Polyimide solvent cast films having a low coefficient of thermal expansion and method of manufacture thereof
A technology of thermal expansion coefficient and polyimide film, which is applied in the field of polyimide solvent casting film with low thermal expansion coefficient and its preparation field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
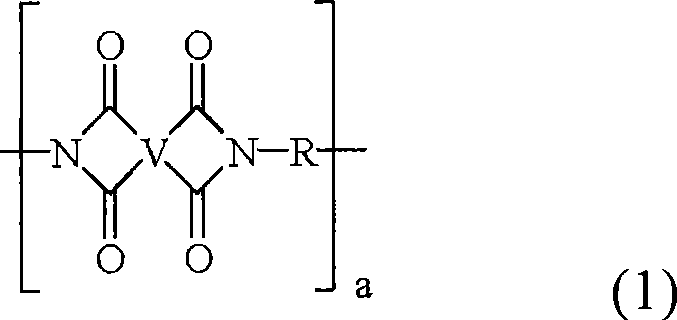
[0057] Solvent cast films according to the present invention may be prepared by any method known in the art. The following patents assigned to GE disclose general methods of making solvent cast films and casting solutions: 4115341; 4157996; 4307226; 4360633; 4374972; and 3847867. A method of preparation may include the steps of forming a polyamic acid solution of a polyamic acid product comprising a monomer component comprising one or more dianhydrides and a dianhydride at least partially dissolved in a solvent system One or more organic diamines; casting the polyamic acid solution onto the substrate so that the polyamic acid is in the form of length, width and depth on the surface of the substrate; removing the solvent, and solidifying the polyamic acid Solution, such as heating the casting film at a certain temperature and for a certain time, so that effectively form a film, the film has a CTE of less than 70ppm / °C, specifically less than 60ppm / °C, and 0.5 microns to 250 mic...
Embodiment 1-43
[0268] The film casting method and experiment of embodiment 1-43:
[0269] Formulations 1-43 of the present invention were prepared using the compositions listed in Table 1. The amount of each monomer is calculated on a stoichiometric basis of 1 amine per anhydride, without correction for purity (correction for purity affects the final molecular weight of the polymer and can affect the final properties of the article). A Microsoft Excel spreadsheet calculator was set up to calculate the grams of each monomer based on the desired total grams of polymer and the monomer feed for dianhydride and amine. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that there are many different ways of ascertaining the correct weight of each ingredient that will be used to make a film according to the invention. Those skilled in the art are able to calculate the weight content of each component based on the total stoichiometry and calculate the final solids percentage based on the reaction mechanism el...
Embodiment 44
[0290] Detailed film casting example:
[0291] On an analytical balance, weigh out 0.5937 g (0.001914 mol) of 4,4′-oxydiphthalic anhydride and 0.4752 g (0.001914 mol) of 4,4′-diaminodiphenylsulfone to the desired weight within ±0.0005g. Transfer the monomer to a 20 mL scintillation vial and rinse the weighing paper with 2.0 mL of dimethylacetamide to ensure complete transfer of the monomer. The remaining solvent (5.47 mL dimethylacetamide) was removed with a volumetric pipette to give a solution of 12.5 wt% solids. The tube was inertized by flowing nitrogen through the tube for 1 minute and then quickly capping the tube. The samples were then placed on a shaker overnight to form a poly(amic acid) solution.
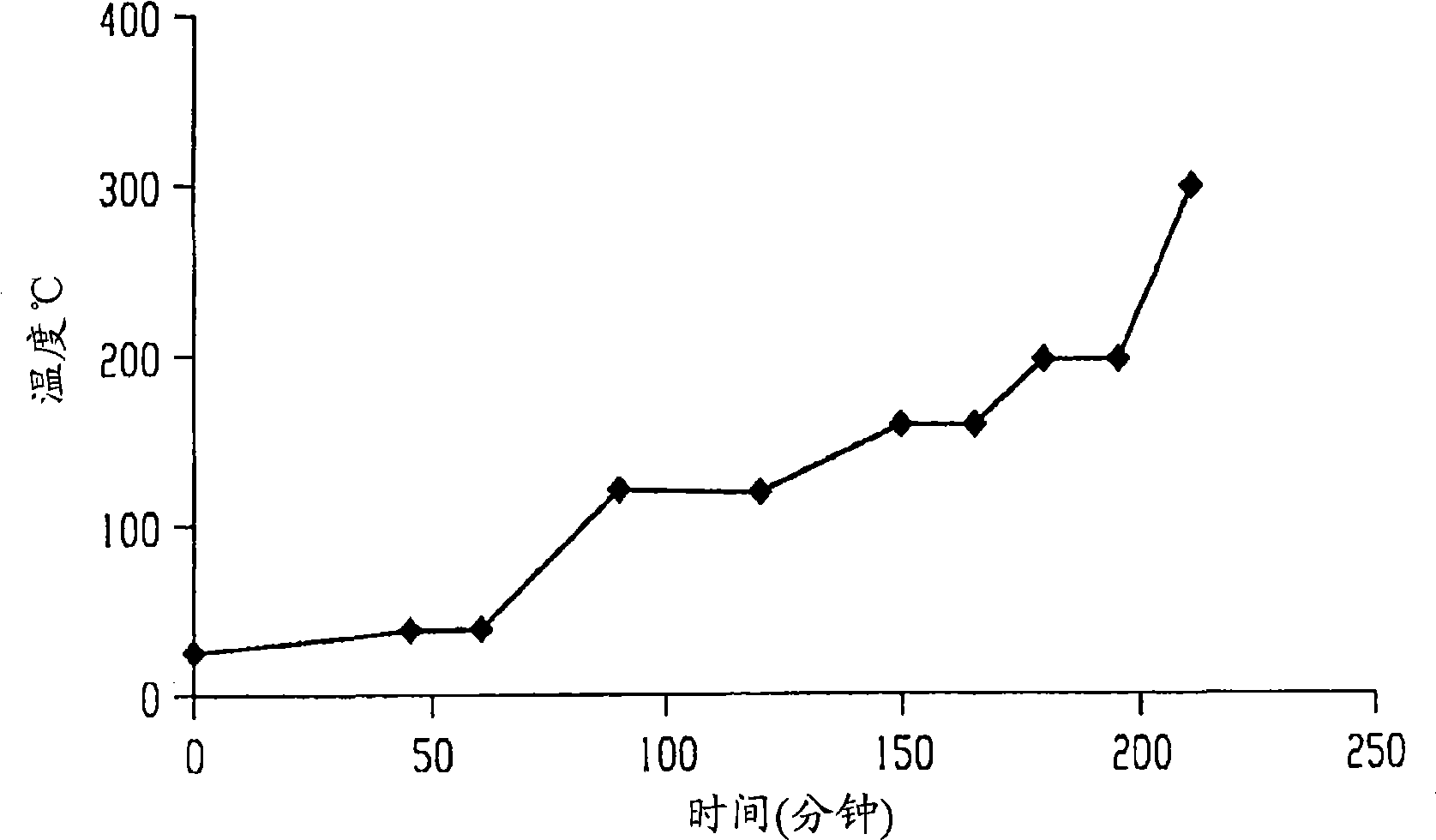
[0292] Slides were washed with hexane (Fisherbrand pre-cleaned microscope slides). The solution (2.0 mL) was then filtered through a 0.45 micron syringe tip filter onto a glass slide. The solution-coated slides were then placed on a hot plate equipped with: temperatur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com