Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35results about How to "Reduces dyspnea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of treating tuberculosis with interferons
InactiveUS20100098660A1Increase appetiteReduction in wheezingAntibacterial agentsBiocideInterferon therapyInterferon alpha
A method of treating tuberculosis comprising administering an aerosolized interferon such as interferon α, interferon β or interferon γ in a therapeutically effective amount is provided herein. Further, a method of reducing the infectivity of tuberculosis or reducing the number of infectious organisms present in the lungs of a patient suffering from tuberculosis comprising administering an aerosolized interferon such as interferon α, interferon β or interferon γ in a therapeutically effective amount is provided herein. Also, pharmaceutical compositions of one or more aerosolized interferon(s) are provided.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
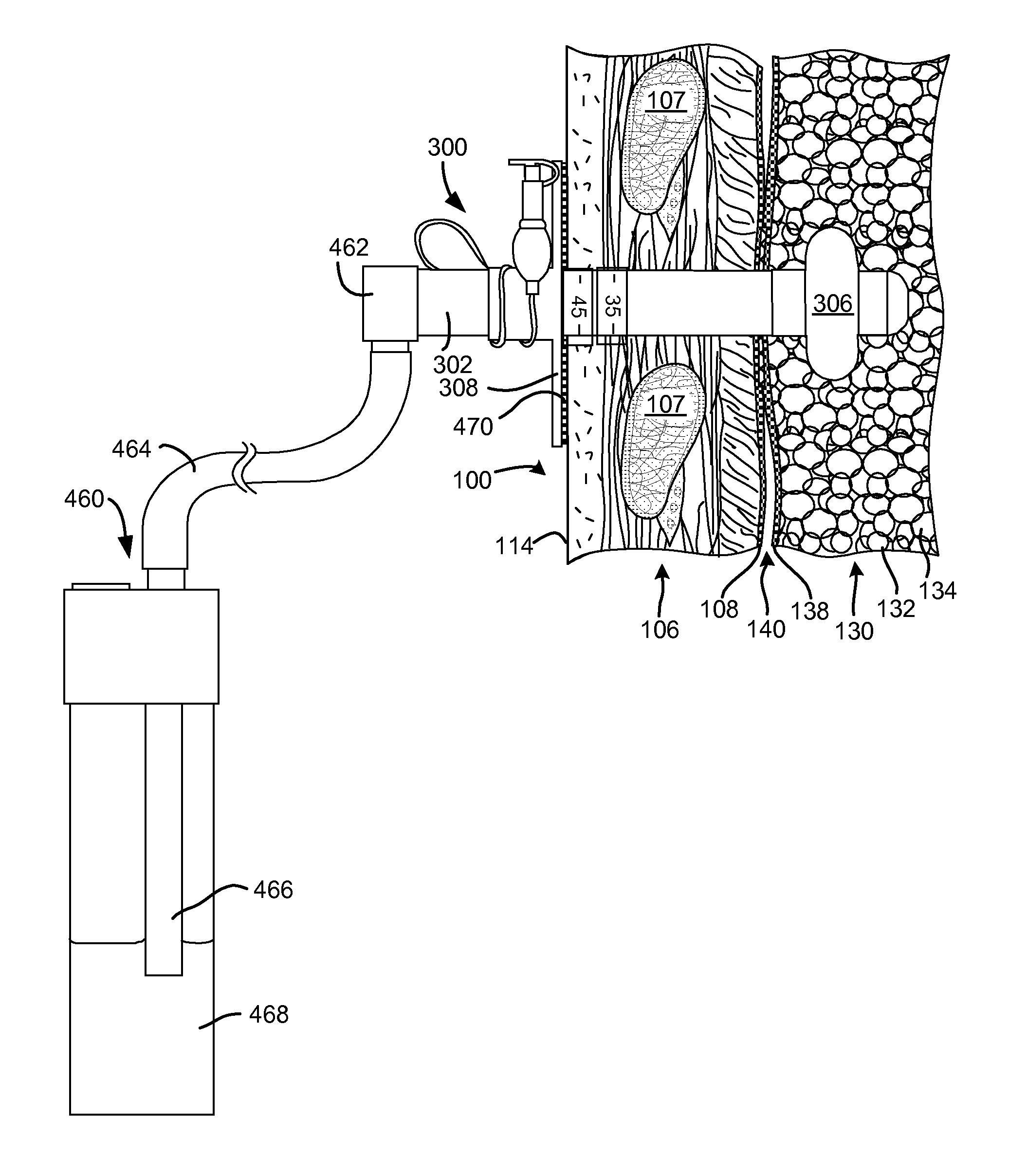
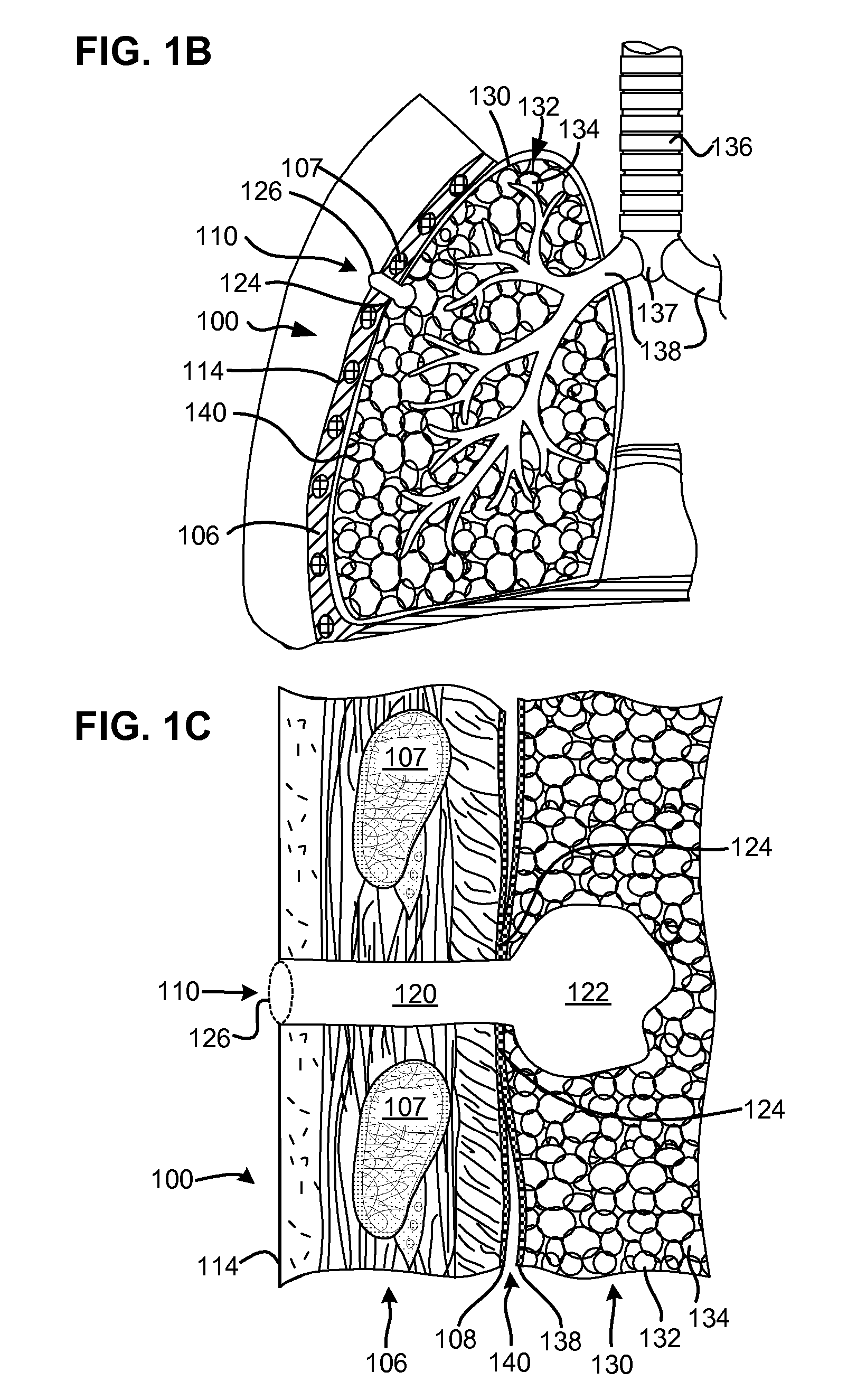
