A biodegradable microsphere composition suitable for the controlled release of glucose controlling peptide and formulation thereof
A technology of biodegradation and glucose, which is applied in the field of preparation of the microspheres, can solve the problems of uncontrolled release rate, incomplete release of encapsulated drugs, complex and low efficiency, etc., and achieves simplicity, economy, high stability, Effect of High Encapsulation Efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] Preparation methods of biodegradable polymer microspheres include:
[0030] adding an organic solvent to the polymer to obtain a polymer solution (step 1);
[0031] Disperse the glucose-regulating peptide in the polymer solution described in step 1 to obtain a dispersion, and then add alcohol or a mixture of alcohol and organic acid to the dispersion to obtain a drug-dispersed solution. solution) (step 2); and
[0032] Microspheres are formed from the drug-dispersed solution described in step 2 (step 3).
[0033] A detailed description of the method will be given step by step.
[0034] First, step 1 is to prepare a polymer solution.
[0035] In step 1, the polymer is dissolved in an organic solvent. The polymer is biodegradable and can be used as a carrier, preferably a biodegradable polyester polymer. Any volatile organic solvent may be used without particular limitation as long as the biodegradable polymer carrier has high solubility therein and can be easily rem...
Embodiment 1
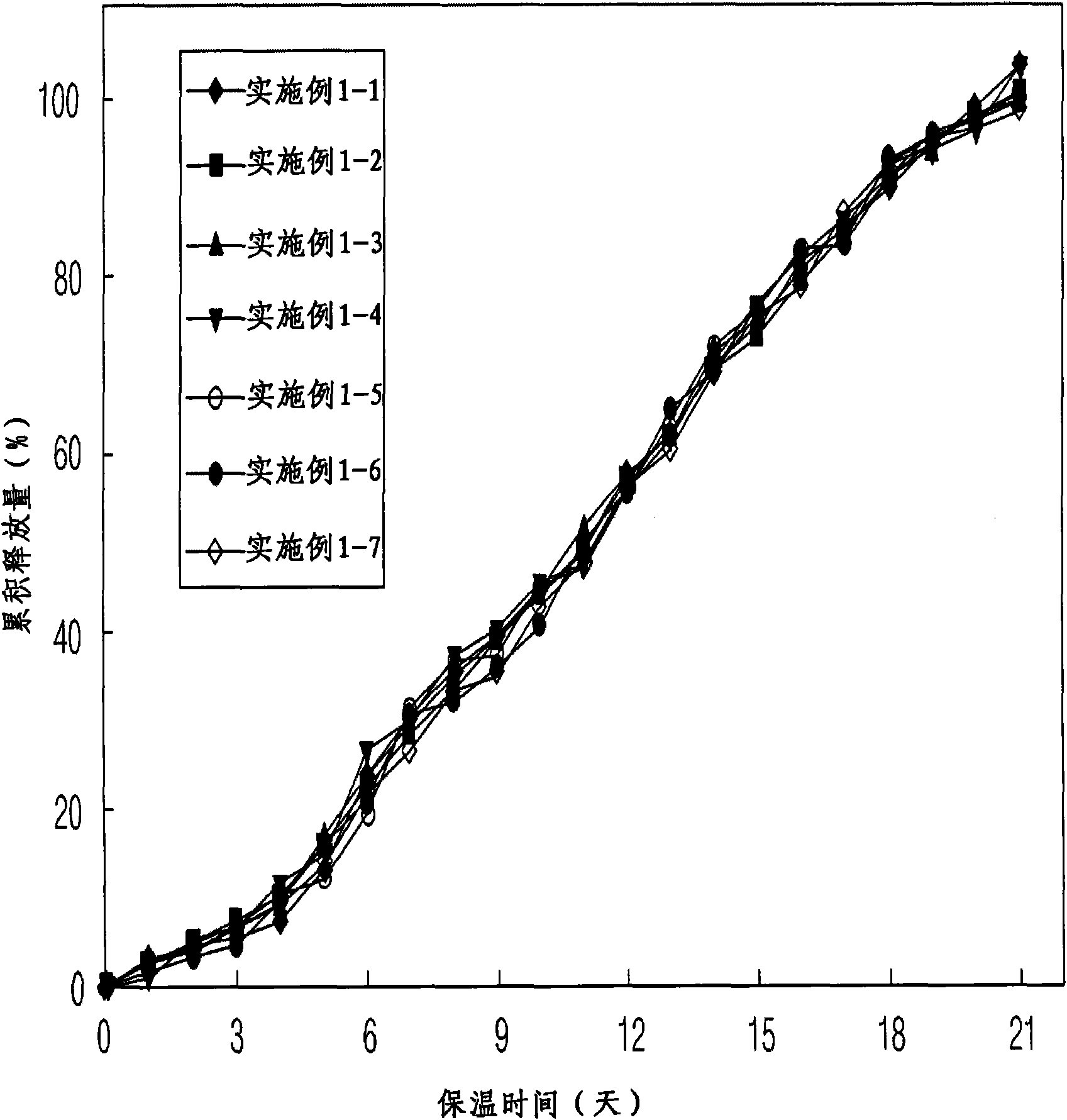
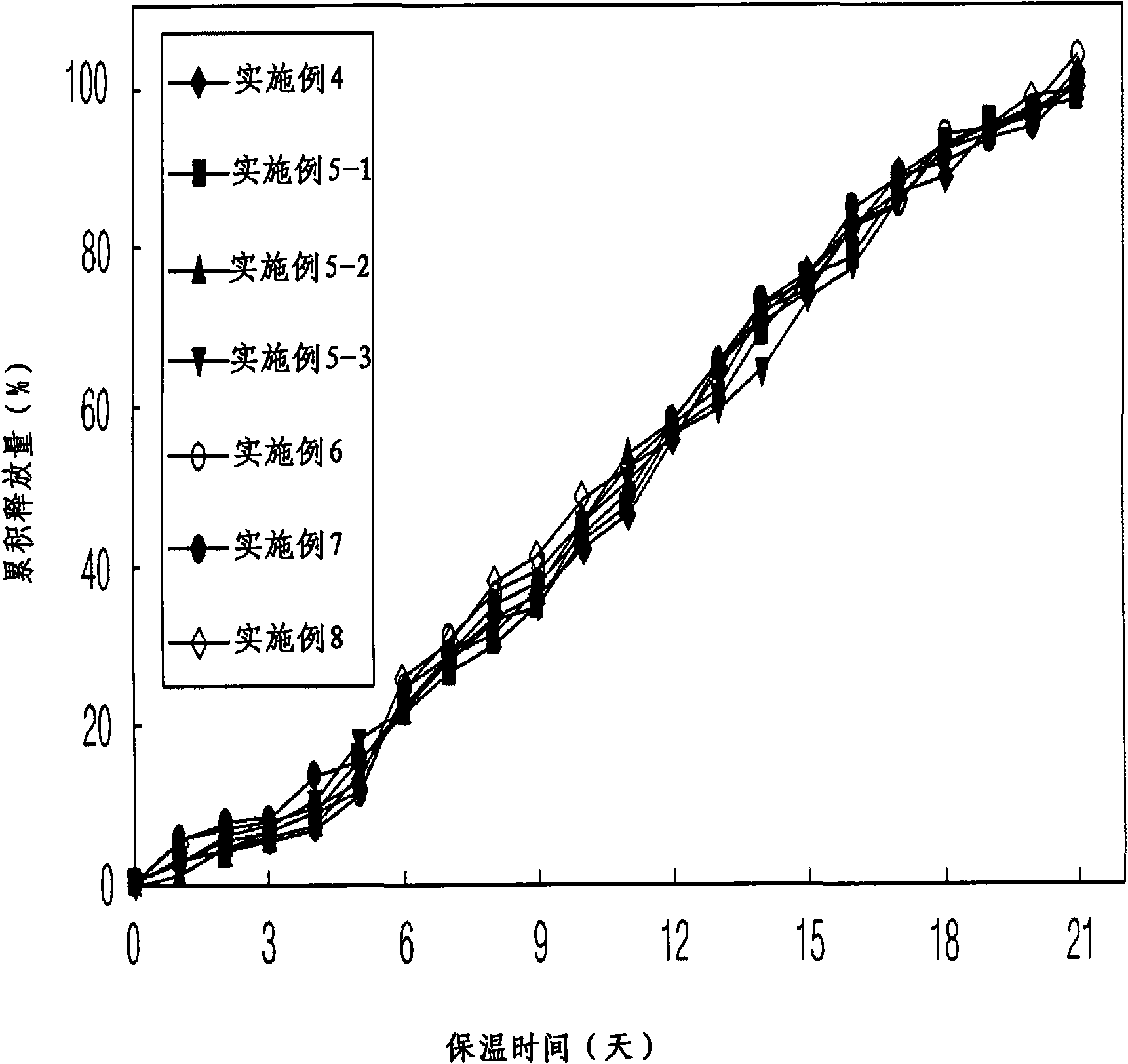
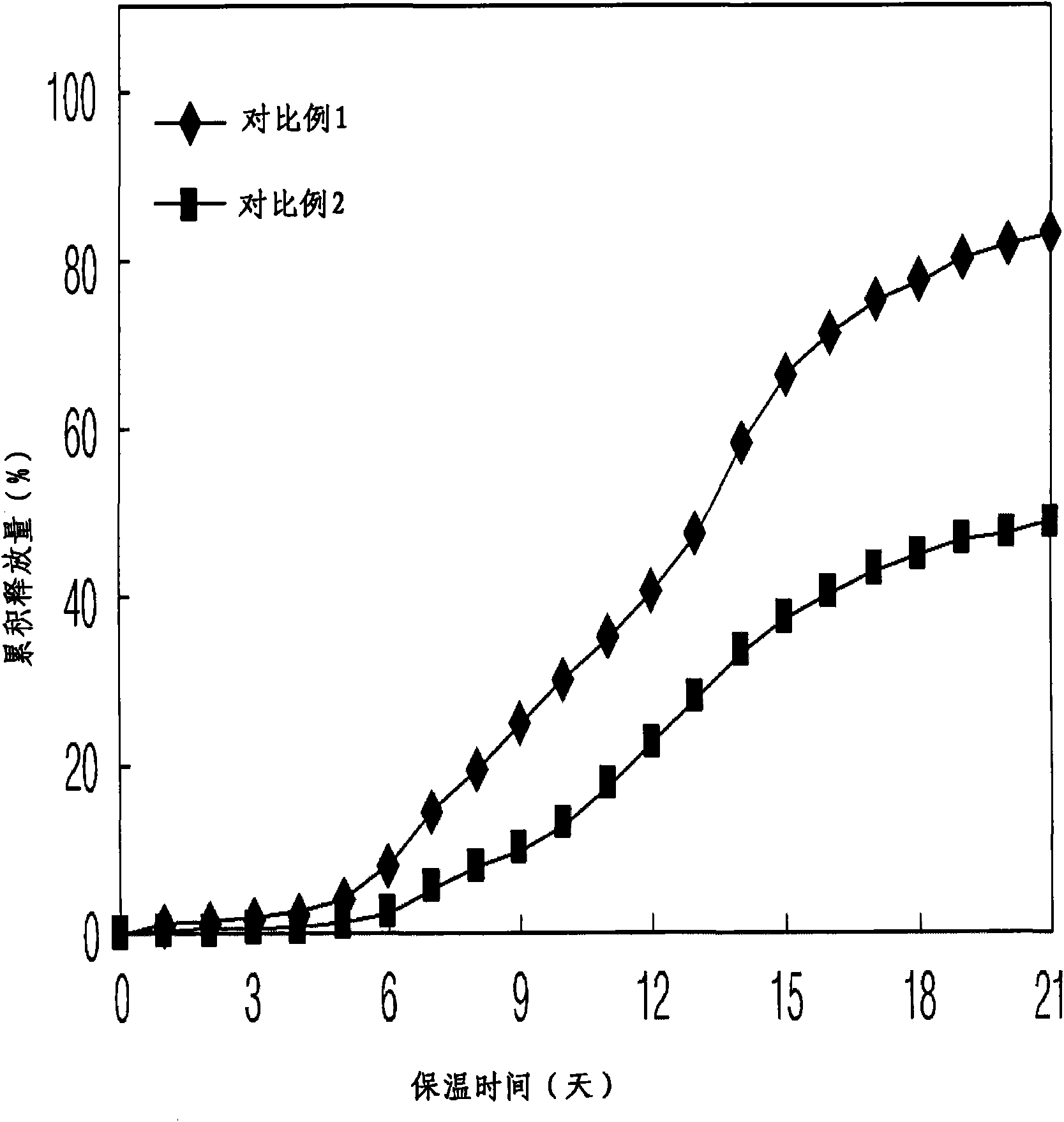
[0063] Embodiment 1: Carry out the preparation of microsphere according to polymer kind and mixing ratio (oil-in-water O / W type lotion)
[0064] 300 mg of polymer (Boehringer Ingelheim) were completely dissolved in dichloromethane. 9 mg of exendin-4 (American Peptide) was dispersed in the polymer solution to obtain an exendin-4 dispersion. The polymers used are shown in Table 1, which are one polymer product or a mixture of two different polymer products in various mixing ratios. A predetermined amount of methanol (the volume ratio of alcohol to drug dispersion is 1:4) was added to each of the drug dispersions having different polymer types and mixing ratios to obtain a drug-dispersed solution. 10 ml of each drug-dispersed solution was taken and emulsified by a stirrer or a homogenizer using 250 ml of a 1% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution saturated with dichloromethane to form microspheres. The microspheres were solidified while stirring at room temperature and a...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2: Carry out the preparation of microsphere according to the ratio of alcohol and drug dispersion (oil-in-water O / W type lotion)
[0068] 300 mg of polymer (RG502H, Boehringer Ingelheim) were completely dissolved in dichloromethane. 9 mg of exendin-4 (American Peptide) was dispersed in the polymer solution to obtain an exendin-4 dispersion. To this drug dispersion was added a predetermined amount of methanol (the volume ratio of alcohol to drug dispersion was 1:1 to 1:7, as shown in Table 2) to obtain a drug-dispersed solution. This was emulsified and dried in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain microspheres.
[0069] Table 2
[0070]
[0071] As shown in Table 2, when the volume ratio of drug dispersion to methanol is 7 or more, no solution can be formed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com