Variable frequency control device and variable frequency control method of variable frequency air-conditioner
A frequency conversion air conditioner and frequency conversion control technology, which is applied in heating and ventilation control systems, heating methods, space heating and ventilation, etc. Power consumption, meeting heat dissipation requirements, and excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
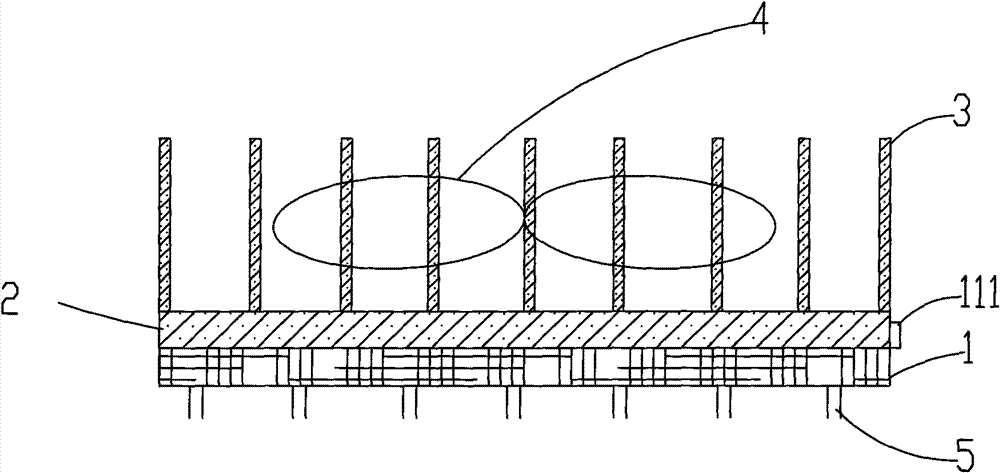
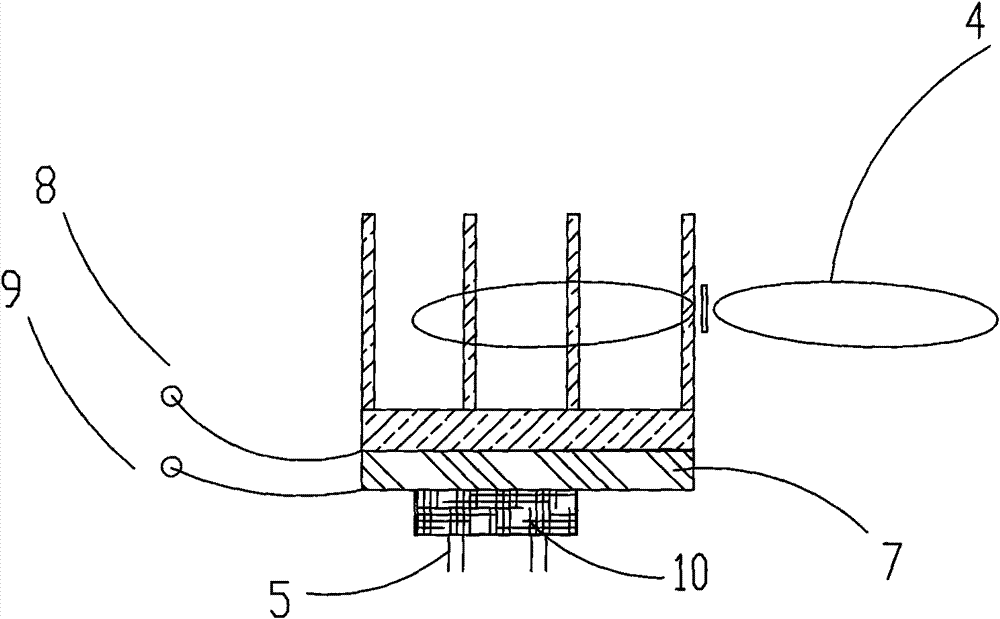
[0042] The structure diagram of the first embodiment of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, a power transistor 1 is included, and the power transistor 1 is connected to the control circuit of the inverter air conditioner through a pin 5 , wherein the power transistor 1 is also provided with a heat dissipation device, and the heat dissipation device includes a heat exchange element 3 in contact with the power transistor 1 .
[0043] The above-mentioned power transistor 1 is an integral transistor or a distributed transistor. In this embodiment, the aforementioned power transistor 1 is an integral transistor.
[0044] The heat dissipation device also includes a fan 4 arranged beside the heat exchange element 3 to deliver air to the heat exchange element 3 to enhance the heat dissipation effect.
[0045] The contact surface between the above-mentioned power transistor 1 and the heat exchange element 3 is coated with thermal conductive silicone grease to enhance heat e...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2 of the present invention The heat exchanging element 2 is a heat pipe, which can conventionally contain a container, such as a vacuum metal tube that hermetically seals a volatile fluid such as alcohol, and the liquid part of the heat pipe is close to the heat generating element, that is, a transistor Components, heat pipes, fins or fins that expand the heat dissipation area, exchange heat with the air, and release the heat absorbed from the heat generating element into the air. The other contents are the same as the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
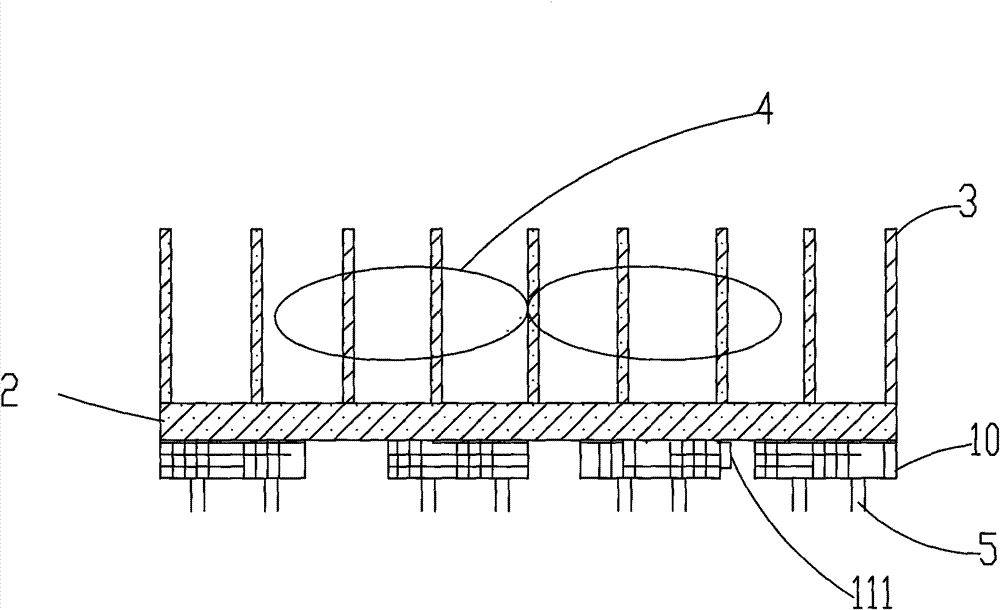
[0056] The structural schematic diagram of the third embodiment of the present invention is as follows figure 2 As shown, it is a cross-sectional view of a distributed transistor element heat sink with a fan. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the transistor elements are distributed, and all the transistor elements face the same heat dissipation surface when they are set, and each heat dissipation The surfaces are on the same plane in order to reduce the thermal resistance between the transistor element and the heat exchange element. In this embodiment, each transistor element can be a commercially available element, without additional customization, and multiple fasteners are required to tightly fix each transistor on the heat exchange element.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com