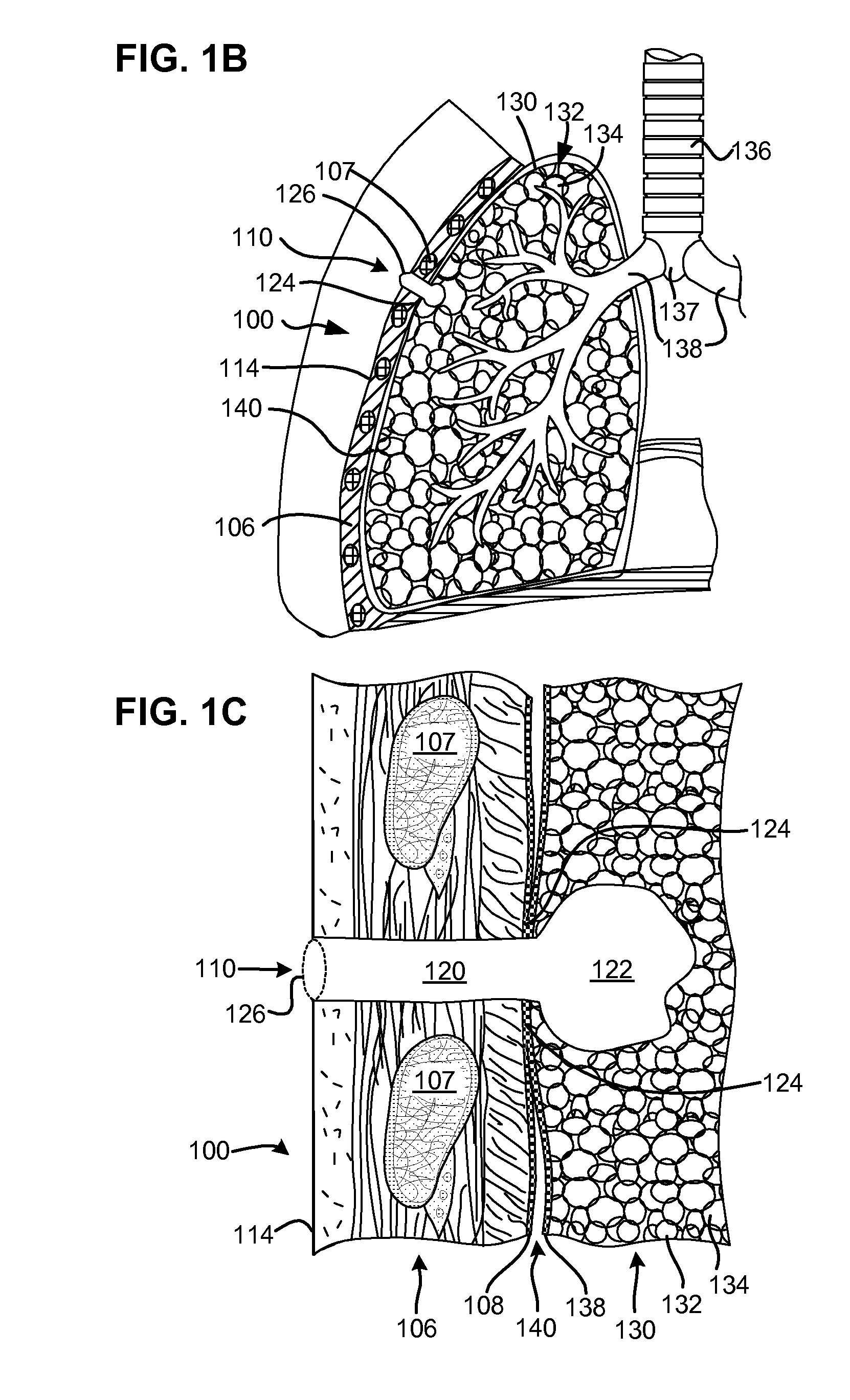
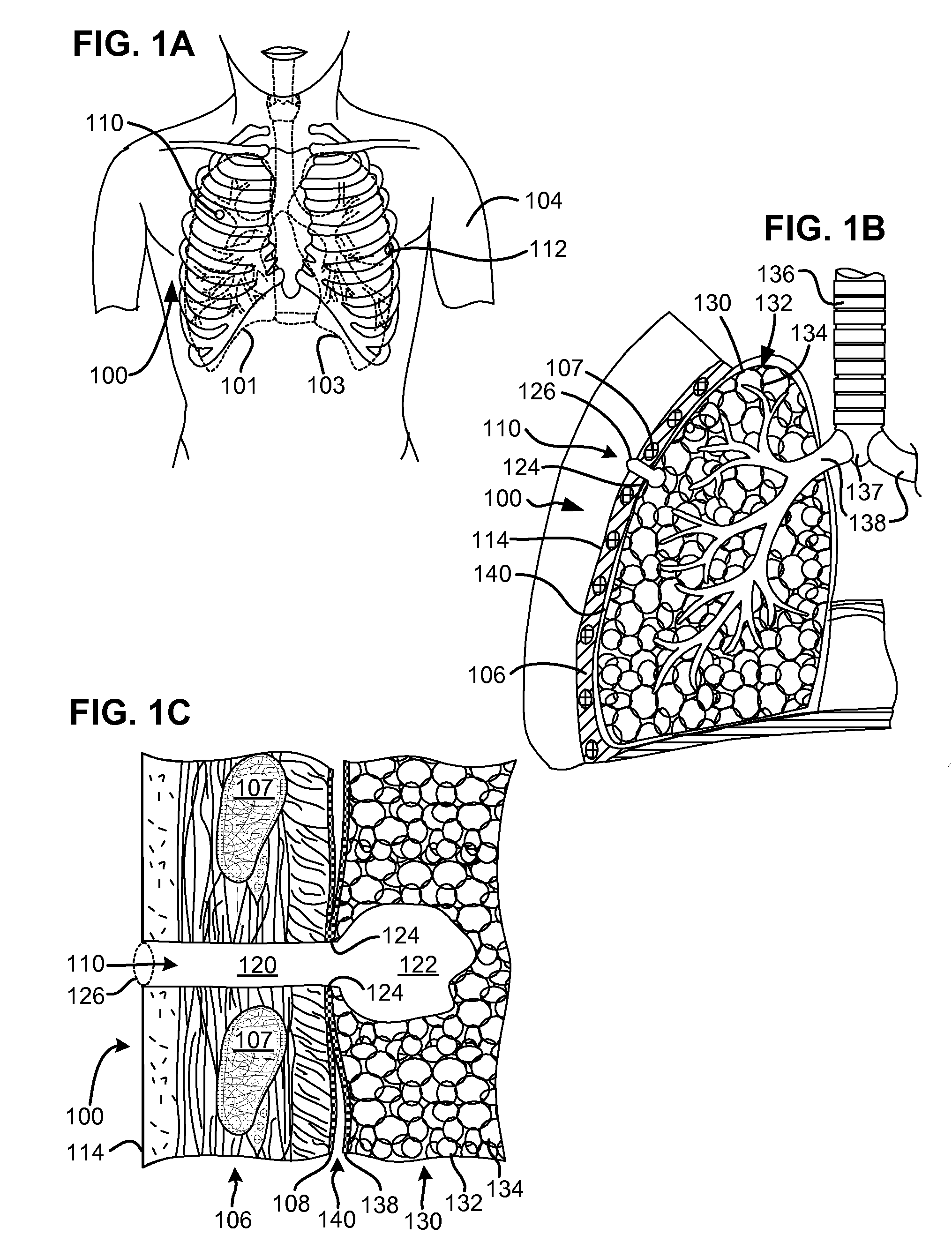
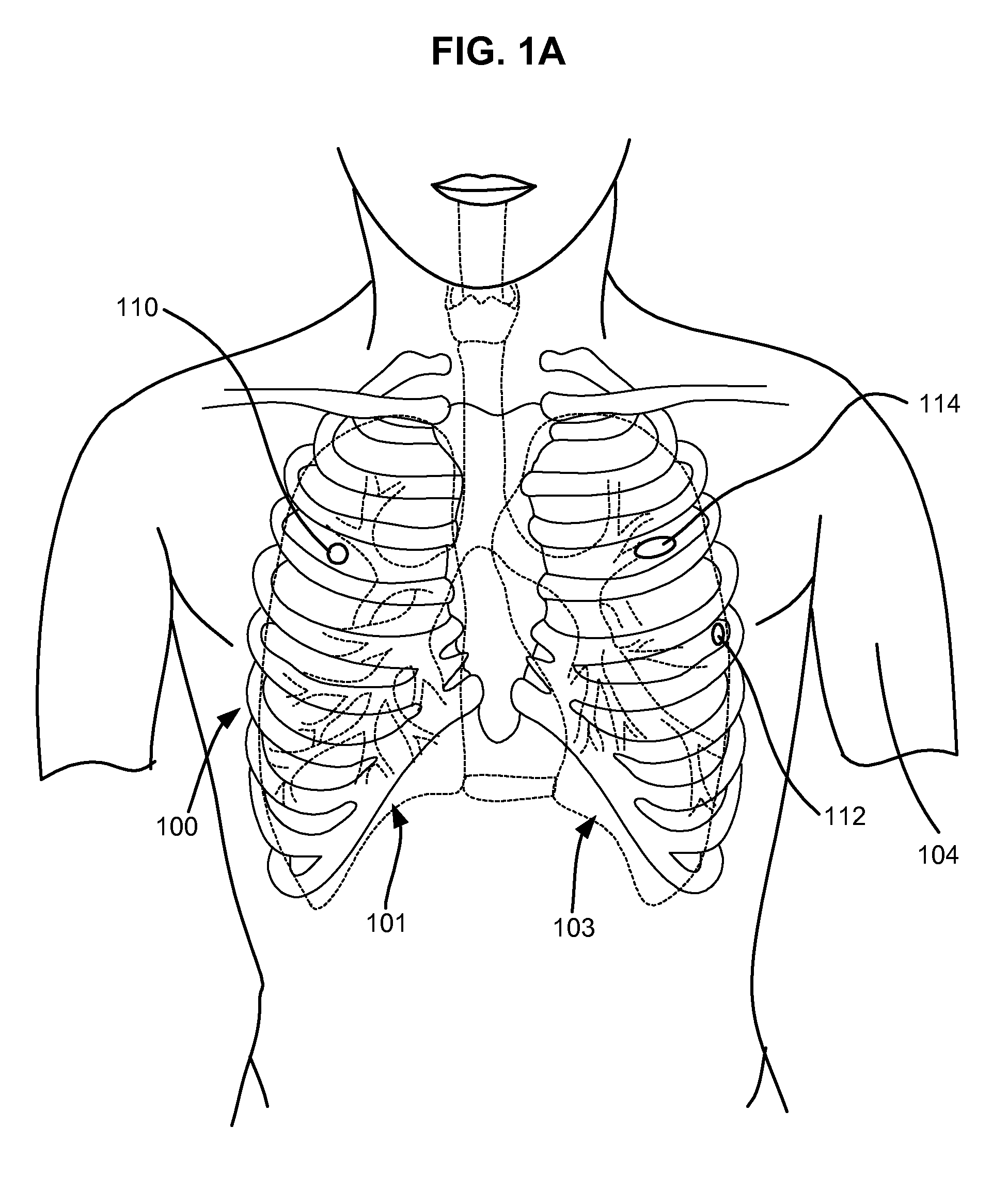
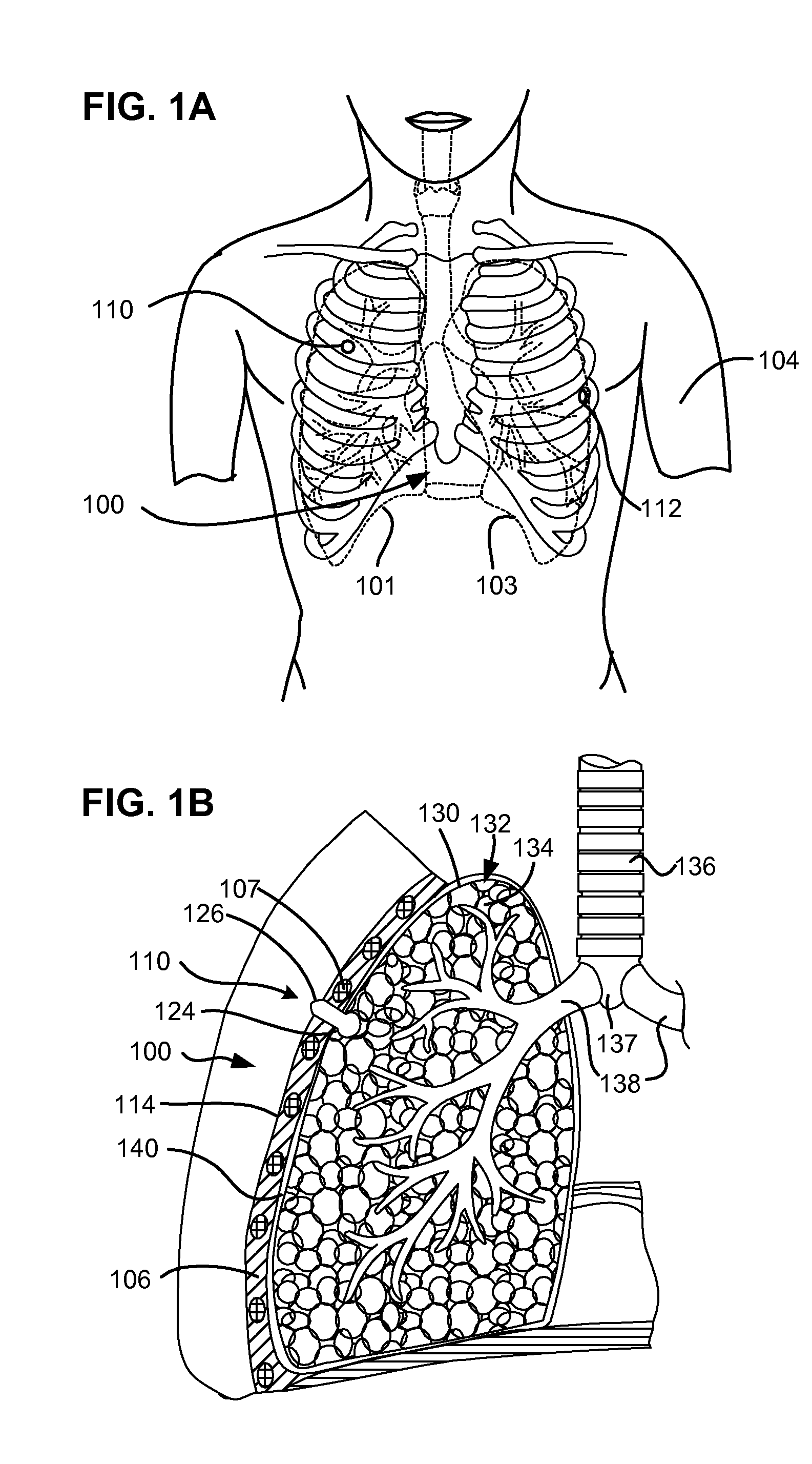
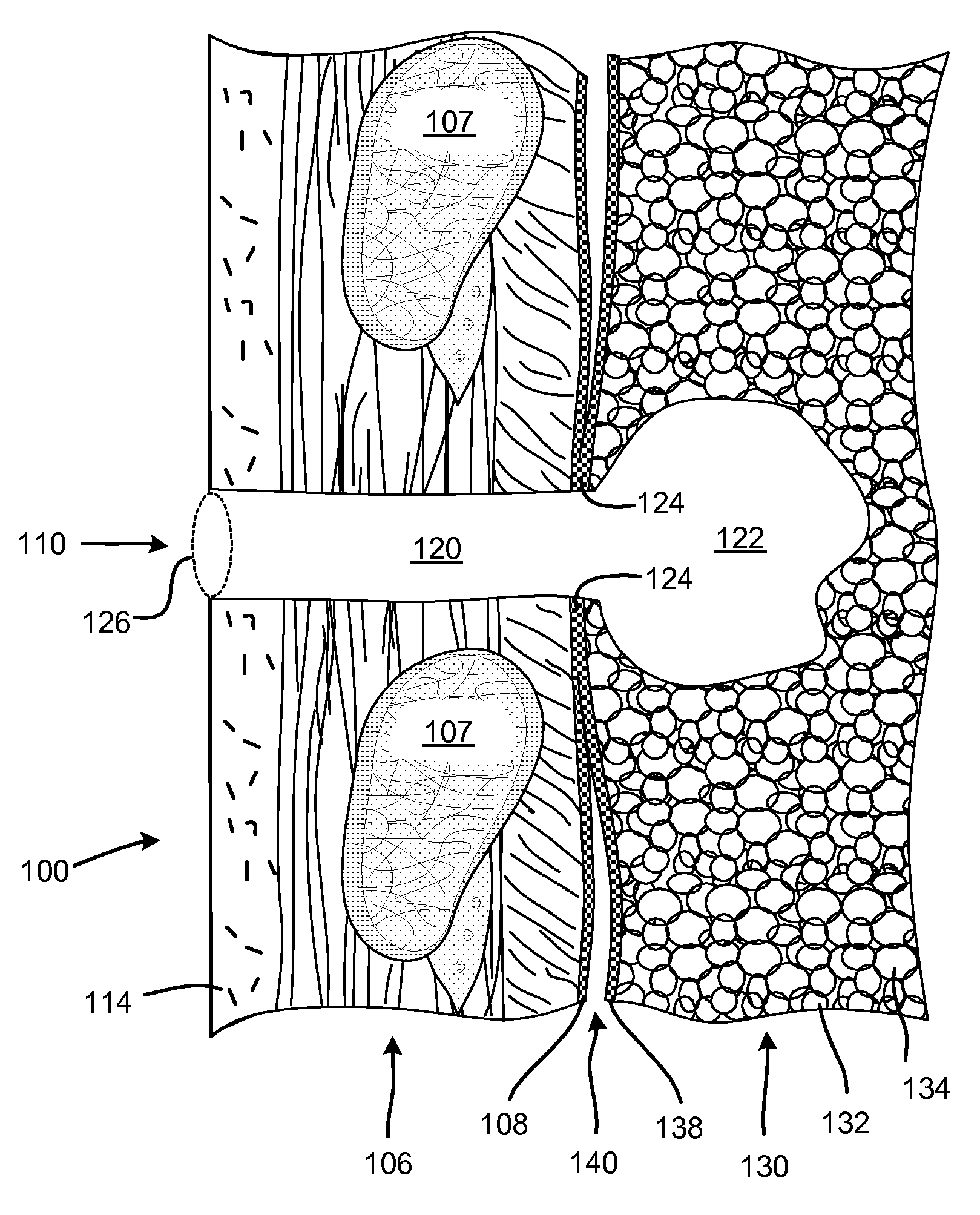
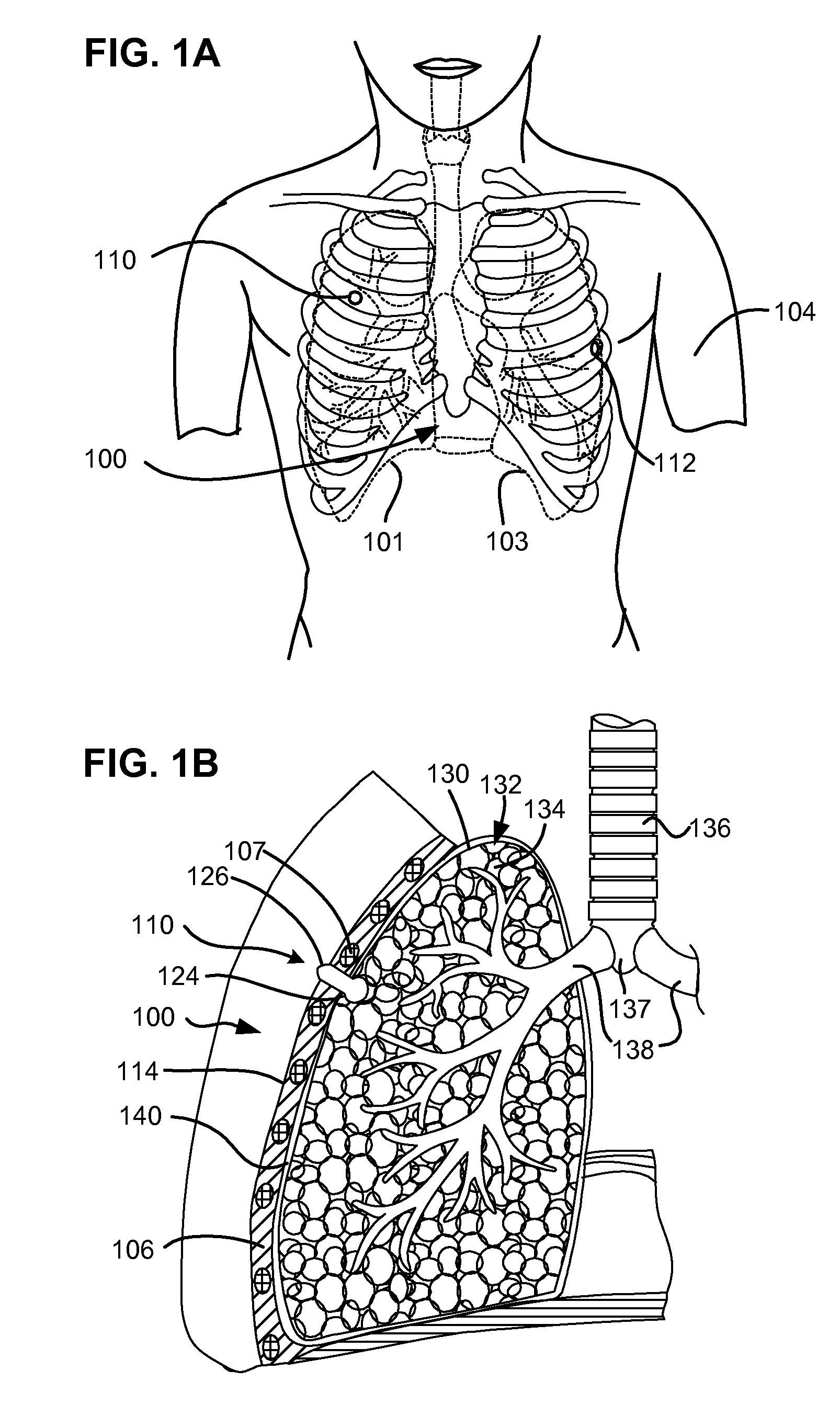
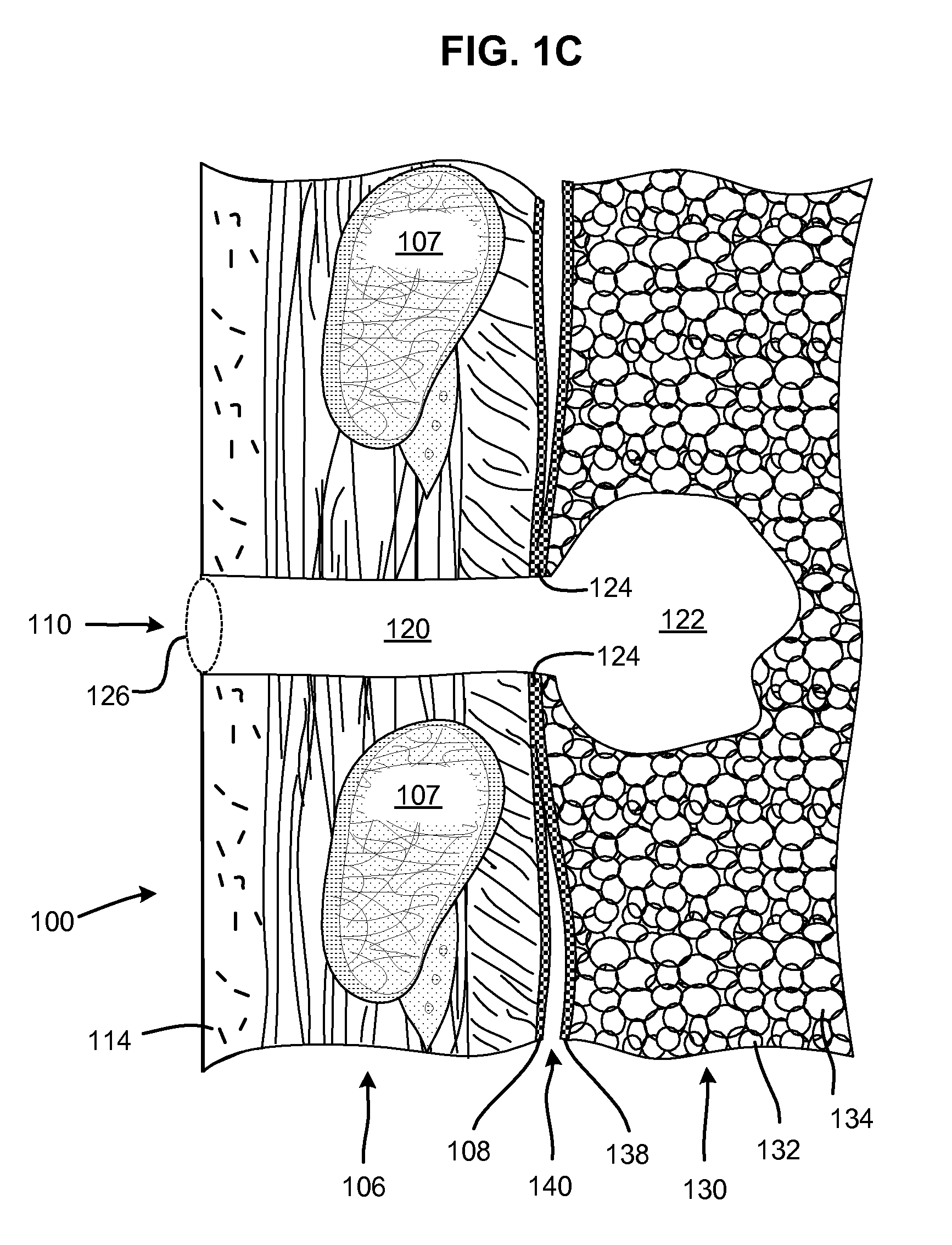
