Tea leaf protein polypeptide and preparation method and application thereof
A protein polypeptide and tea technology, which is applied in food preparation, protein food processing, plant protein processing, etc., can solve problems such as poor water solubility, waste of tea protein resources, and difficulty in purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
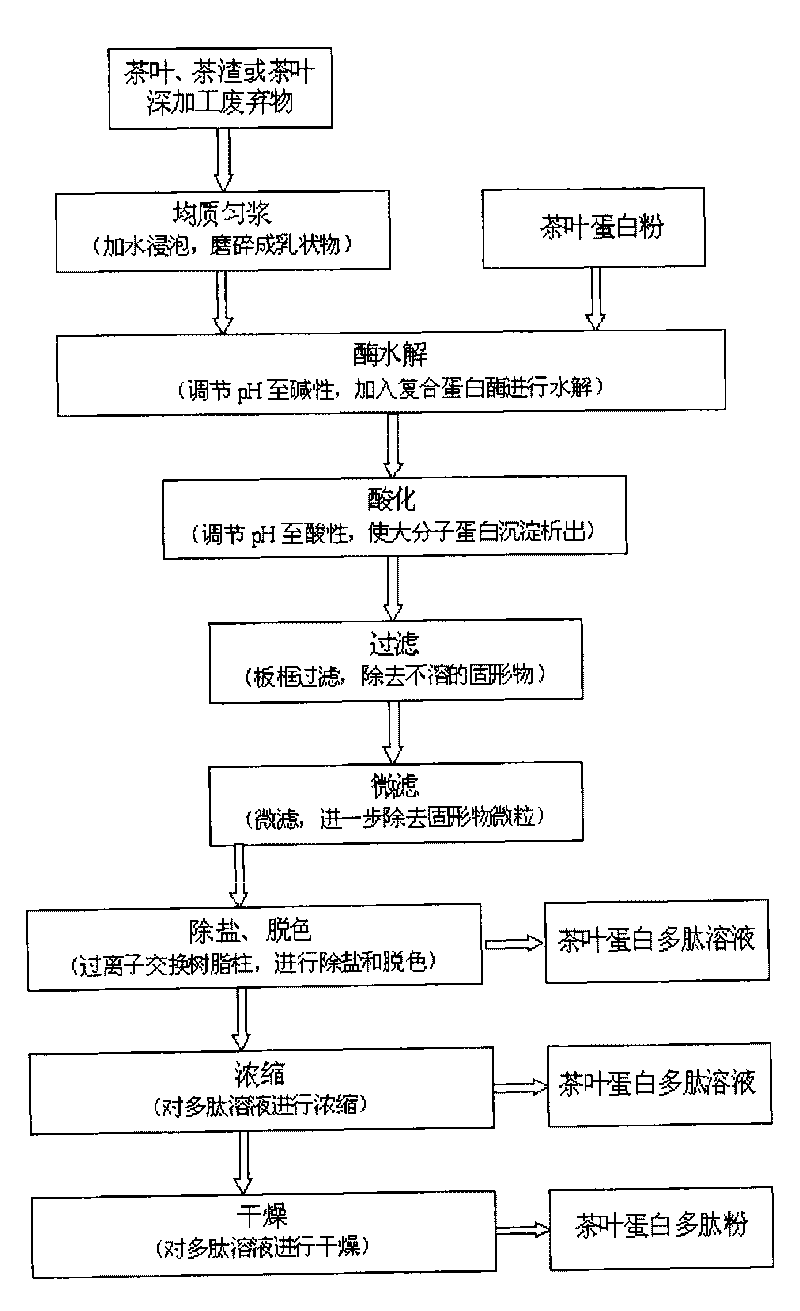
[0087] The invention provides a preparation method of tea protein polypeptide, which comprises the steps of: taking tea leaves, tea dregs or tea deep-processing wastes as raw materials, soaking in water, making emulsion or suspension by grinding or homogenizing, and then adding Compound enzyme A hydrolyzes, and the hydrolyzed product is micro-filtered, desalted and decolorized by ion exchange resin, and finally made into tea protein polypeptide.
[0088] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the solid content of said emulsion or suspension is between 10%-20% (w / v), and the addition of complex enzyme A is 0.5% of the solid content. -2% added (w / w).
[0089] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the hydrolysis used is under the conditions of 40°C-55°C and pH 8-10 for 3-6 hours.
[0090] In another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the method for preparing tea protein polypeptides includes the following steps:
[0091] 1) Pretreatment of...
