CMP of copper/ruthenium/tantalum substrates
A chemical-mechanical, substrate-based technology that is applied in the direction of polishing compositions containing abrasives, other chemical processes, chemical instruments and methods, and can solve problems such as circuit interruption, complicated processing steps, and uneven substrate surfaces
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
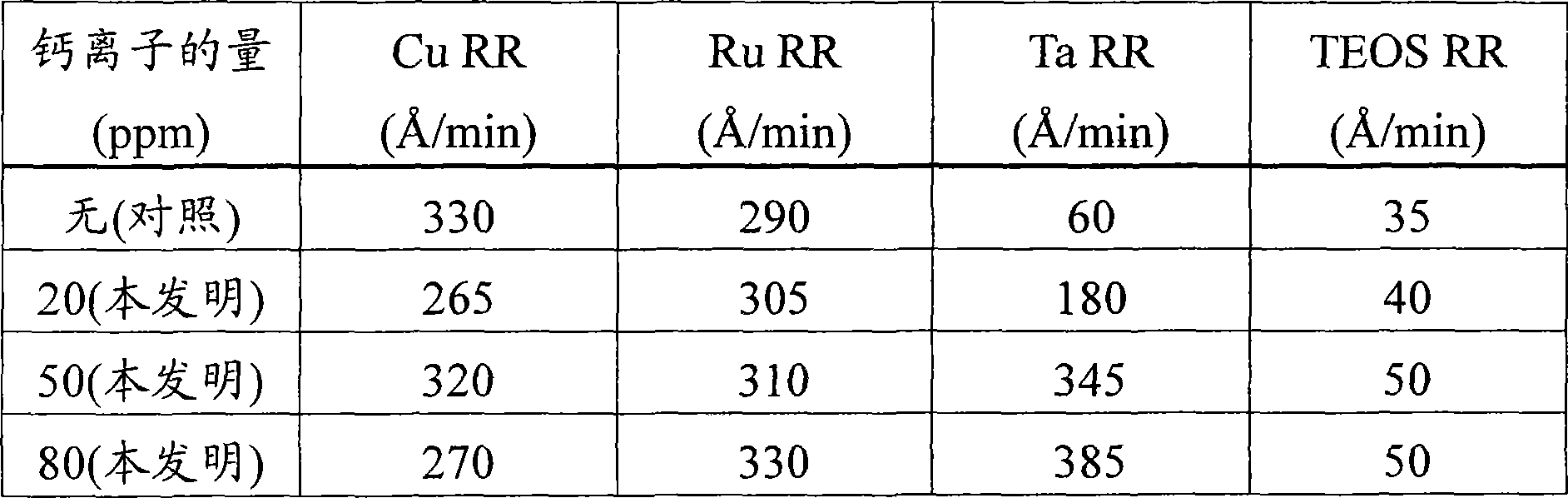
[0053] This example demonstrates the effect of calcium ions achievable by the method of the present invention on the observed removal rates of copper, ruthenium, tantalum, and silicon oxide dielectric materials produced from tetraethyl orthosilicate. This silicon oxide dielectric material is referred to herein as "TEOS".
[0054] 4 similar groups were polished with the control polishing composition without calcium ions and the polishing composition of the present invention containing different amounts of calcium ions. Each group had 4 substrates, each substrate comprising copper, ruthenium, tantalum and TEOS. Each composition contained 0.7% by weight negatively charged polymer-treated alpha-alumina, 0.8% by weight tartaric acid, 3% by weight hydrogen peroxide, 0.0303% by weight benzotriazole, and 0.05% by weight Alcosperse 630 polymer in water. Acrylic dispersant with pH adjusted to 8.4 with ammonium hydroxide. The source of calcium ions was calcium acetate monohydrate.
[...
Embodiment 2
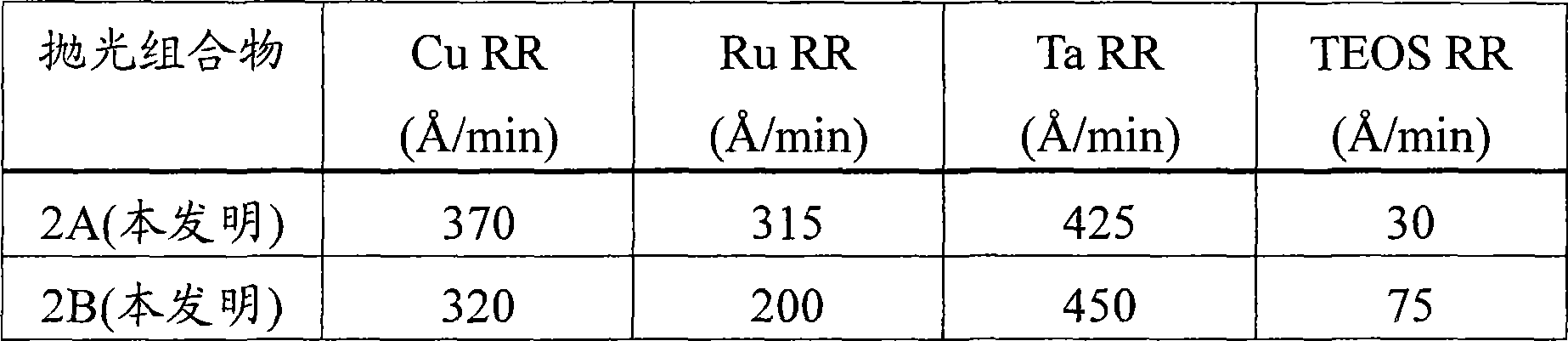
[0060] This example demonstrates the effect of adding a silica abrasive to a polishing composition comprising alpha-alumina on the observed removal rates of copper, ruthenium, tantalum and TEOS.
