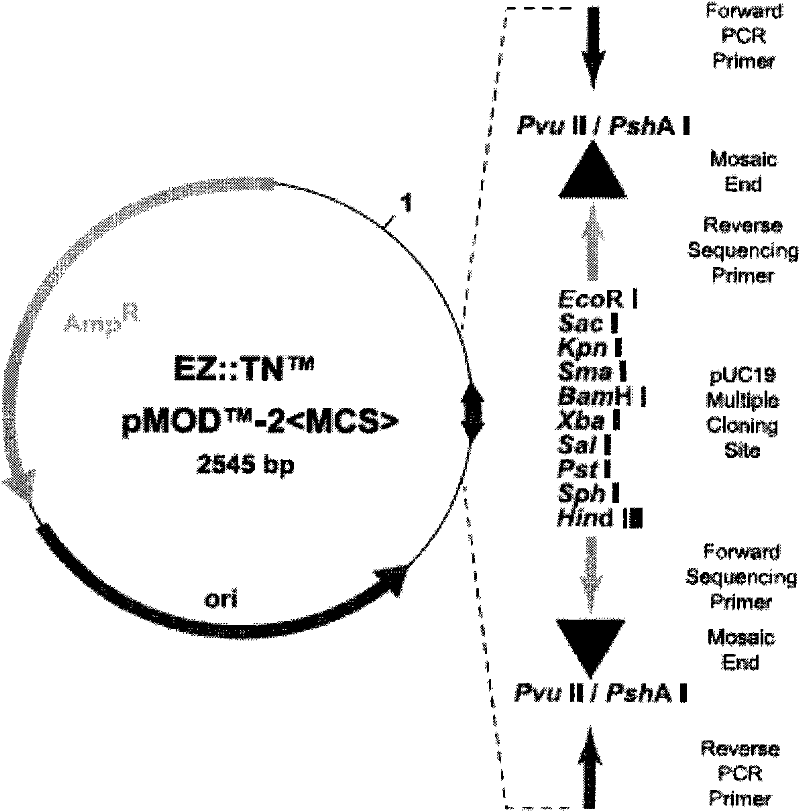
[0033] The gene expression cassette was completely excised through the Nru I and Bst1107 I sites, and inserted into the shuttle vector pMOD-2 using T4 ligase The Sma I site between the two transposon sequences in figure 1 ), transform Escherichia coli DH5α...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: the preparation method of rabies-recombinant herpes virus type I
[0046] 1. Construction of GFP and rabies glycoprotein gene expression cassettes
[0047] The commercially available eukaryotic expression plasmid vector pIRESneo ( figure 2 ) into the rabies virus glycoprotein gene (refer to GenBank: M31046 for the sequence) using the multiple cloning restriction sites EcoRV and BamHI, and insert the green fluorescent protein reporter gene (refer to the universal plasmid pEGPF-C1 for the sequence) using the Sma I and Xba I sites, and construct Expression cassette for parallel expression of glycoprotein and green fluorescent protein genes.
[0048] 2. Construction of recombinant transposons
[0049] The gene expression cassette was completely excised through the Nru I and Bst1107 I sites, and inserted into the shuttle vector pMOD-2 using T4 ligase The Sma I site between the two transposon sequences in figure 1 ), transform Escherichia coli D...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: Preparation method of classical swine fever-recombinant canine adenovirus type 2
[0062] 1. Construction of gene expression cassettes for green fluorescent protein and classical swine fever virus E2 protein
[0063] The commercially available eukaryotic expression plasmid vector pIRESneo ( figure 2 ) into the E2 protein gene of classical swine fever virus (refer to GenBank: AF091507 for the sequence) using the multiple cloning restriction sites EcoRV and BamHI, and insert the green fluorescent protein reporter gene (refer to the universal plasmid pEGPF-C1 for the sequence) using the SmaI and XbaI sites, and construct a parallel Expression cassettes expressing the glycoprotein and green fluorescent protein genes.
[0064] 2. Construction of recombinant transposons
[0065] The gene expression cassette was completely excised through the Nru I and Bst1107 I sites, and inserted into the shuttle vector pMOD-2 using T4 ligase The Sma I site betwe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com