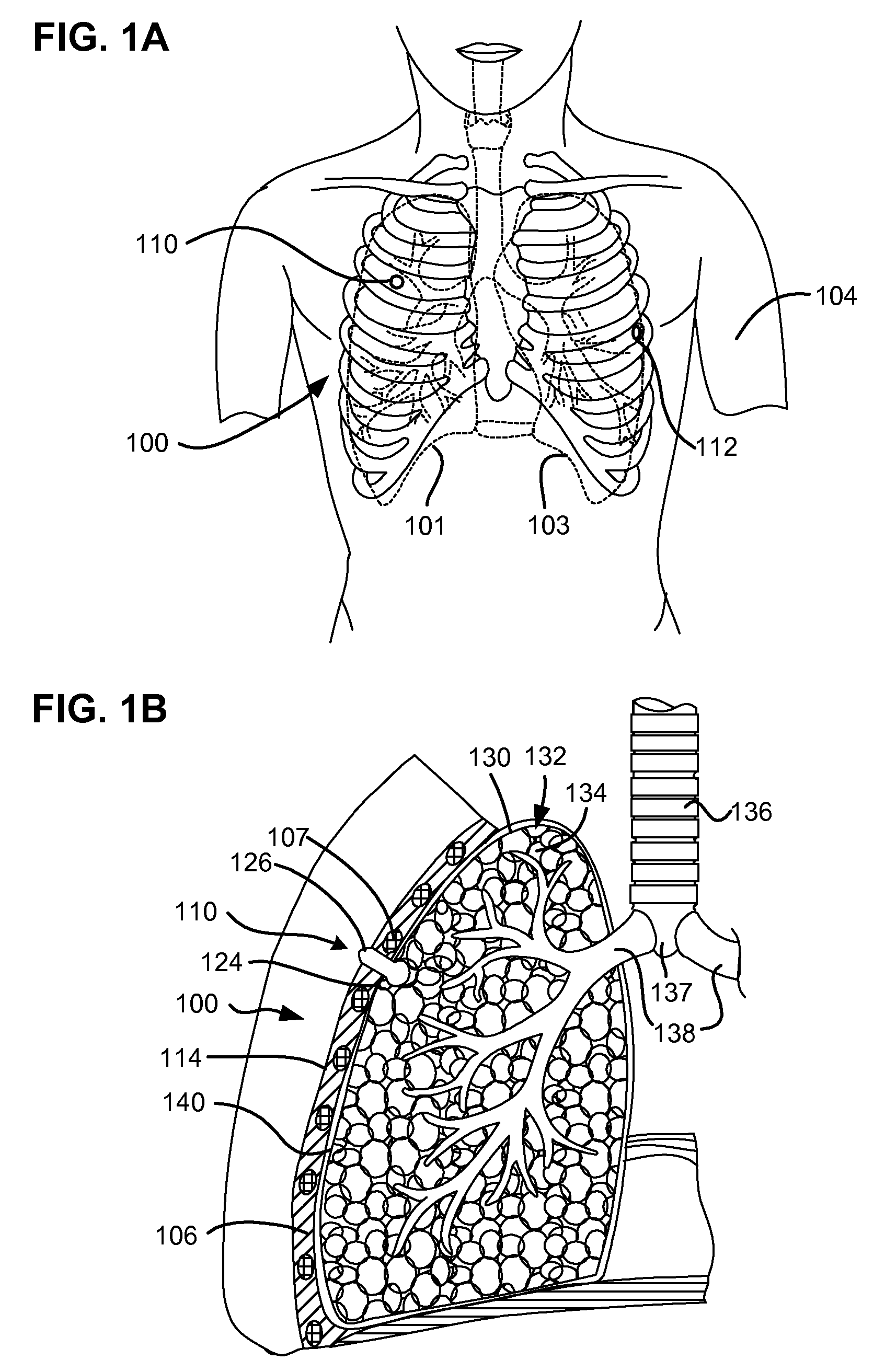
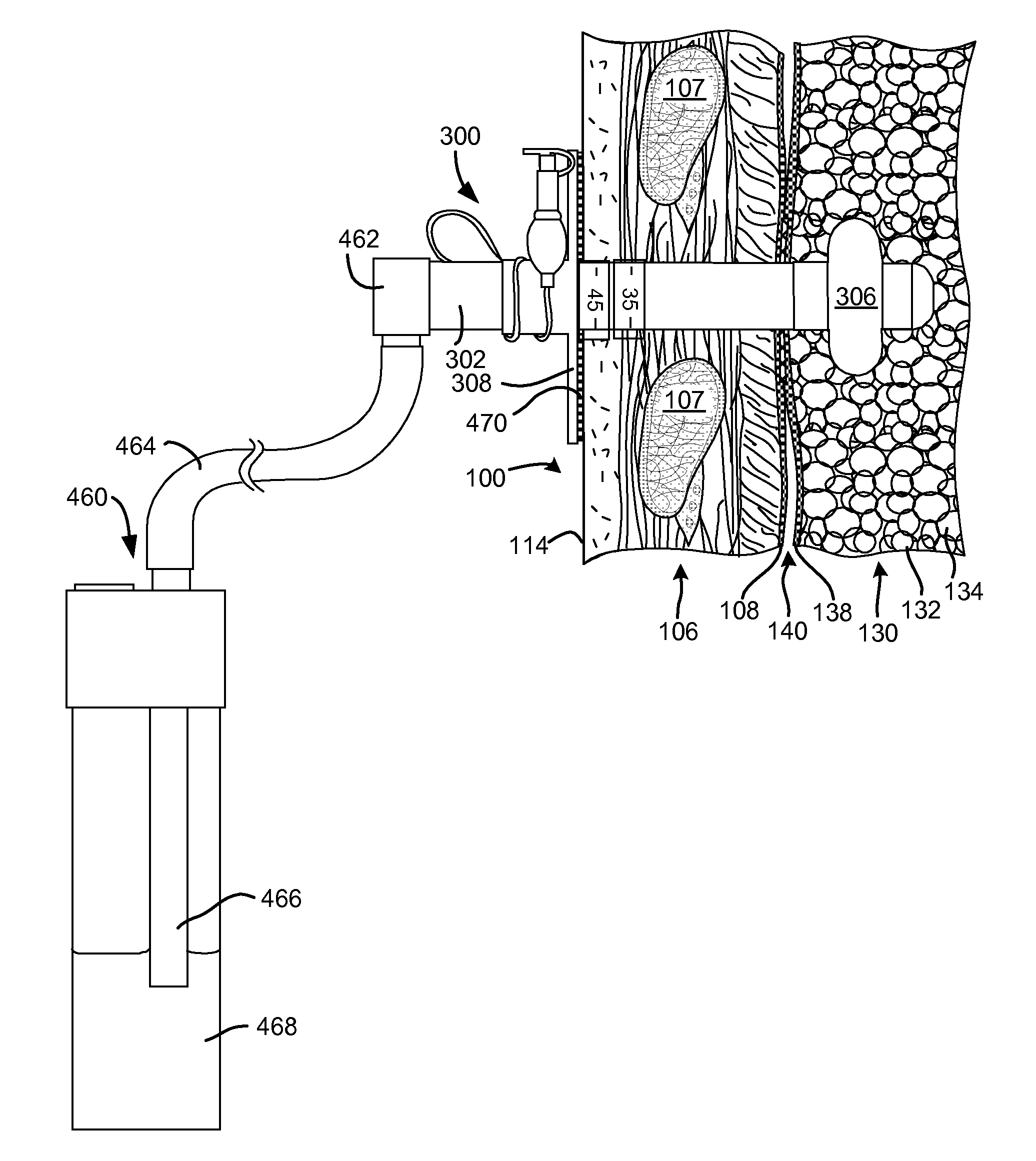
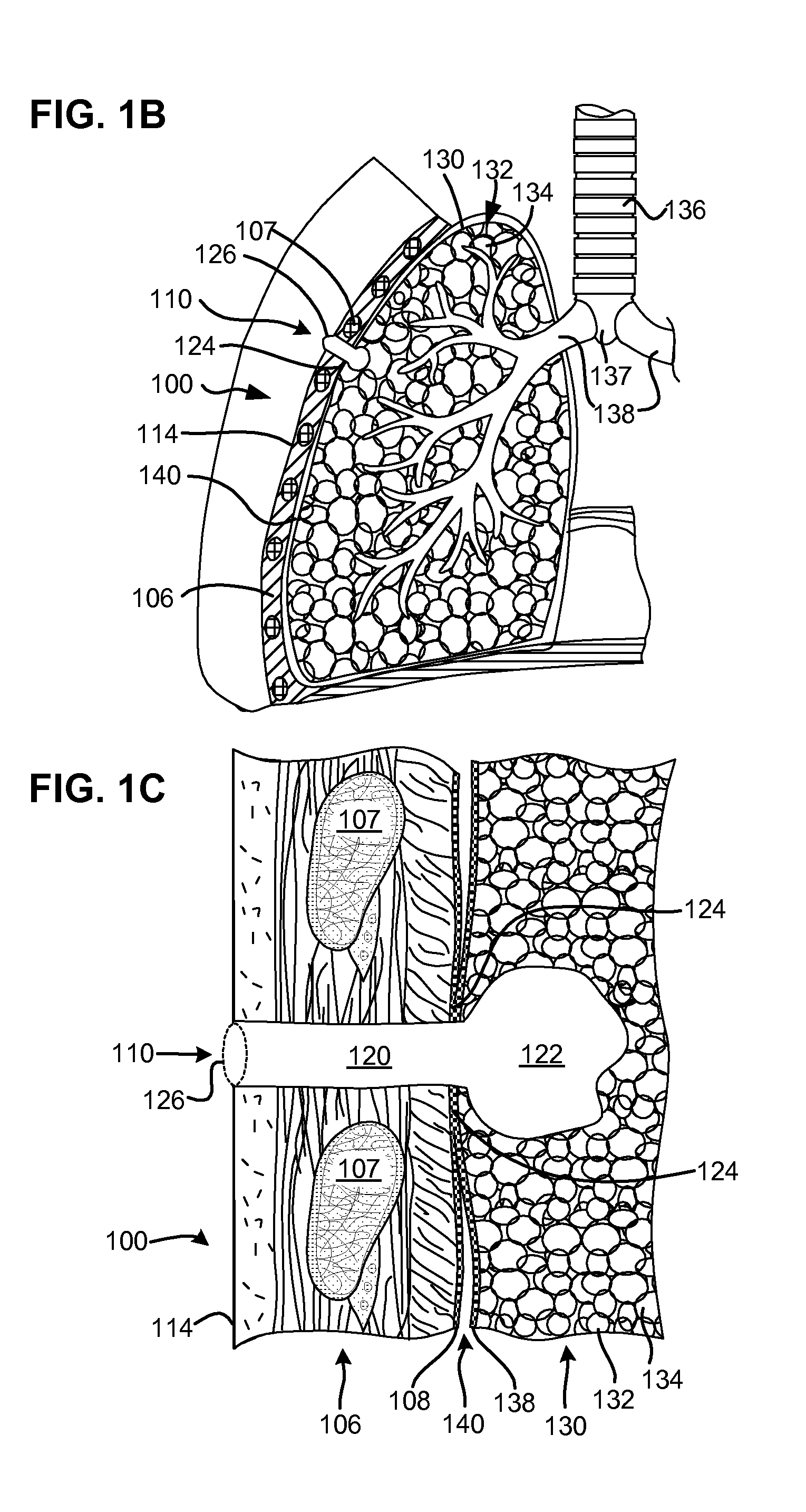
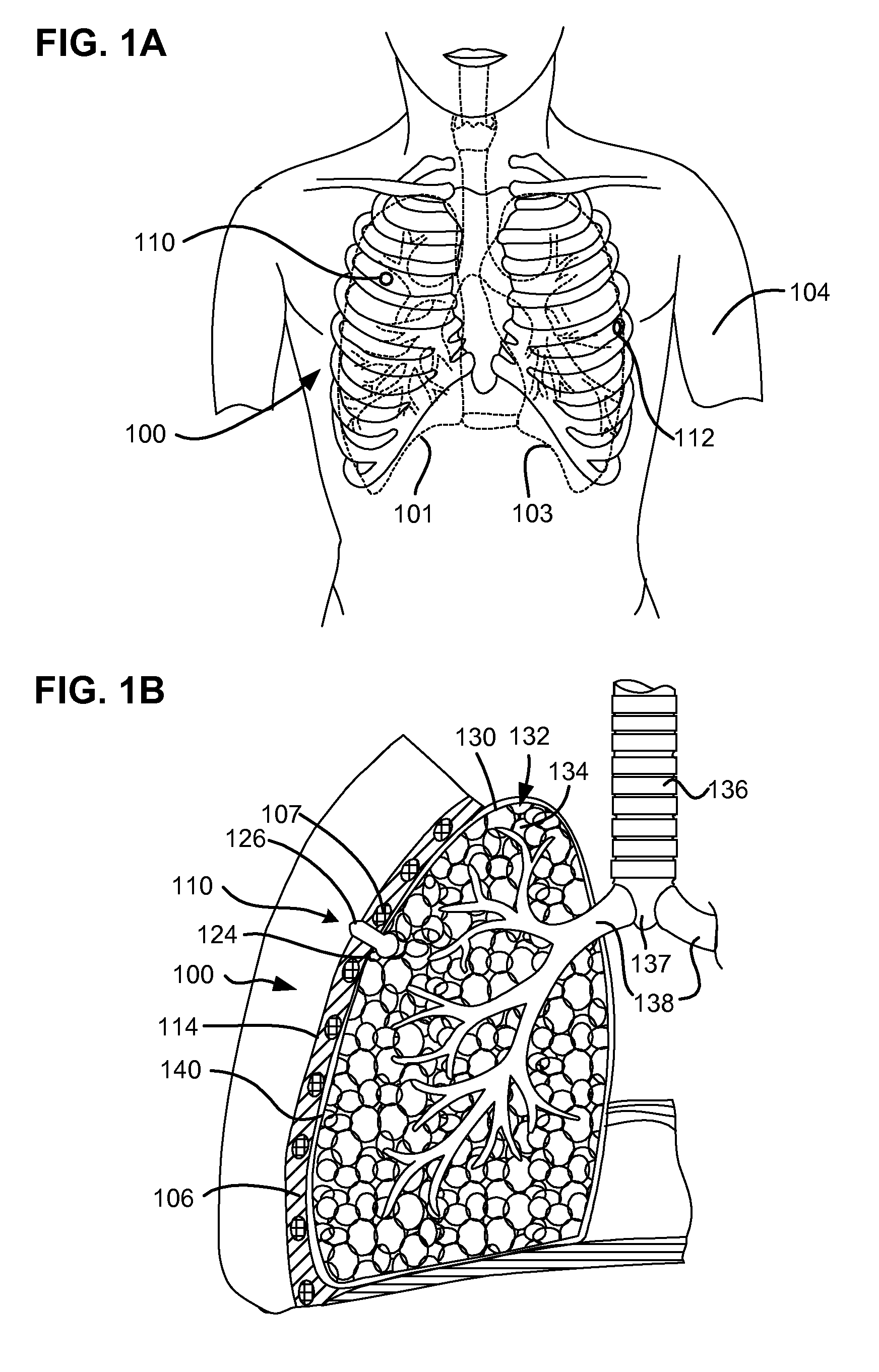
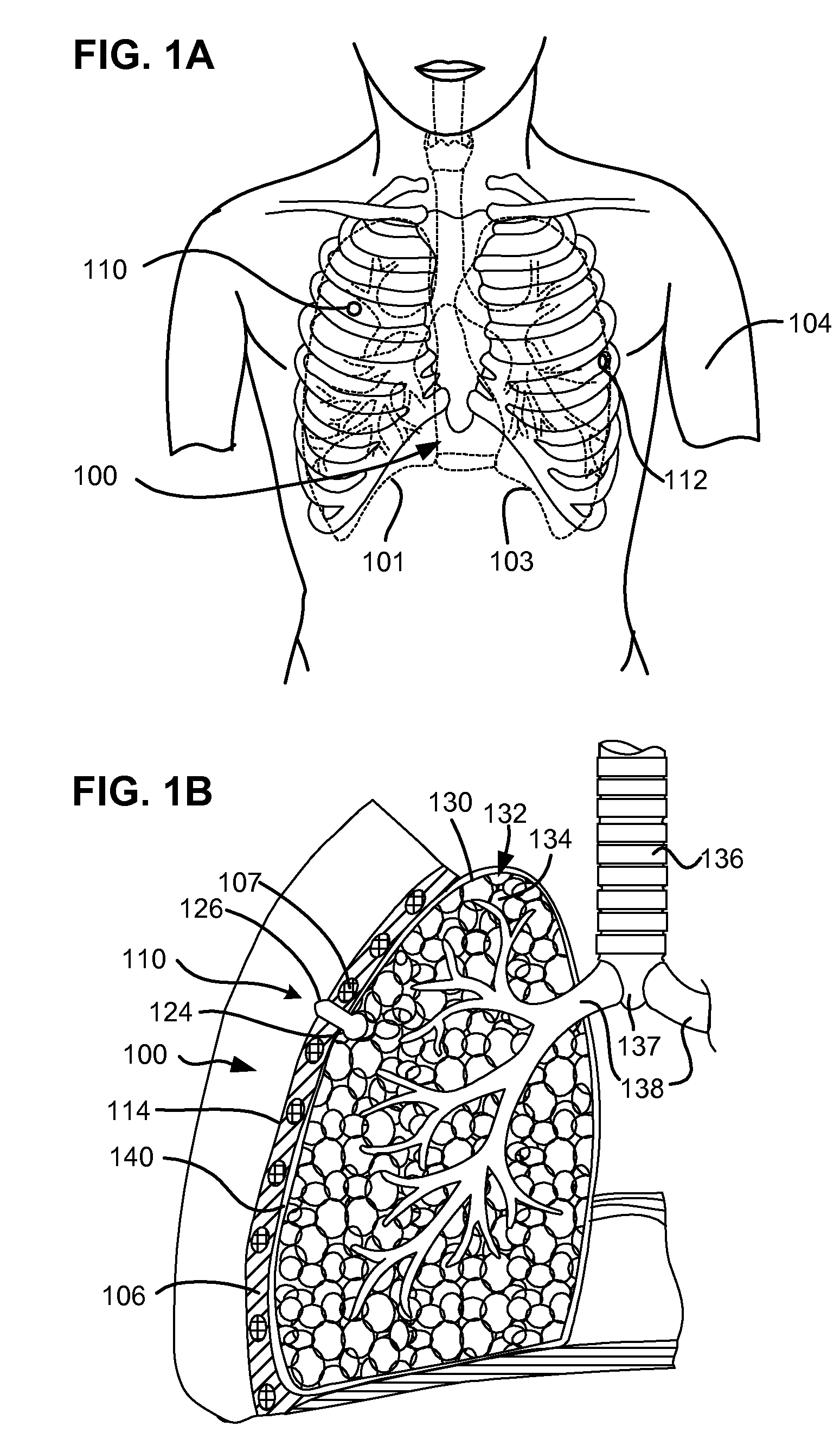
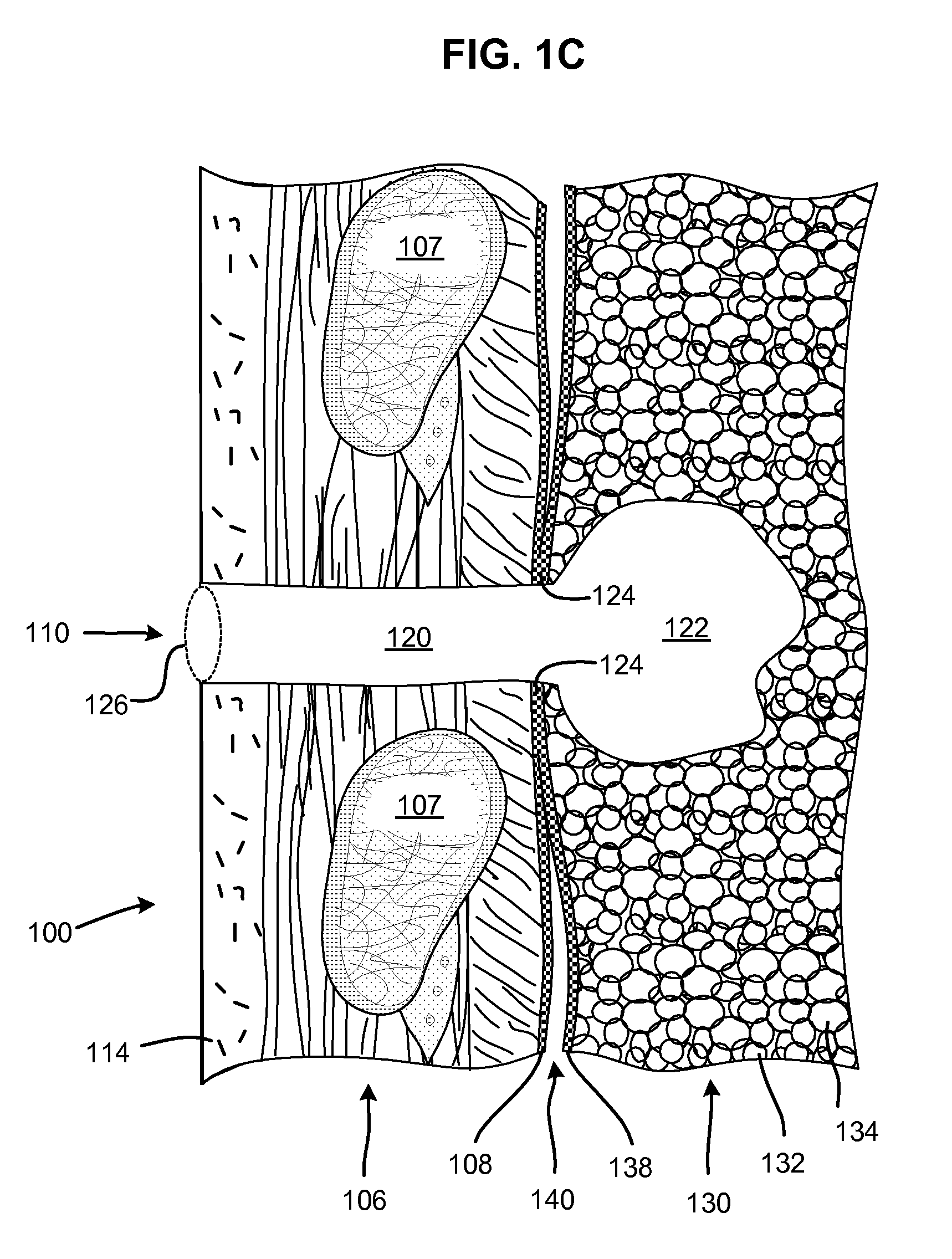
