Oxygen-doped II-VI semiconductor material, thin-film and prepared solar energy battery
A solar cell, II-VI technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of high material cost, low conversion efficiency, and limited sources, and achieve the effects of low production cost, high photoelectric conversion efficiency, and low preparation temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
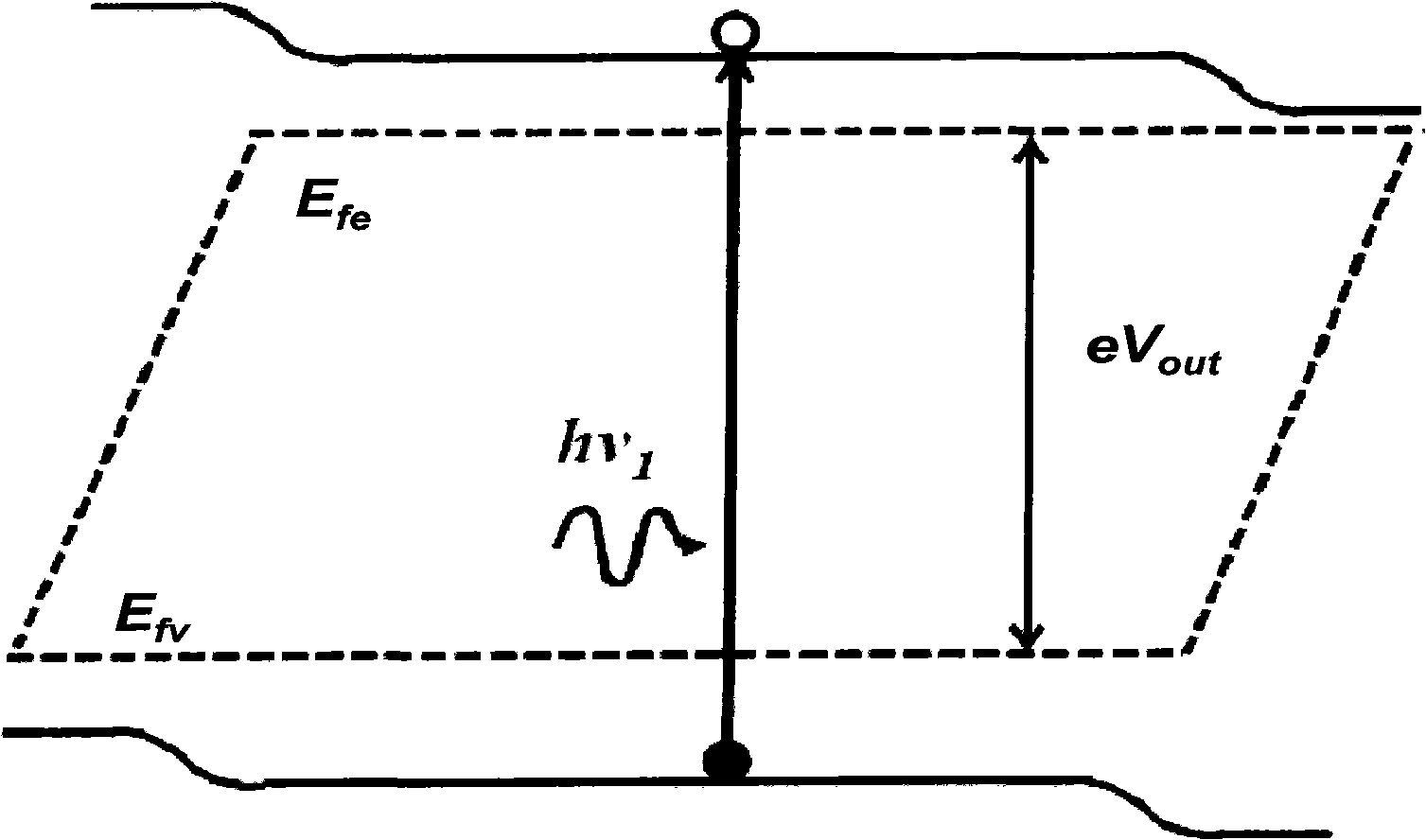
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 : Oxygen-doped ZnTe semiconductor material and preparation method thereof
[0044] This embodiment is oxygen-doped zinc telluride (ZnTe:O) and its preparation method provided by the present invention.
[0045] Oxygen-doped zinc telluride provided by the present invention is made by passing in oxygen with a pressure of 1mTorr to 1Torr at about 200°C, and mixing it with argon to form a working gas with a pressure of 10Torr to 100Torr, and sputtering with high purity (>99.9995%) The ZnTe target is formed, and the oxygen doping concentration of the prepared oxygen-doped zinc telluride is 10 18 cm -3 ~10 21 cm -3 , with a thickness of about 2000 nm.
[0046] The above preparations were completed on an Enerjet III sputtering platform (purchased from KDF, USA).
