Bridge type surface acoustic wave transducer in micro-optical-electro-mechanical gyroscope
A micro-opto-electromechanical, surface acoustic wave technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, impedance networks, etc., can solve the problems of large absorption loss, large device size, reduced output optical power and acousto-optic coupling efficiency, etc., to reduce absorption, reduce metal The effect of lengthening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The bridge-type surface acoustic wave transducer in the micro-opto-electromechanical gyroscope of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
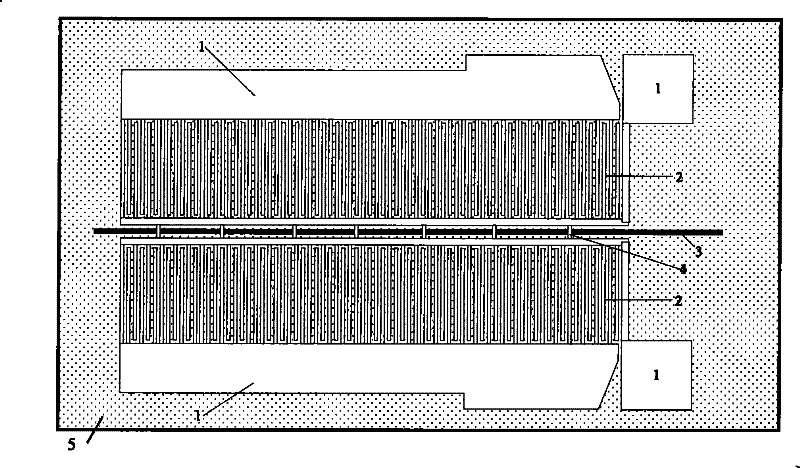
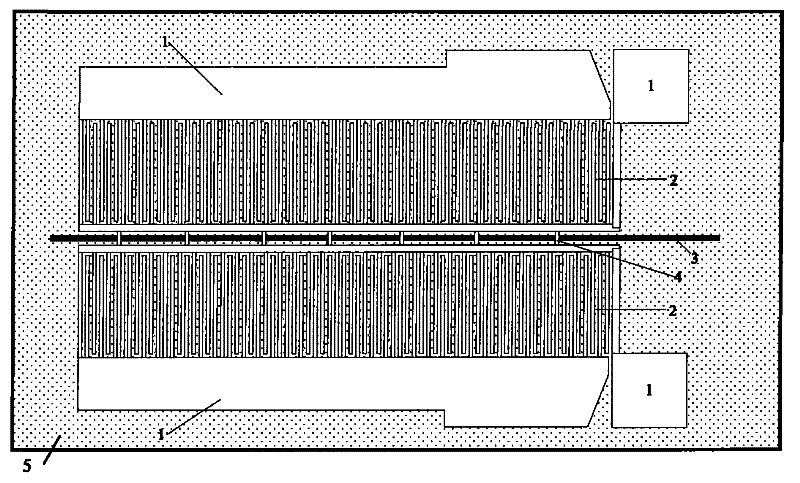
[0021] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the bridge-type surface acoustic wave transducer in the micro-opto-electromechanical gyroscope of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the surface acoustic wave transducer of the present invention is a surface acoustic wave transducer with a grouped bridging electrode structure in a micro-opto-electromechanical gyro device based on an acousto-optic waveguide structure. On the base material 5, photolithography, The embedded strip-shaped acousto-optic waveguide area 3 is made by coating, diffusion or etching processes. In addition, on the base material 5, there are also: pressure welding electrodes 1, interdigital electrodes 2 and bridges spanning the upper part of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com