Non-magnetic hard alloy powder and method for preparing the same
A technology of cemented carbide and hard phase powder, which is applied in the field of non-magnetic cemented carbide powder and its preparation, can solve problems such as difficulty in adapting to high temperatures, and achieve the effects of improved corrosion resistance, good fluidity, and high agglomeration density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
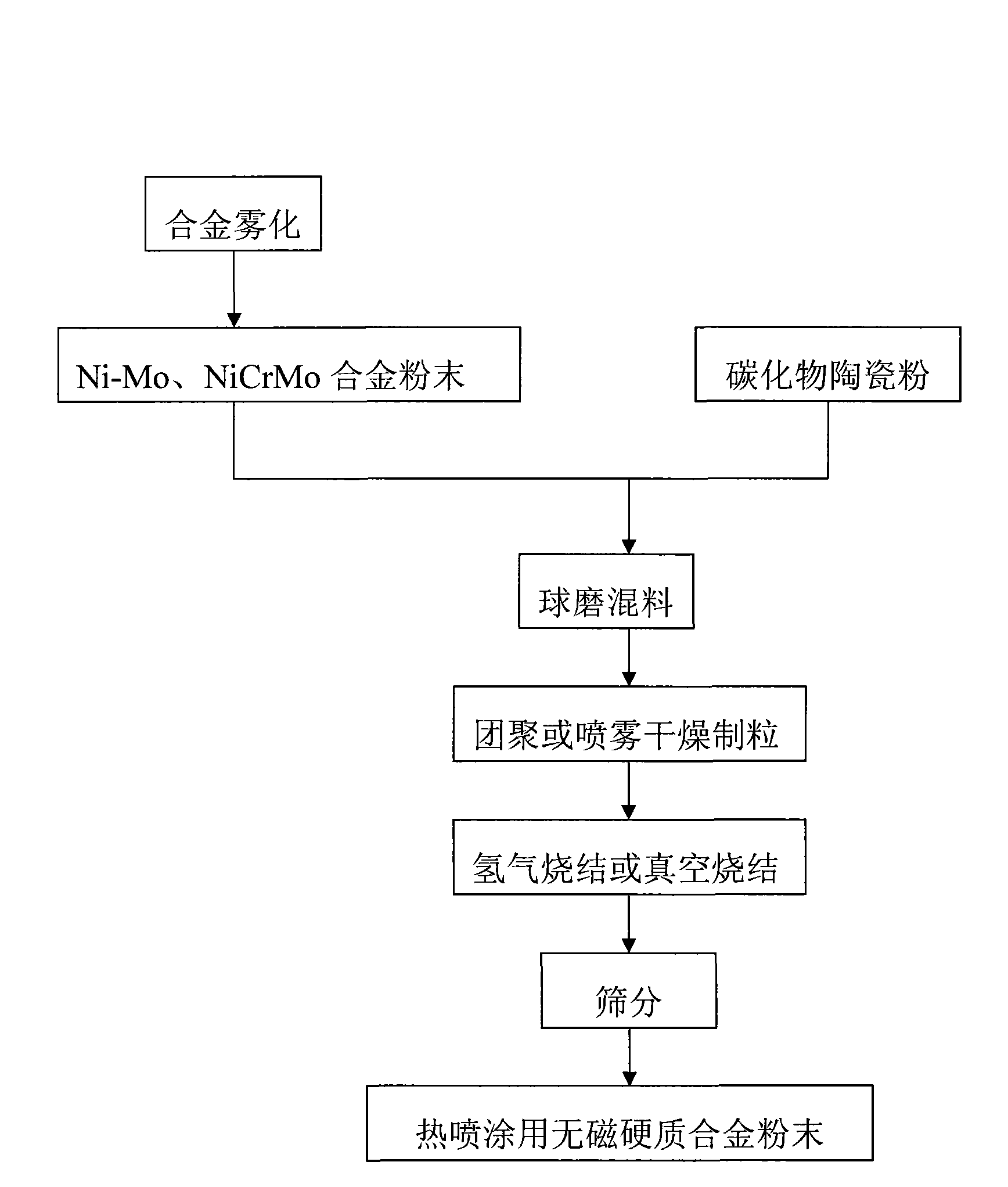
[0029] 1 Atomization
[0030] The nickel, molybdenum metal or nickel-molybdenum alloy block is placed in the smelting furnace according to the required alloy ratio (the Mo content is 6-15wt%), and the alloy solution is smelted for gas atomization. The inert gas used for gas atomization is nitrogen, and the gas pressure is controlled between 1.5 and 2.5 MPa. Afterwards, the produced nickel-molybdenum non-magnetic binder phase alloy powder is sieved.