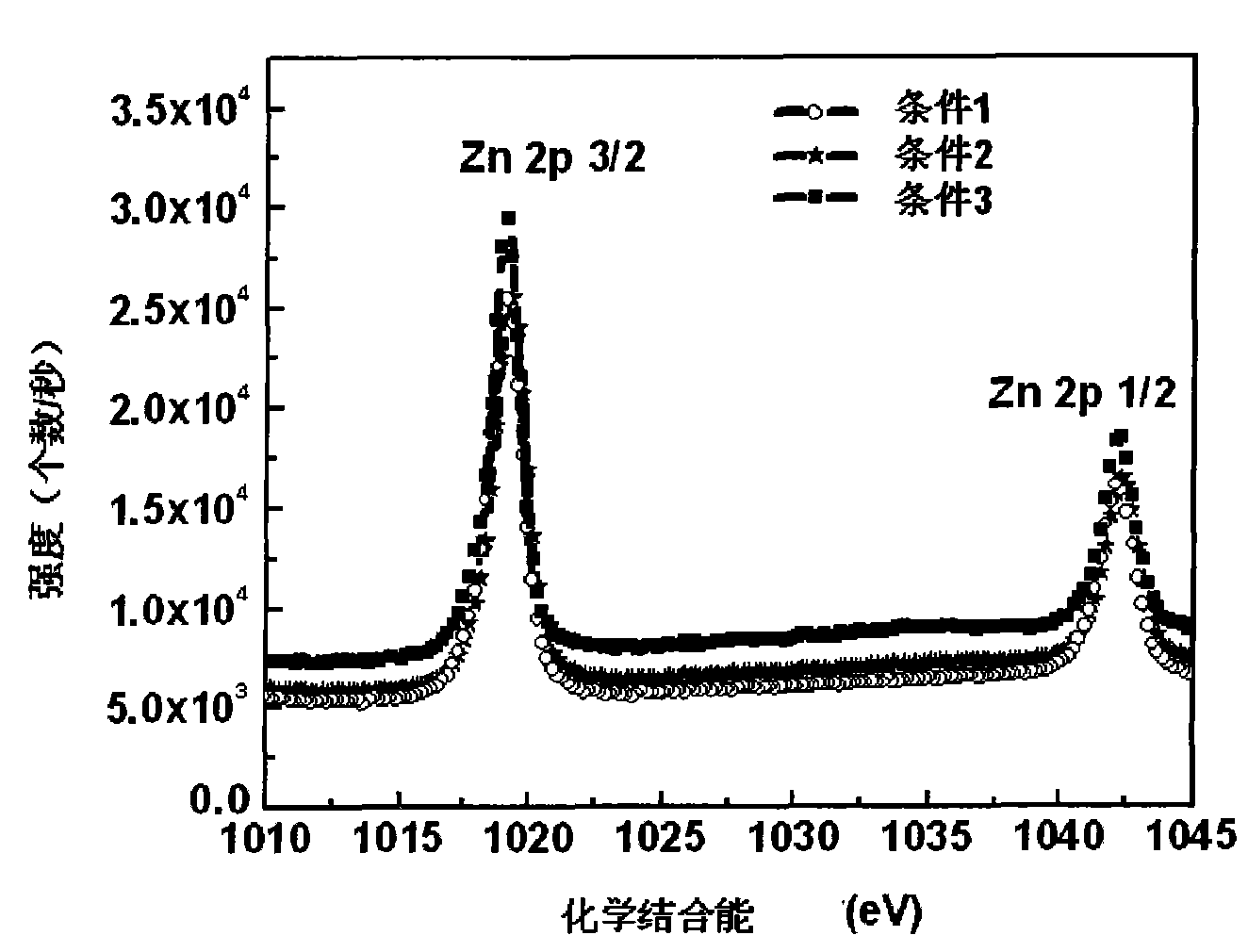
[0047] Adopt X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Kratos AxisUltra XPS) to measure the prepared oxygen-doped zinc telluride semiconductor material, the results are as fo...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 : Oxygen-doped zinc telluride thin film solar cell and preparation method thereof
[0049] This embodiment is an oxygen-doped zinc telluride thin-film solar cell and a preparation method thereof provided by the present invention.