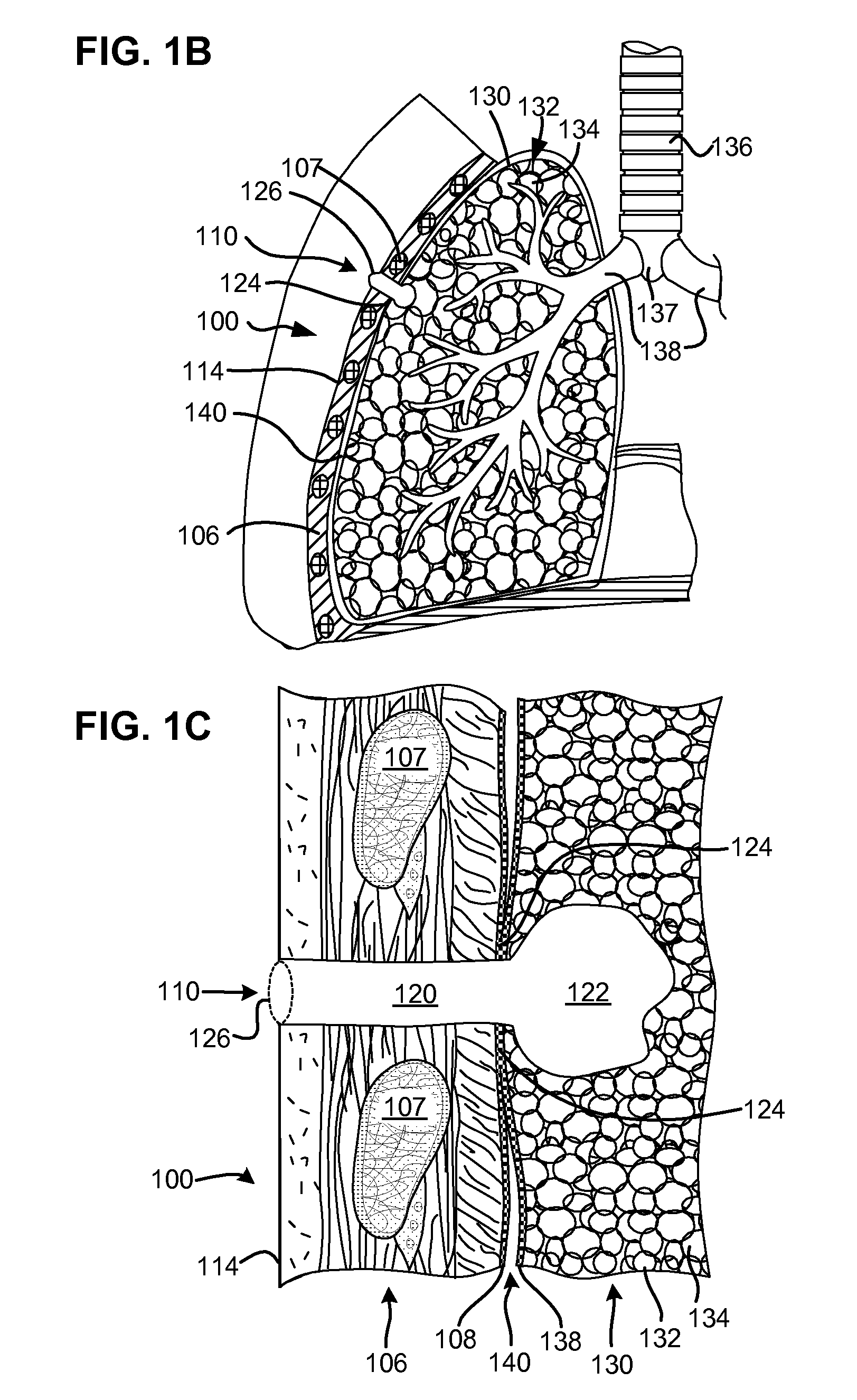
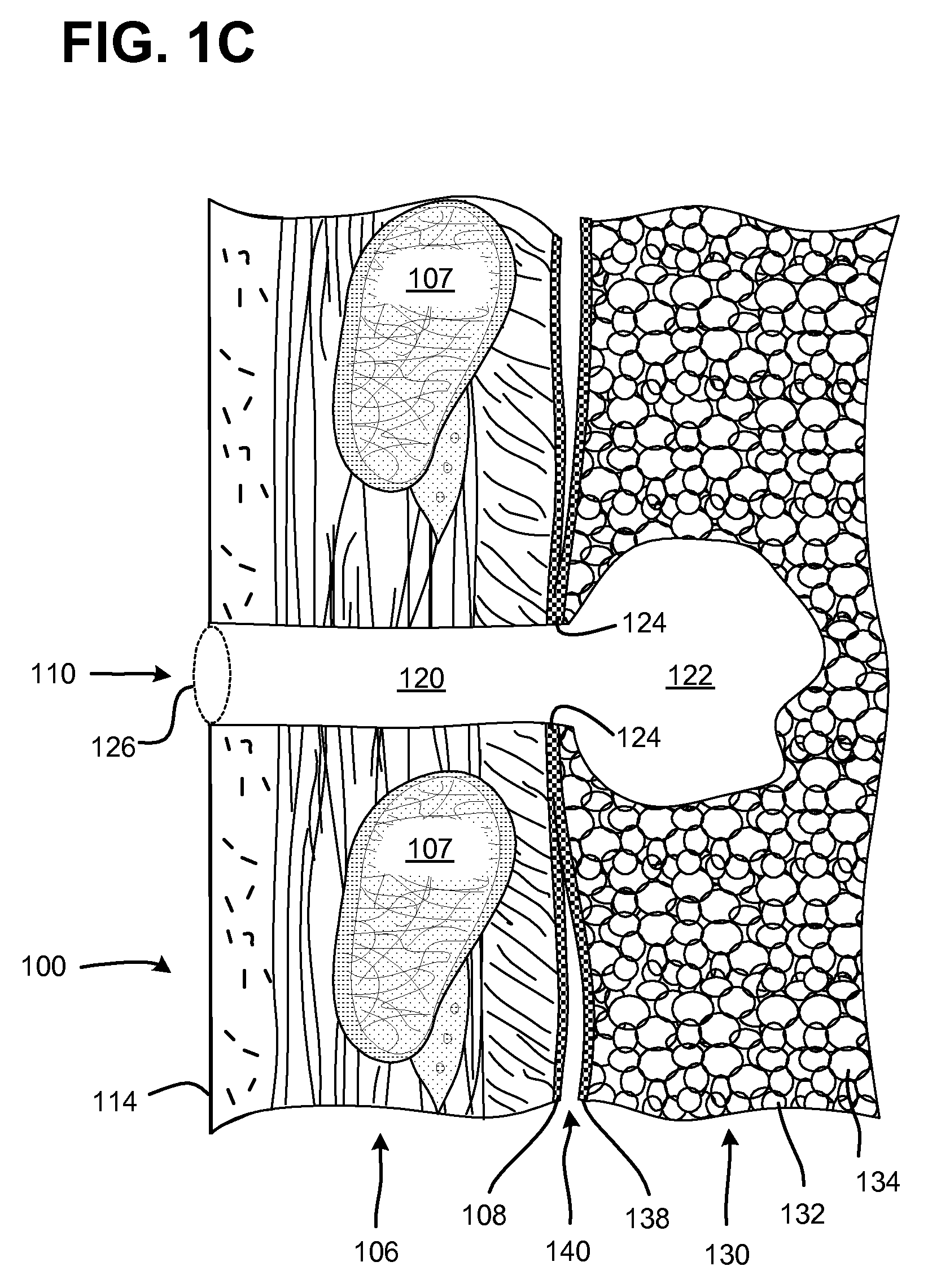
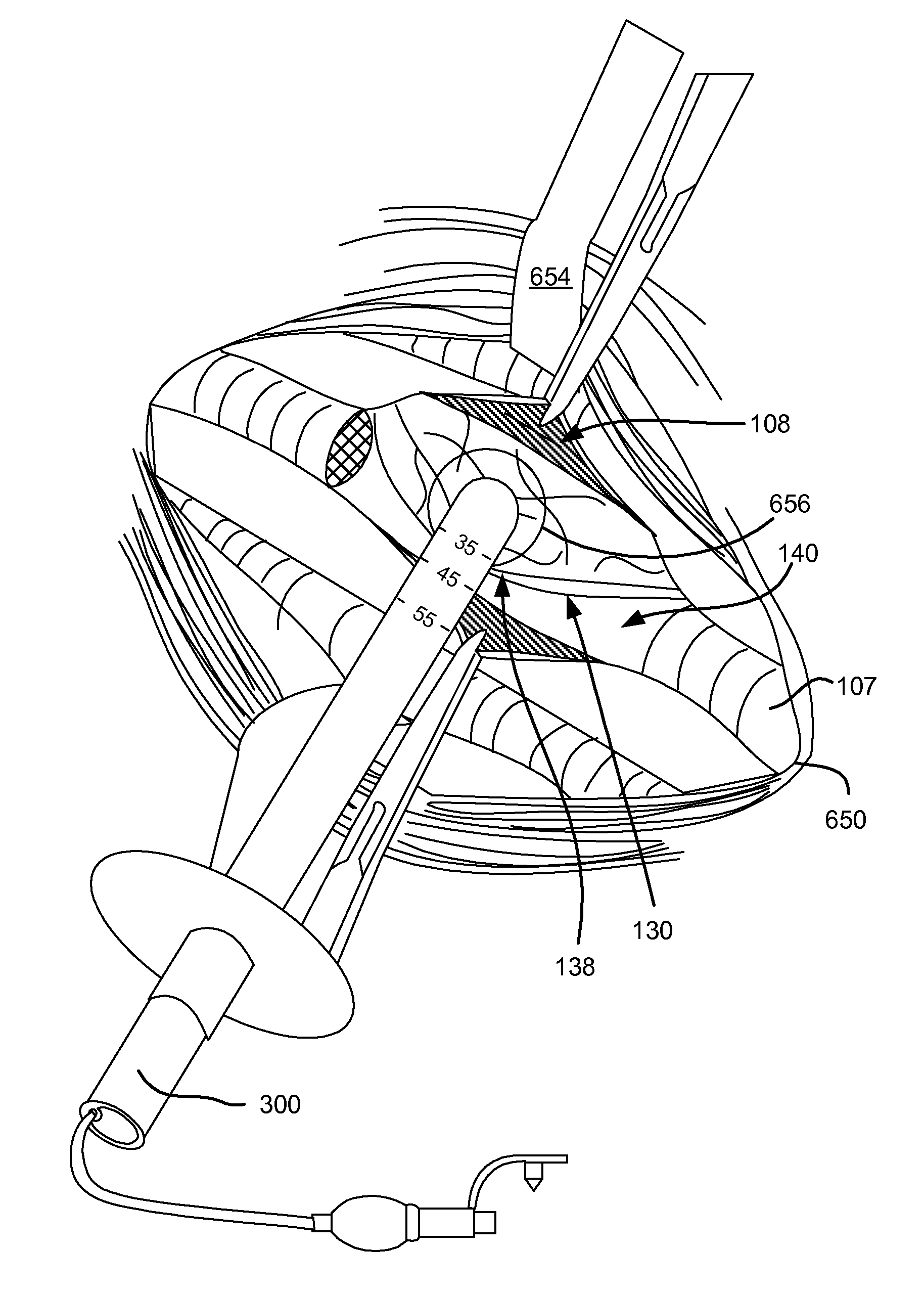
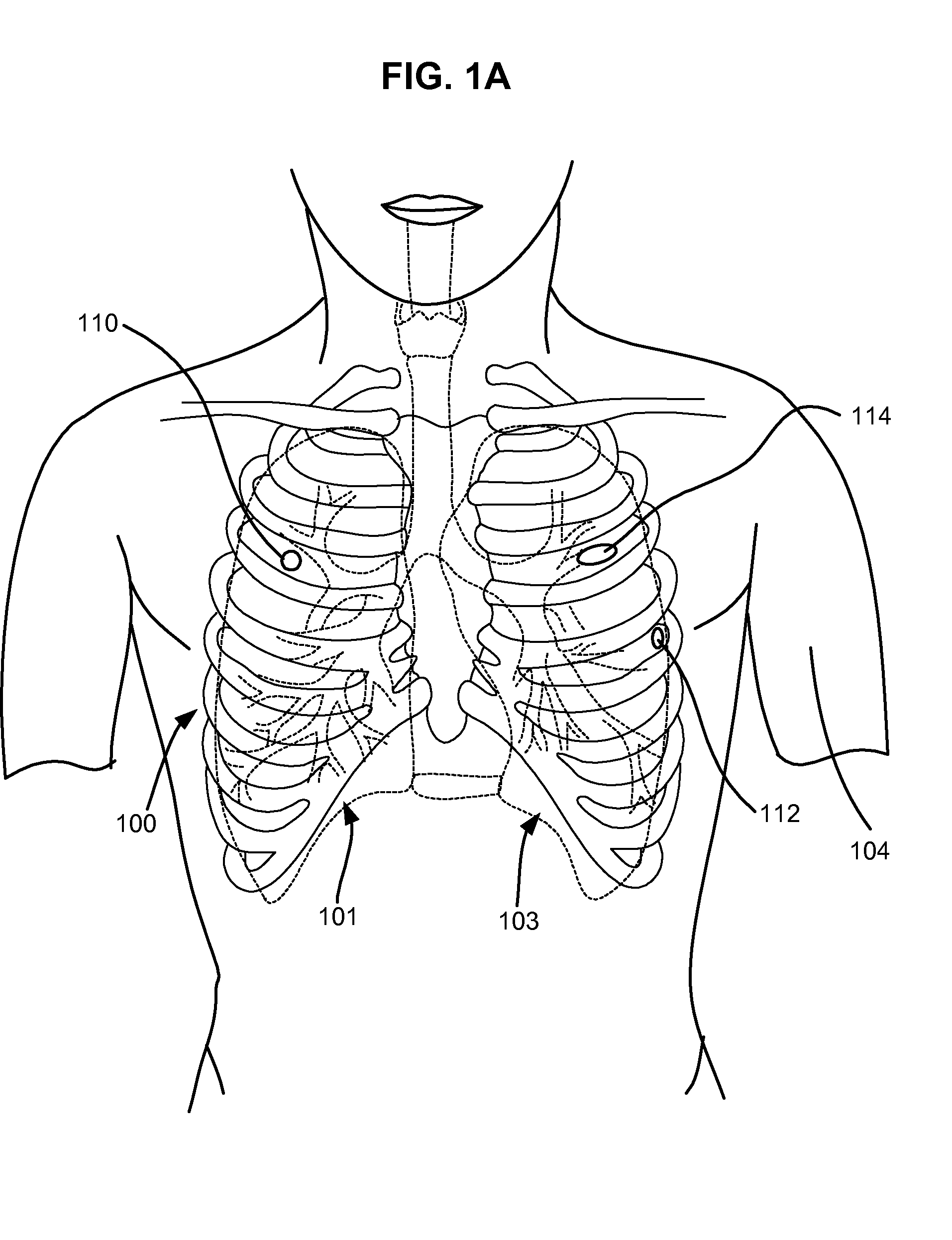
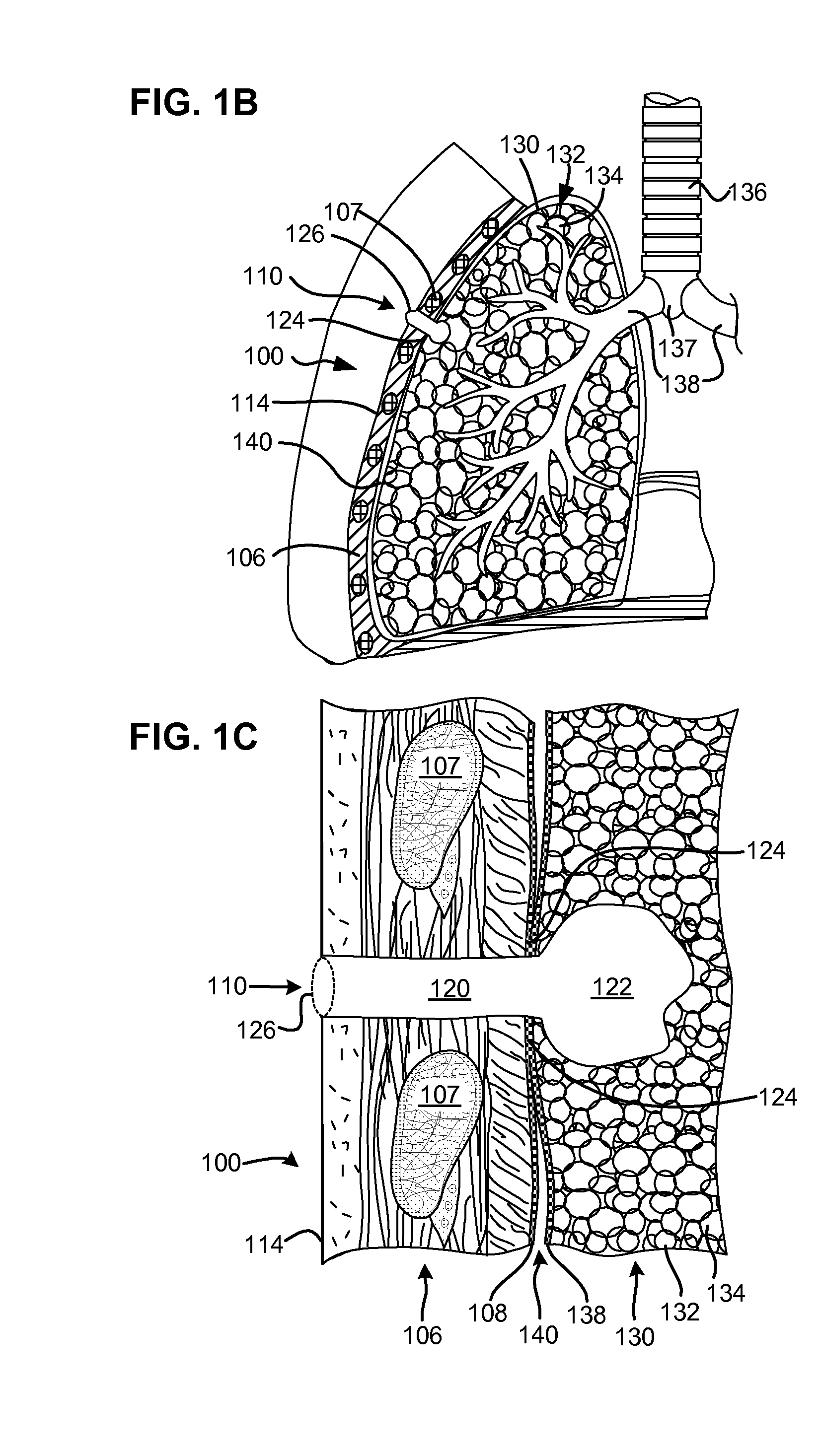
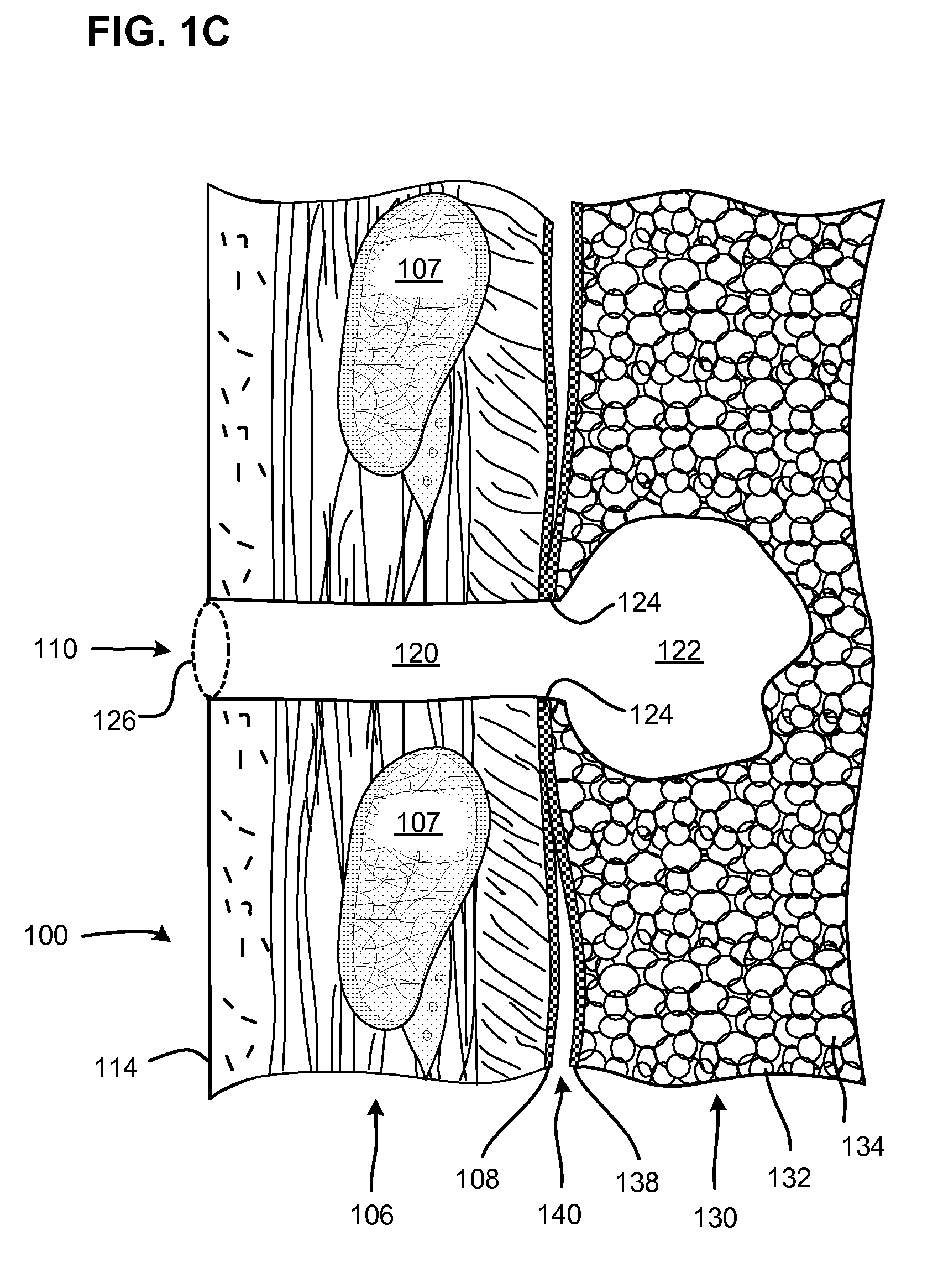
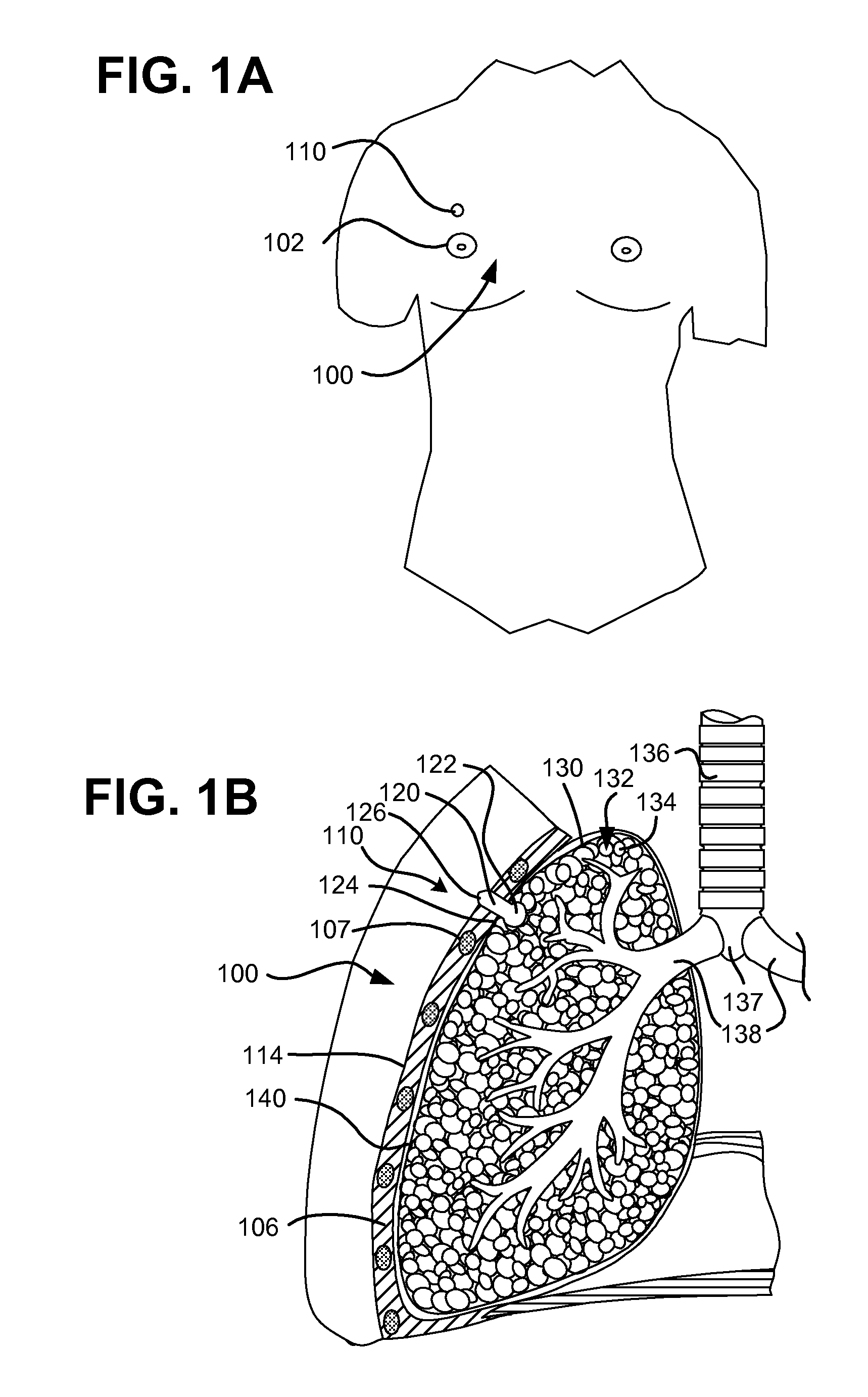