[0031] 2 mix
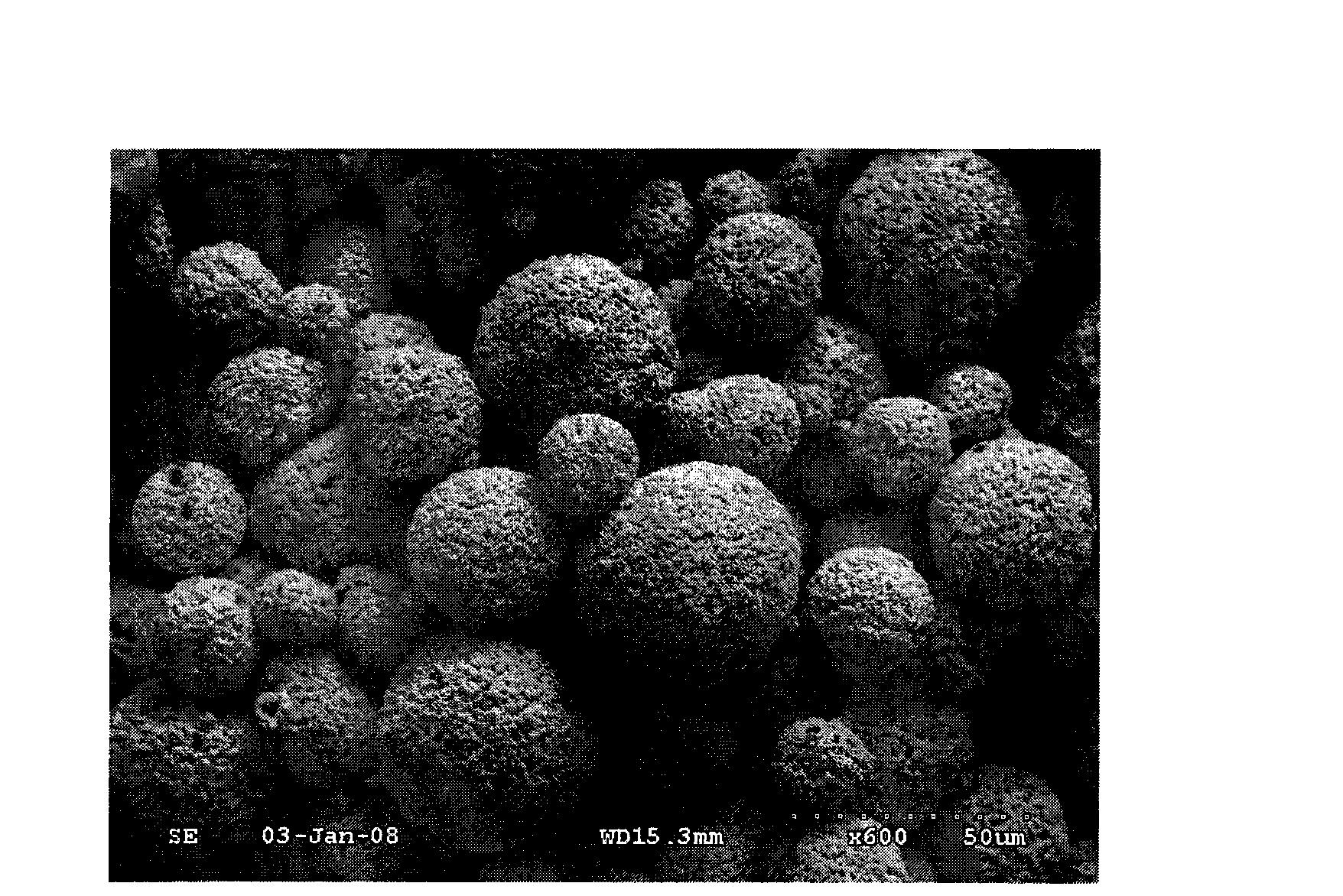
[0032] Nickel-molybdenum alloy powder with a particle size range of 2.5-38 μm is selected as the binder phase powder, and tungsten carbide with a particle size range of 1.25-25 μm is used as the hard phase powder. The mass ratio of nickel-molybdenum alloy powder is 12-17%, and tungsten carbide is the balance. The two powders are mixed and ball milled, the ball milling medium is alcohol, the ball, material and medium ratio in the ball milling is 3:1:1, and the ball milling time is 12 hours.
[0033] 3 Spray dryin...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1 Atomization
[0039] Put nickel, molybdenum metal or nickel-molybdenum alloy in the smelting furnace according to the required alloy ratio (Mo content is 15-25wt%), and vacuum atomize after smelting into alloy solution. Afterwards, the produced nickel-molybdenum non-magnetic binder phase alloy powder is sieved.
[0040] 2 mix
[0041] Nickel-molybdenum alloy powder with a particle size range of 38-106 μm is selected as the binder phase powder, and chromium carbide with a particle size range of 1.25-25 μm is used as the hard phase powder. The mass ratio of nickel-molybdenum alloy powder is 12-17%, and chromium carbide is the balance. The two powders were mixed and ball milled. The ball milling medium is alcohol, the ratio of balls, material and medium in the ball milling is 3:1:1, and the ball milling time is 24 hours.
[0042] 3 Spray drying
[0043]The ball-milled powder is stirred for 20 to 30 minutes according to the ratio of material, polyvinyl alcohol and al...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1 Atomization
[0048] Put nickel, chromium, molybdenum metal or alloy in the melting furnace according to the following ratio (wt%): Cr 5-18, Mo 1-10, Ni balance. After smelting into an alloy solution, water atomization is carried out, and the atomization pressure is 20-40MPa. Afterwards, the produced nickel-chromium-molybdenum non-magnetic binder phase alloy powder is sieved.
[0049] 2 mix
[0050] The nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy powder with a particle size range of 38-106 μm is selected as the binder phase powder, and the particle size range is 25-75 μm, containing 10-20wt% Cr 3 C 2 The mixture of tungsten carbide and chromium carbide is hard phase powder. The mass ratio of nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy powder is 17-25%, and the mixture of tungsten carbide and chromium carbide is the balance. The three powders were mixed and ball milled. The ball milling medium is alcohol, the ratio of balls, material and medium in the ball milling is 3:1:1, and the ba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com