Method for preparing hydrogen storing alloy powder
A technology for hydrogen storage alloy and alloy powder, which is applied in the field of manufacturing hydrogen storage alloy powder, can solve the problems of poor battery performance reproducibility, unstable alloy performance, slow melt cooling, etc., and achieves improvement of composition and structure uniformity, Comprehensive performance improvement, temperature uniformity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: The process steps of this embodiment are given below.
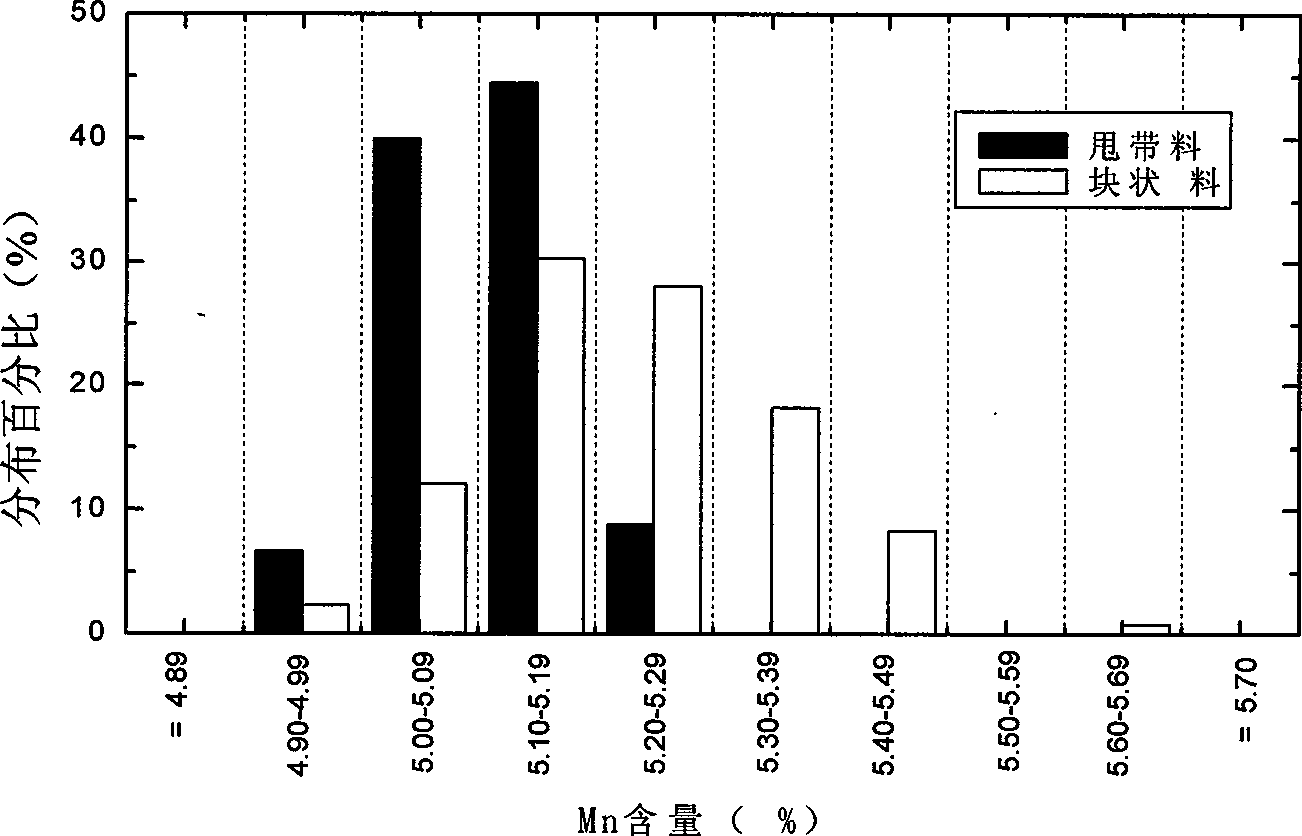
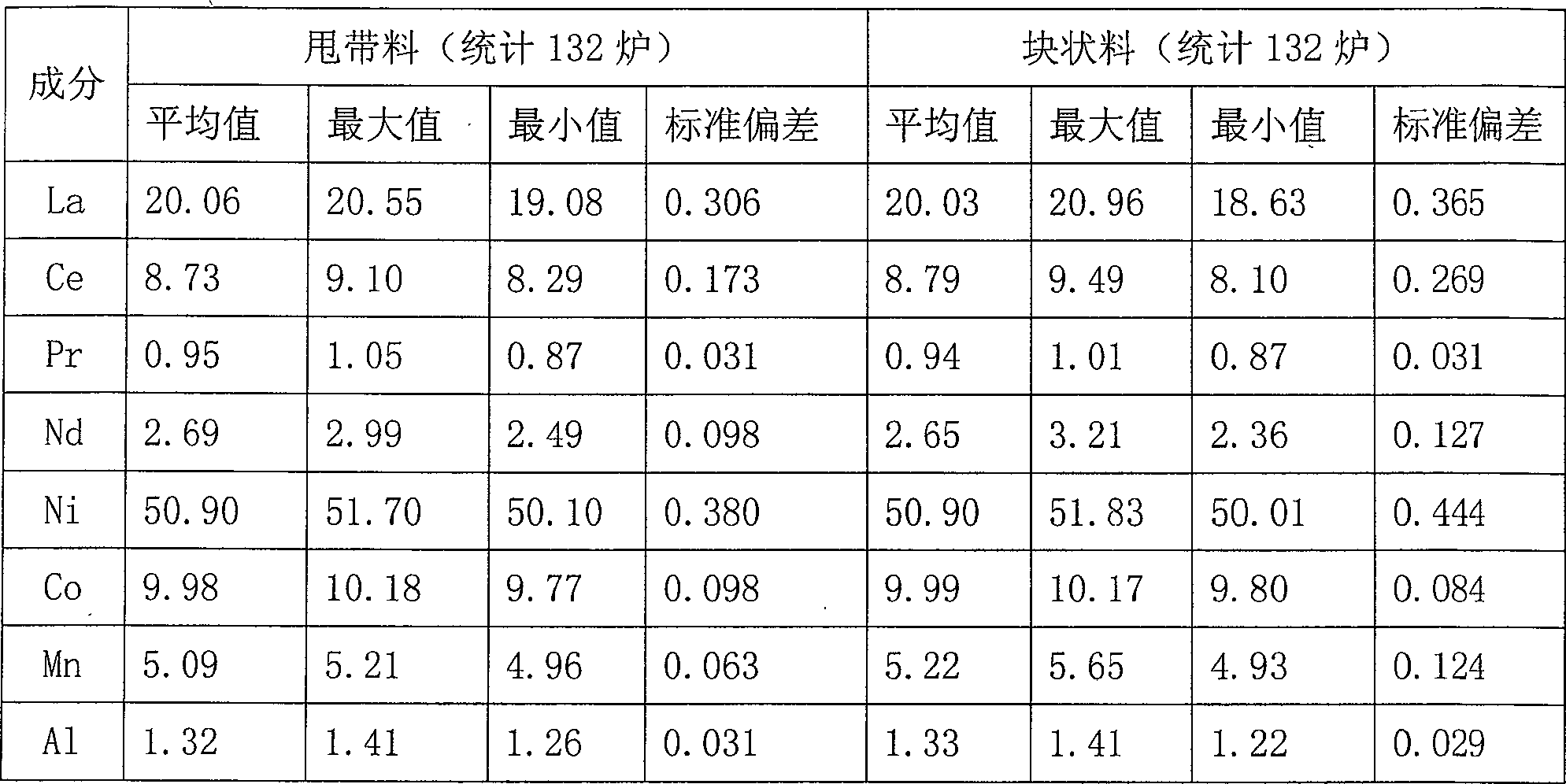
[0036] 1) Batching and composition control: Use a polishing machine and a dryer to pretreat the raw materials to remove some impurities and moisture in the raw materials. The raw materials are nickel, misch, magnesium, cobalt, manganese, aluminum and copper, and the misch Containing "lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium" after refining each raw material and its content (in Kg) is nickel: lanthanum: cerium: praseodymium: neodymium: magnesium: cobalt: manganese: aluminum: copper = 55:5:15 :1:2:1.5:7:4.5:1.2:2.5;
