Wet-laid non-woven fabric and filter
A wet non-woven and non-woven technology, applied in membrane filter, filtration separation, textile and other directions, can solve the problems of insufficient filter quality, uneven fiber length, fiber diameter, and no capture efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
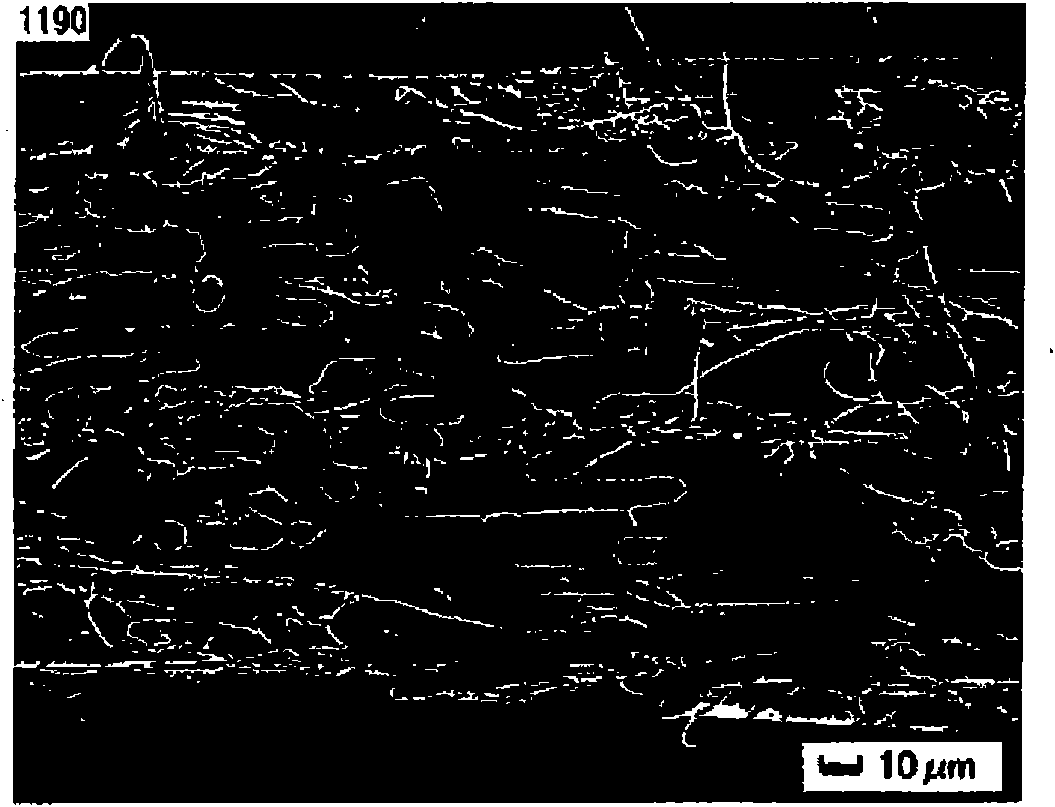
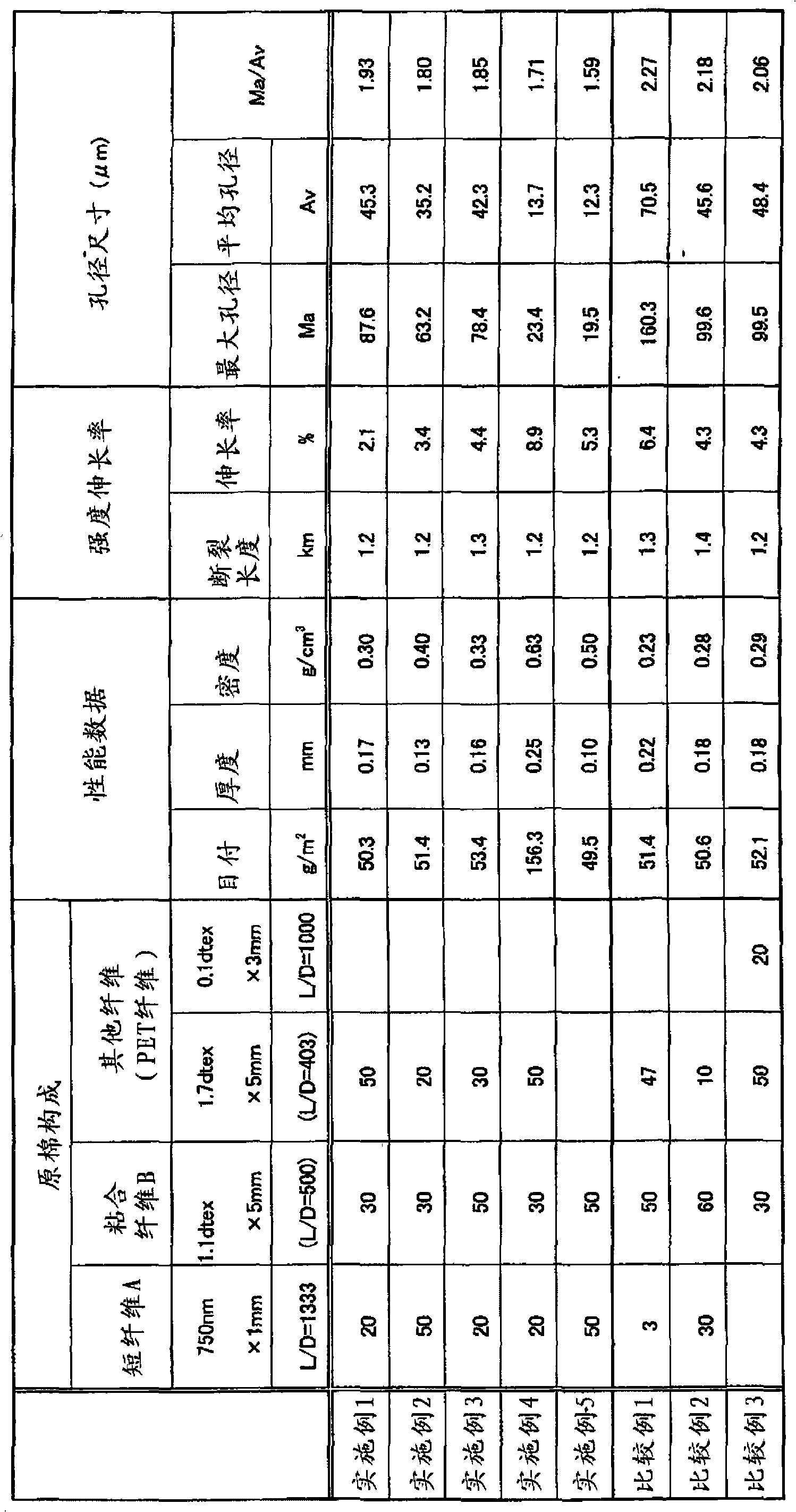
[0076] The island component uses polyethylene terephthalate with a melt viscosity of 120 Pa·sec at 285°C, and the sea component uses 4% by weight of polyethylene glycol with an average molecular weight of 4000 and a melt viscosity of 135 Pa·sec at 285°C. Modified polyethylene terephthalate obtained by copolymerization with 9 mol% sodium isophthalic acid-5-sulfonate, using a spinneret with 400 islands at a weight ratio of sea:island=10:90 Spinning and winding were performed at a spinning speed of 1500 m / min. The difference in alkali decrement speed is 1000 times. This was stretched to 3.9 times, and cut to 1000 μm with a guillotine cutter to obtain a conjugate fiber for staple fiber A. Use 4% NaOH aqueous solution to reduce its weight by 10% at 75 ° C. As a result, it can be seen that the ultrafine short fibers with relatively uniform fiber diameter and fiber length are produced. This fiber is used as short fiber A (fiber diameter 750nm, fiber length 1mm, L / D=1333, circular ...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Except for changing the ratio of the fibers used in Example 1 (short fiber A / binder fiber B / other fibers=50 / 30 / 20), the treatment / processing was performed under the same conditions to obtain a wet-laid nonwoven fabric. Table 1 shows the physical properties of the obtained wet-laid nonwoven fabric.
Embodiment 3
[0082] Except for changing the ratio of the fibers used in Example 1 (short fiber A / binder fiber B / other fibers=20 / 50 / 30), the treatment / processing was performed under the same conditions to obtain a wet-laid nonwoven fabric. Table 1 shows the physical properties of the obtained wet-laid nonwoven fabric.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com