High-efficiency directed evolution method of lipase gene
A lipase gene and directed evolution technology, which is applied in the fields of directed evolution of lipase gene, directed evolution of enzyme gene, and molecular transformation, can solve problems such as complex operation steps and difficulty in screening mutants, achieve improved enzymatic properties, and avoid extracellular Genetic manipulation, the effect of facilitating high-throughput screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Implementation example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae display vector mediated by Flop membrane protein
[0027] The protein Flo1p is a condensin-like cell wall protein encoded by the F01 gene in S. cerevisiae. According to the complete sequence of the reported F01 gene (GenBank NO.NC_01133), a primer for the coding sequence of the flocculation functional region of Flo1p was designed: FOLf-Hind III and FOLr-Bgl II (FOLf-Hind III: 5'-acataagcttatgacaatgcctcatcgctatatgtttttg-3'FOLr-Bgl II: 5'-gatagatctggtgatttgtcctgaagatgatgatgacaaa-3'), obtained by PCR amplification using the total DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC 60715 as template The coding sequence fragment of the flocculation functional region of Flo1p was ligated with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector pYES2 / NT after Hind III and Bg1 II double digestion with Hind III and BamH I under the action of T4DNA ligase (Bg1 II and BamHI are mutually homologous enzymes), and the expression vector p...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Implementation Example 2: Construction of Lipase Gene Saccharomyces cerevisiae Display Expression Recombinant Plasmid
[0029] 2.1. Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae display expression vector for lipase gene derived from Pseudomonas fluorescens
[0030] The full-length gene primers LipB52Pf (5'-aaagaattcccaacaaaaagagaggcaacagcaatg-3') and LipB52Pr (5'-aaagcgcgcgctccctccccacccttgtcgtcagg-3') were designed based on the lipase gene lipB52 (Genbank NO.AY623009) sequence, and the P.fluorescens B52 genomic DNA was used as a PCR template The lipB52 full-length gene fragment was amplified, and after purification, the fragment was digested with restriction endonucleases Eco RI and Not I, and the double-digested lipB52 gene fragment was recovered from the gel and Saccharomyces cerevisiae was digested with Eco RI and Not I. The display expression vector pLHJ042 was ligated under the action of T4DNA ligase to obtain the lipB52 gene Saccharomyces cerevisiae display expression...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Implementation Example 3: Obtaining lipase gene fragments with carrier homologous sequences and construction of expression mutation library
[0036] 3.1 Obtaining the lipase gene fragment with carrier homologous sequence
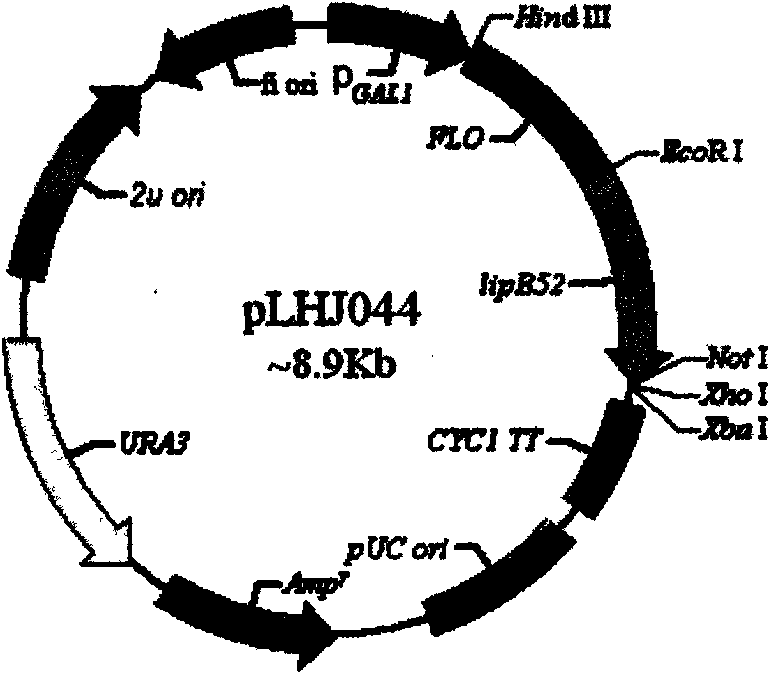
[0037] The primers pLHJ042F and pLHJ042R located at both ends of the multiple cloning site were designed according to the sequence of the expression vector pLHJ042 displayed by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The sequence of primer pLHJ042F (5'-cactgaaccatggaccggaacttt-3') is located in the coding sequence of the Flo1p flocculation functional region, and the sequence of primer pLHJ042R (5'-ggggggagggcgtgaatgta-3') is located in the terminator CYCC1TT sequence. Using pLHJ044, pLHJ052, pLHJ053 and pLHJ042-B68 as templates and pLHJ042F and pLHJ042R as primer pairs, PCR amplification obtained fragments of lipase genes from different sources with homologous sequences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae display expression vectors.
[0038] 3.2 Construction of lipase gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com