[0037] 2) Melting process: use a vacuum induction melting furnace to melt the raw materials at a temperature of 1500 ° C, pour the melt on the quenching belt equipment, and the cooling rate is 5×10 5 K / s, made of hydrogen storage alloy flakes with a thickness of 0.2mm;
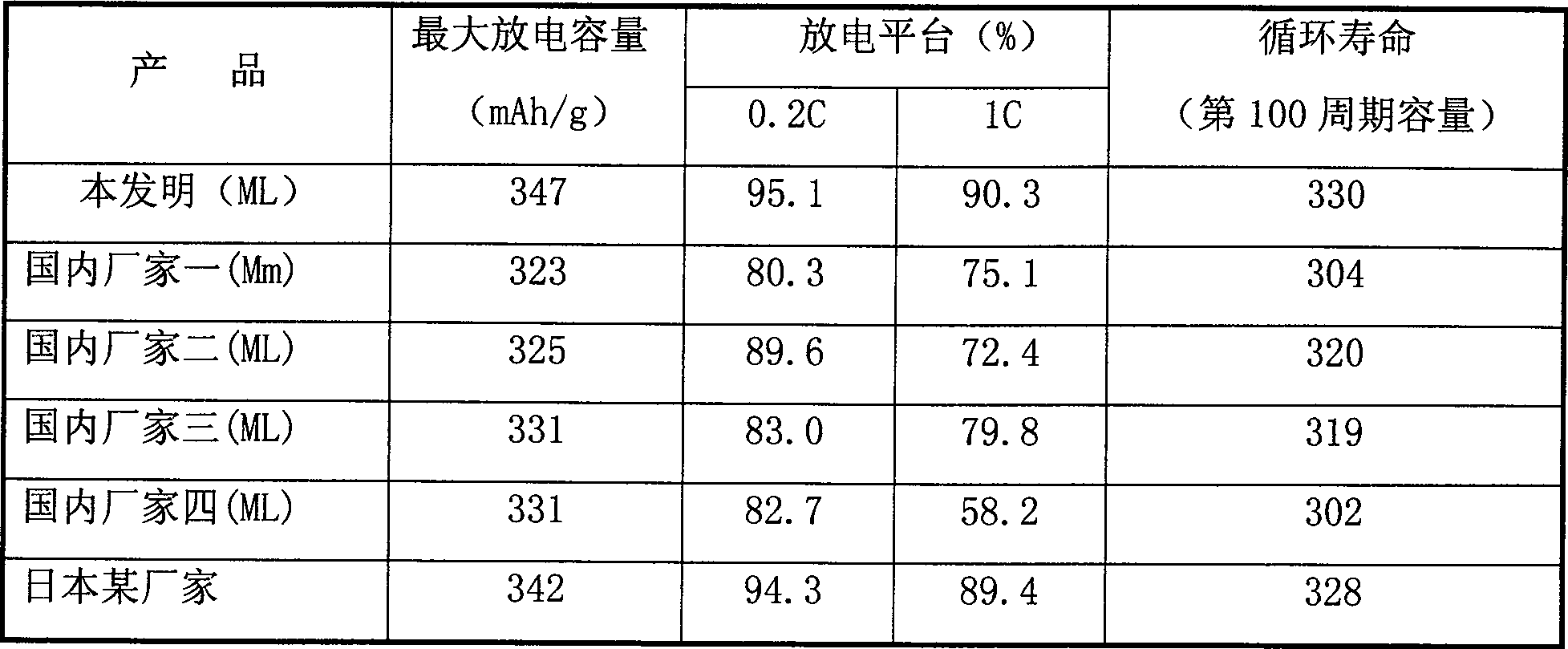
[0038] 3) Annealing process: annealing the fabricated hydrogen storage alloy flakes in a vacuum annealing furnace, t...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Similar to Example 1, ingredients and composition control: use a polishing machine and a dryer to pretreat the raw materials to remove some impurities and moisture in the raw materials, and the mixed rare earths contain "lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, and neodymium" The refined raw materials and their contents (in Kg) are nickel: lanthanum: cerium: praseodymium: neodymium: magnesium: cobalt: manganese: aluminum: copper=55:10:25:0.3:3:3:8:5 :1:2; Melt the raw materials at a temperature of 1400°C, pour the melt on a quenching belt equipment, and the cooling rate is 6×10 5 K / s, made into a hydrogen storage alloy sheet with a thickness of 0.15mm. Anneal the prepared hydrogen storage alloy flakes, the annealing temperature is 900°C, and the annealing time is 8h; the annealed hydrogen storage alloy flakes are made into powder in an inert atmosphere of 5 MPa after nitrogen and argon are compressed by an air compressor, Obtain hydrogen storage alloy powder.
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: Similar to Example 1, each raw material and its content (in Kg) after refinement of "lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium" contained in the mixed rare earth are nickel: lanthanum: cerium: praseodymium: neodymium: magnesium: Cobalt: Manganese: Aluminum: Copper = 55:15:8:1.5:2.5:0.1:5:6.5:2.5:3 The raw materials are smelted at a temperature of 1300°C, and the melt is poured on the quenching belt equipment, and the cooling rate is 8×10 5 K / s, made into a hydrogen storage alloy sheet with a thickness of 0.25mm. The hydrogen storage alloy flakes were annealed, the annealing temperature was 800°C, and the annealing time was 5h; the annealed hydrogen storage alloy flakes were compressed by an air compressor to form a powder in an inert atmosphere of 5 MPa, Obtain hydrogen storage alloy powder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com