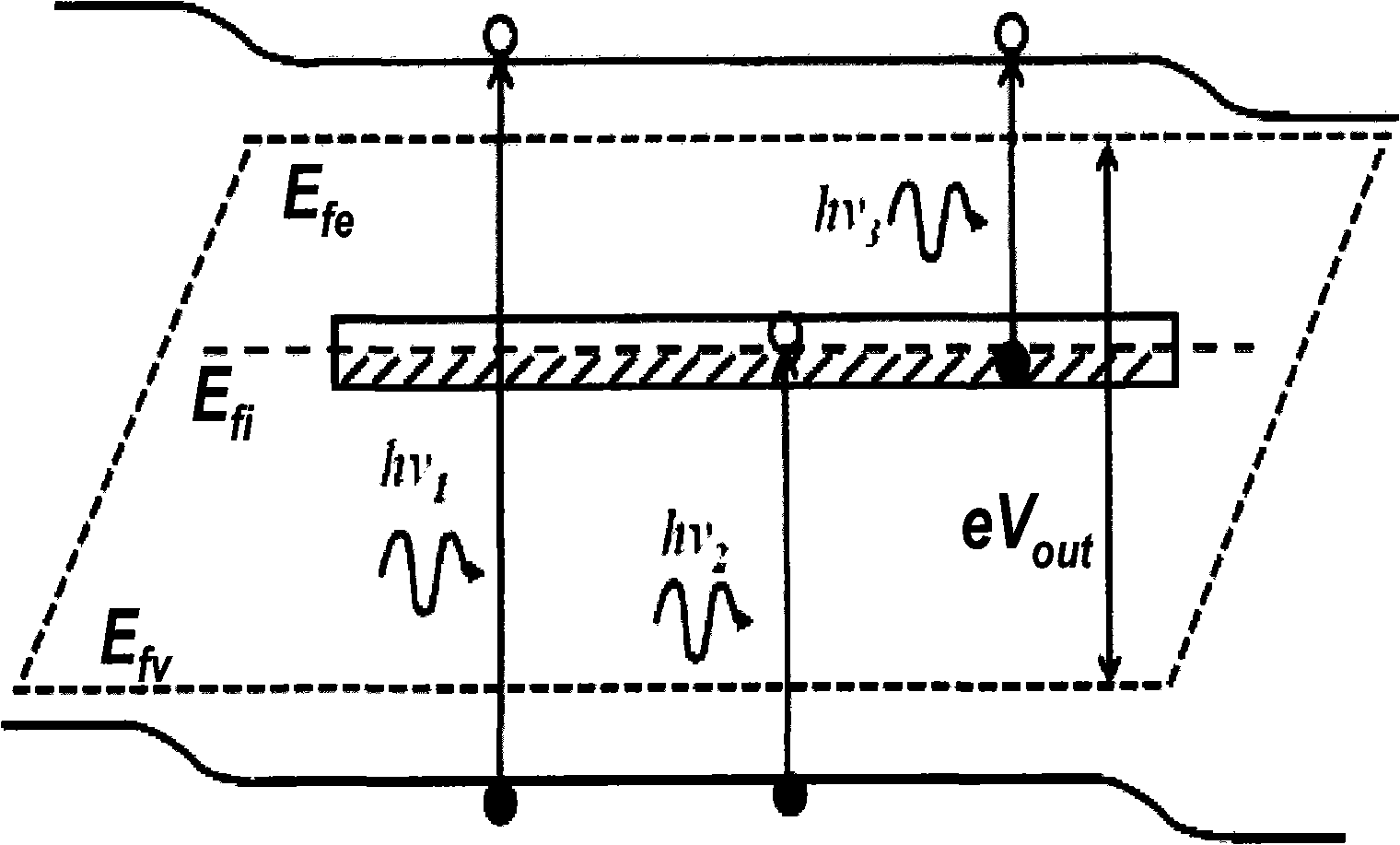
[0050] The structure of the oxygen-doped zinc telluride thin film solar cell provided by the present invention is shown in FIG. 3 . The thickness of the thin-film solar cell does not exceed 10 microns, and its structural composition is detailed as follows:
[0051] The substrate (Sub) is glass or transparent plastic;
[0052] The fourth layer (EP4) is a highly conductive n-type semiconductor, specifically n-type doped zinc oxide (ZnO), or zinc magnesium oxide (ZnMgO), with a thickness of 300 nanometers and an electron concentration greater than 10 18 cm -3 , the resistivity is less than 0.05 ohm cm.
[0053] The third layer (EP3) is a buffer layer, which is zinc selenide (ZnSe) that can grow at room temperature, with a thickne...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 : Application of Oxygen-doped ZnTe Thin Film Solar Cells
[0067] This embodiment is the application of the oxygen-doped zinc telluride thin film solar cell of the present invention.
[0068] The oxygen-doped zinc telluride thin-film solar cell developed by the present invention can be widely used in the field of solar power generation, including civil and commercial rooftop power generation, power supply and charging of personal portable electronic products, medium-scale and large-scale grid-connected solar cells in suburban cities. Large-scale solar power plants, etc.
[0069] 1. Application of the solar cell of the present invention in the field of solar power generation
[0070] Oxygen-doped zinc telluride thin-film solar cells have the characteristics of easy integration, high reliability, long service life, lightness, beauty, environmental protection and low cost, ordinary residents, factories and mines, commercial building roofs, and car shells can b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com