Embodiment 1
[0134] Extraction and Refining of Tea Protein
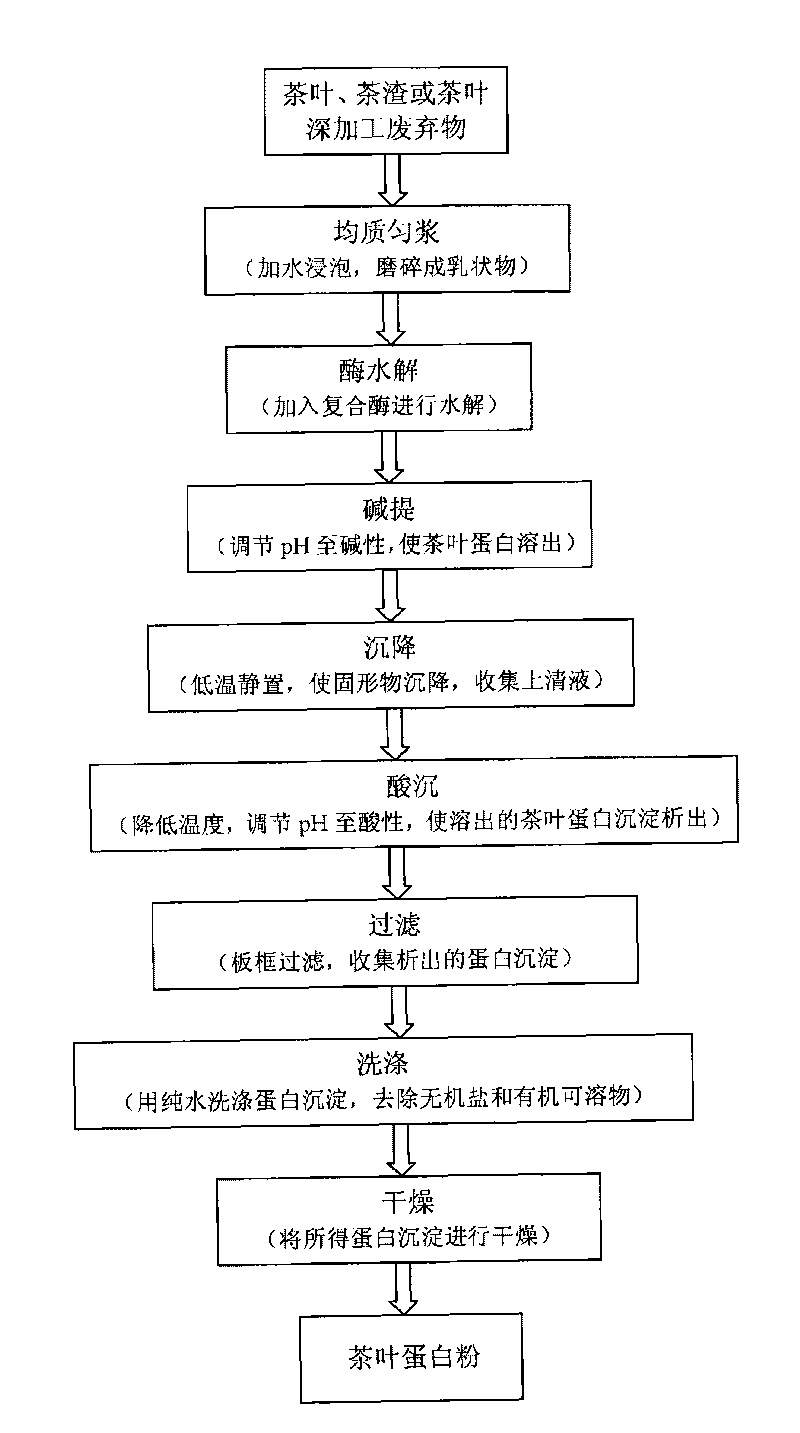
[0135] The extraction and refining of tea protein are carried out according to the following steps, the technological process is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0136] 1) Weigh 6kg of tea leaves, tea dregs or tea deep-processing waste into a 50L batching tank, add 24L of water (material-to-liquid ratio 1:4, w / v), mix well, and soak at room temperature for 30 minutes;
[0137] 2) Grinding the mixed solution into an emulsion through a colloid mill, adding the emulsion into a 50L reaction tank, adding 6g of compound enzyme B (the amount of compound enzyme B is added according to 0.1% of the solid content, w / w), After mixing evenly, keep warm at 45°C-55°C for 2-3 hours;
[0138] 3) Add 600ml of 5N sodium hydroxide solution so that the final concentration is 0.1N, mix well, and keep warm at 85°C-95°C for 1-2 hours;
[0139] 4) cooling with ice water, so that the temperature of the tea protein mixed solution obtained by the reaction i...
Embodiment 2
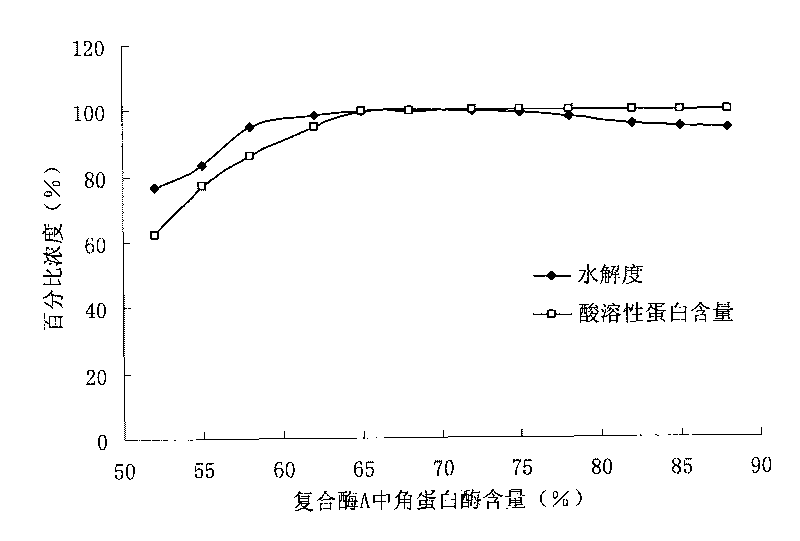
[0149] Hydrolysis of tea protein by compound enzyme A
[0150]In the range of 50-90w / w%, gradually adjust the percentage concentration of keratinase in the composite enzyme A, and then implement the hydrolysis of the tea protein by the composite enzyme A according to step 1) to step 4) described in Example 3 (composite The amount of enzyme A is added according to 1w / w% of the amount of raw materials). After the hydrolysis, take 5ml of the enzymatic solution and centrifuge at 12000rpm for 5 minutes, take the supernatant and use the Folin-phenol method to measure the soluble protein content, and calculate the degree of hydrolysis according to the following formula DH:
[0151] DH ( % ) = ( N 2 - N 1 ) × V ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com