[0061] Two similar sets of substrates were polished with two different polishing compositions (Polishing Compositions 2A and 2B), each set containing 4 substrates, each substrate comprising copper, ruthenium, tantalum, and TEOS, respectively. Each composition contained 0.8% by weight tartaric acid, 3% by weight hydrogen peroxide, 0.0453% by weight benzotriazole, 200 ppm calcium acetate monohydrate, 0.6% by weight aminophosphonic acid, and 0.05% by weight Alcosperse 630 polyacrylic acid in water Dispersion agent in which the pH was adjusted to 8.4 with ammonium hydroxide. Polishing Composition 2A further included 0.7% by weight negatively charged polymer-treated alpha-alumina and no silica. Polishing Composition 2B further included 1% by weight negatively charged polymer-treated alph...
Embodiment 3
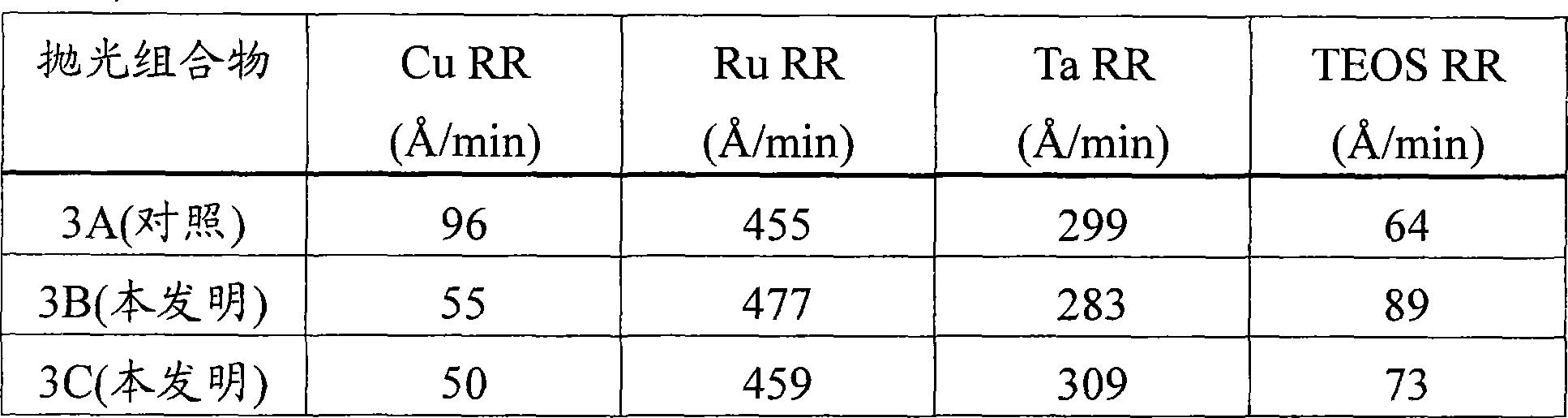
[0067] This example demonstrates the effect of amphiphilic nonionic surfactants on the removal rates of copper, ruthenium, tantalum and TEOS.
[0068] Three similar sets of substrates were polished with three different polishing compositions (Polishing Compositions 3A, 3B, and 3C), each set containing four substrates, each containing copper, ruthenium, tantalum, and TEOS . Each composition contained 1.4% by weight negatively charged polymer-treated alpha-alumina, 0.8% by weight tartaric acid, 3% by weight hydrogen peroxide, 0.085% by weight benzotriazole, 200 ppm calcium acetate in water Monohydrate, and 0.05% by weight of Alcosperse 630 polyacrylic acid dispersant with pH adjusted to 8.4 with 0.3% by weight of ammonium hydroxide. Polishing compositions 3B and 3C further comprise two One of the surfactants (BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany). Polishing Composition 3B (invention) further comprises 150 ppm of HLB of 5 and molecular weight of 1100 L31 Surfactant. Polishing Compo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com