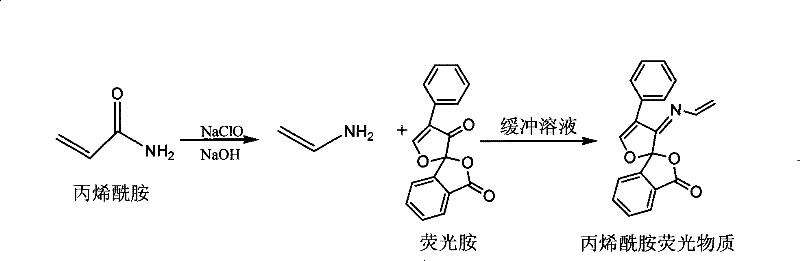
Method for testing acrylic amide in food
A technology for acrylamide and detection methods, which is applied in the preparation of test samples, fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, cumbersome and time-consuming acrylamide analysis methods, and achieve short detection time, The effect of low requirements for testing personnel and simple and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Weigh 1 to 5 g of potato chips ground into powder into a container, add 5 to 10 mL of double-distilled n-hexane, degrease with ultrasonication for 10 to 20 minutes, add 7 mL of 1 to 3 mol / L NaCl solution, and ultrasonically extract for 10 to 20 minutes. After centrifugation for 5-10 min, the residue was extracted once more with 5-10 ml of the above solution. Combine the extracts.
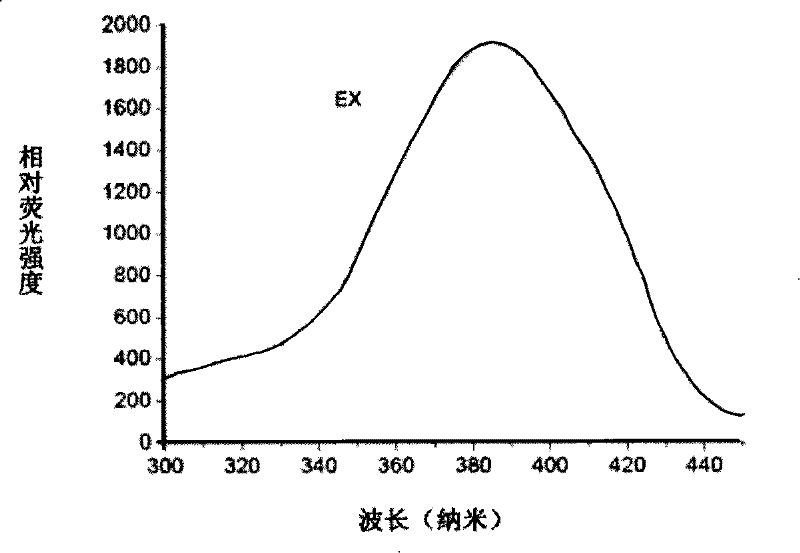
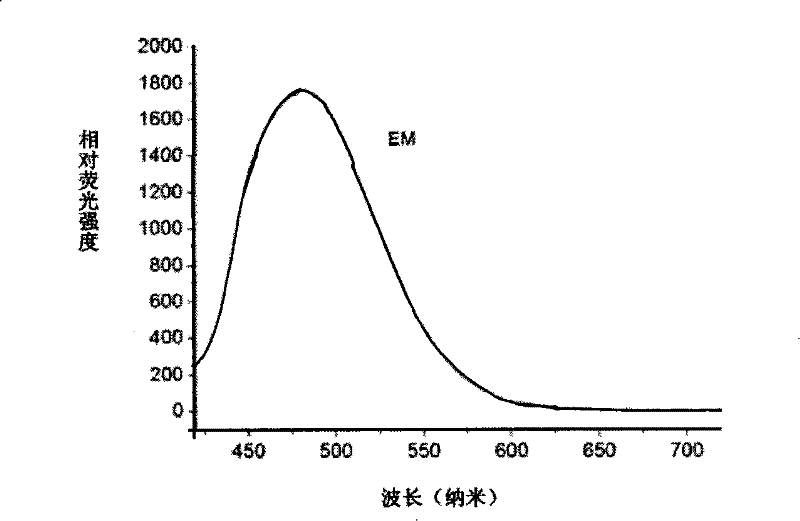
[0028] Take 5-10 times the amount of the above-mentioned extract of the sample, add NaOH solution and NaClO solution with a molar ratio of (40-50): (0.8-2.0), react at 0-4°C for 30-60 minutes, and then use phosphoric acid Adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0-9.2 with a salt buffer solution, and finally add a fluorescamine solution with a molar ratio of (0.8-2.0):(3.0-4.2) to NaClO, and mix thoroughly for 5-10 minutes. Adjust the excitation wavelength to 385±5.0nm, put it into a fluorometer to detect the fluorescence intensity, and calculate the content of acrylamide. Depend on ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: Weigh 1-5 g of bread that is ground into flour into a container, and operate according to the above-mentioned experimental steps. Measure the fluorescence intensity of the product and calculate the content of acrylamide.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: Weigh 1-5 g of fried dough sticks ground into powder into a container, and operate according to the above-mentioned experimental procedures. Measure the fluorescence intensity of the product and calculate the content of acrylamide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| emission peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com