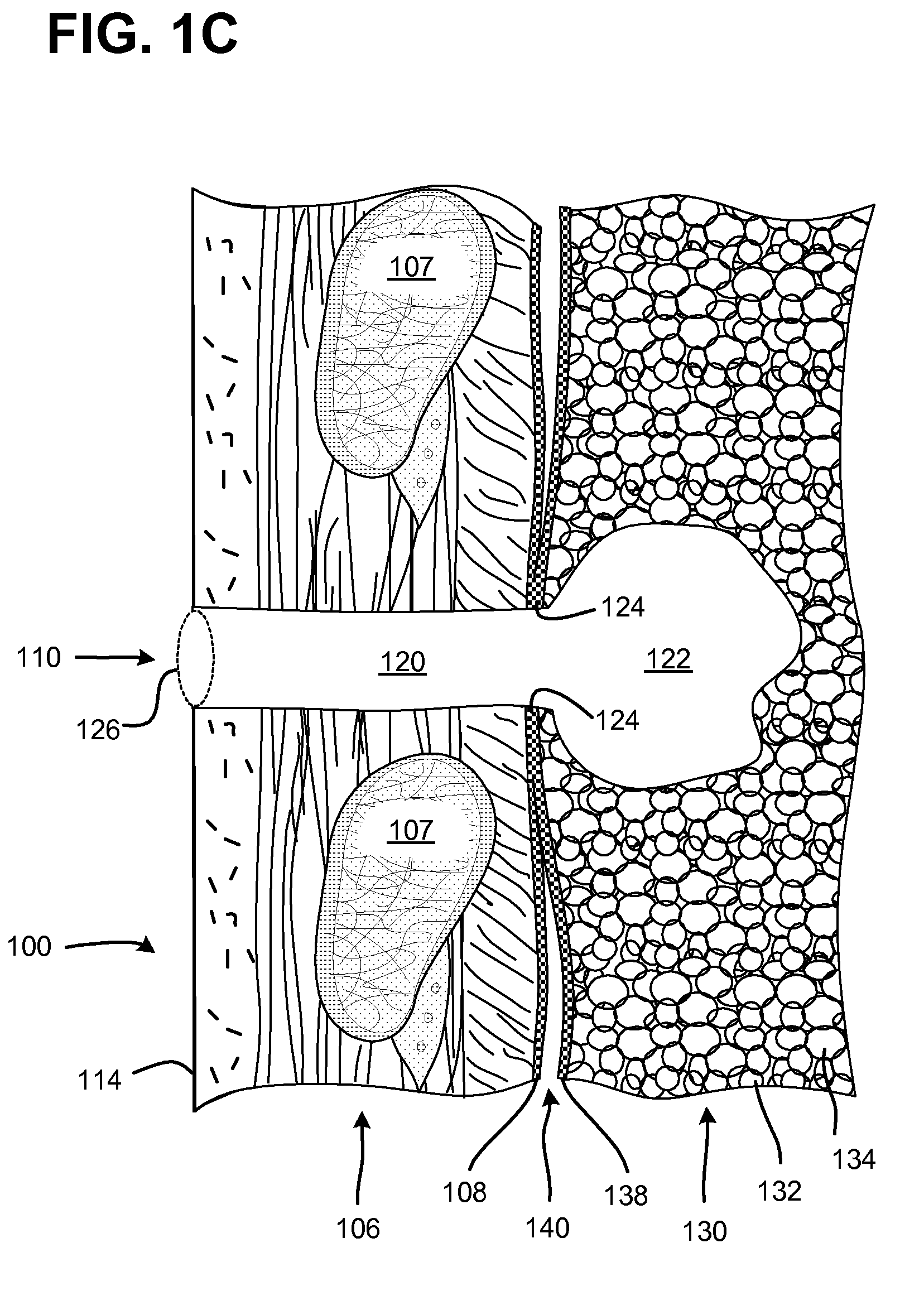
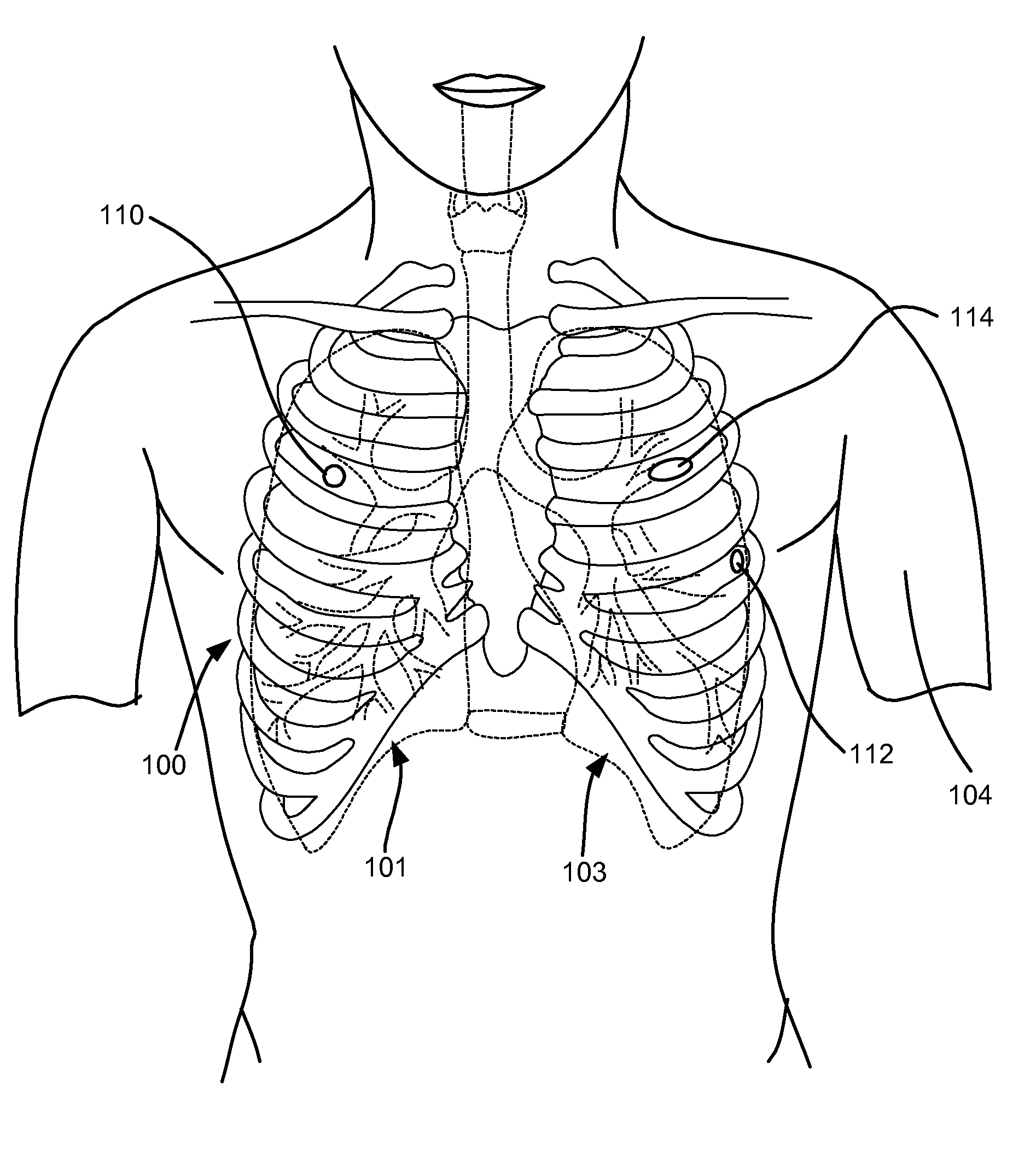
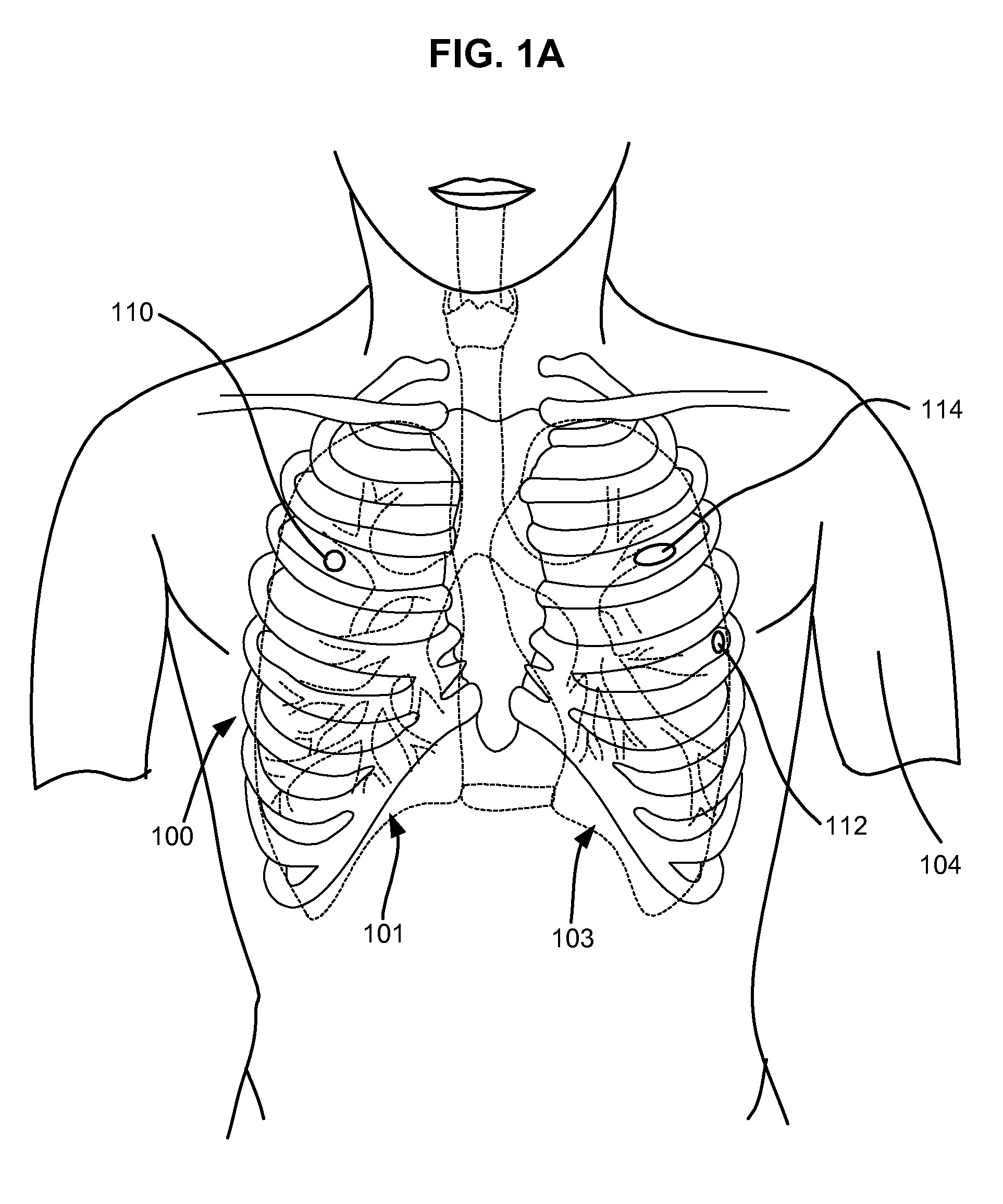
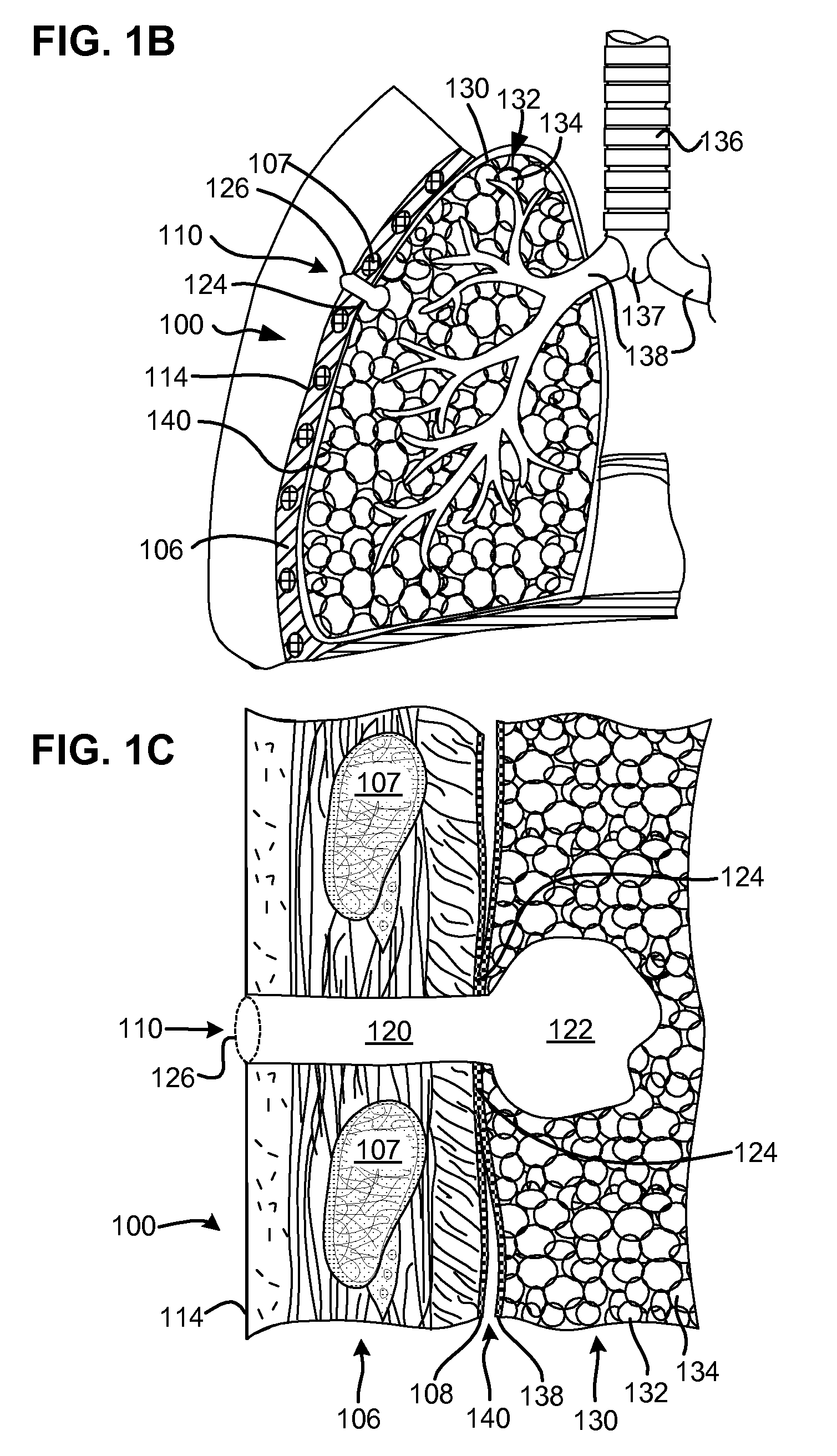
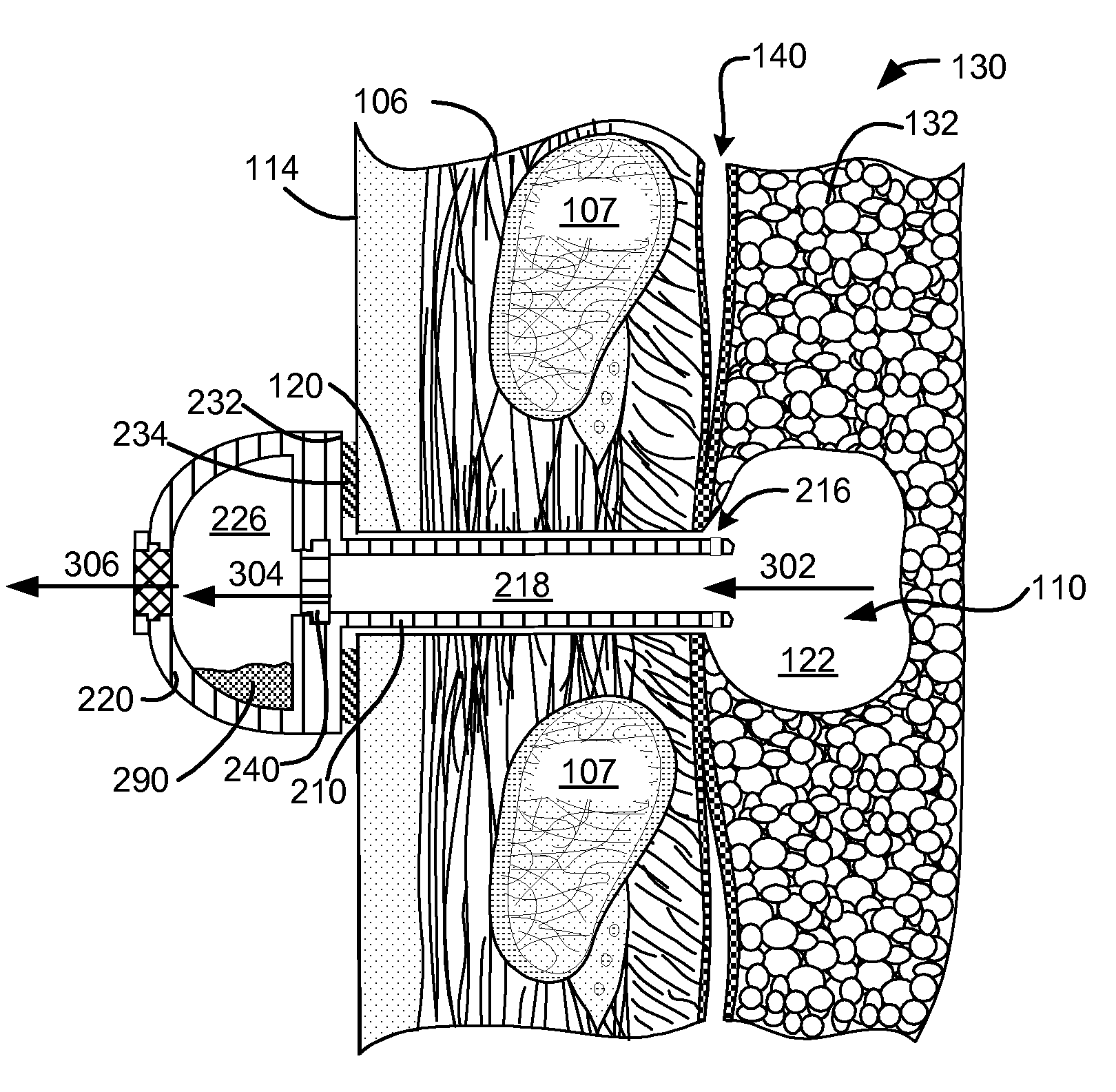
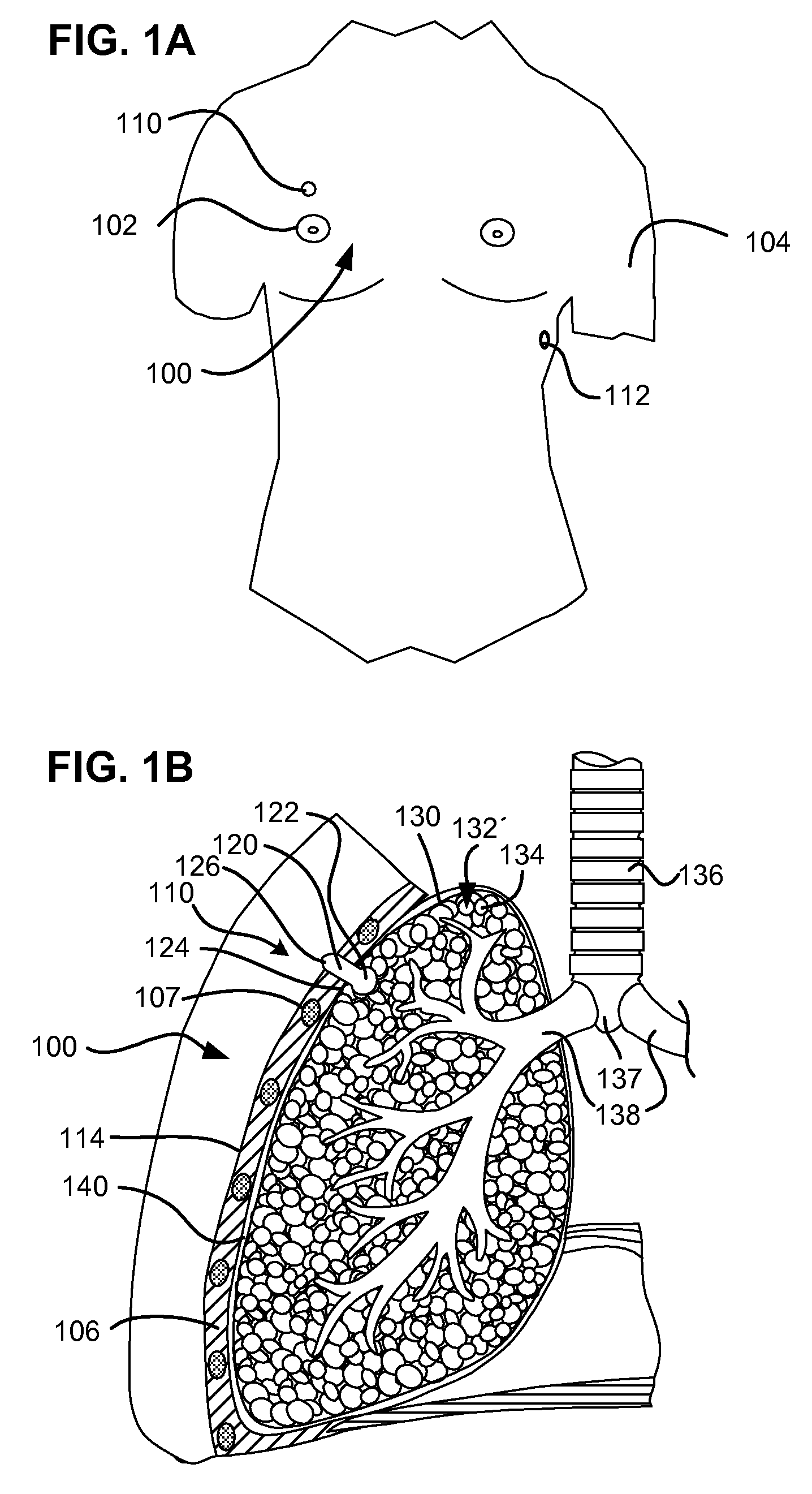
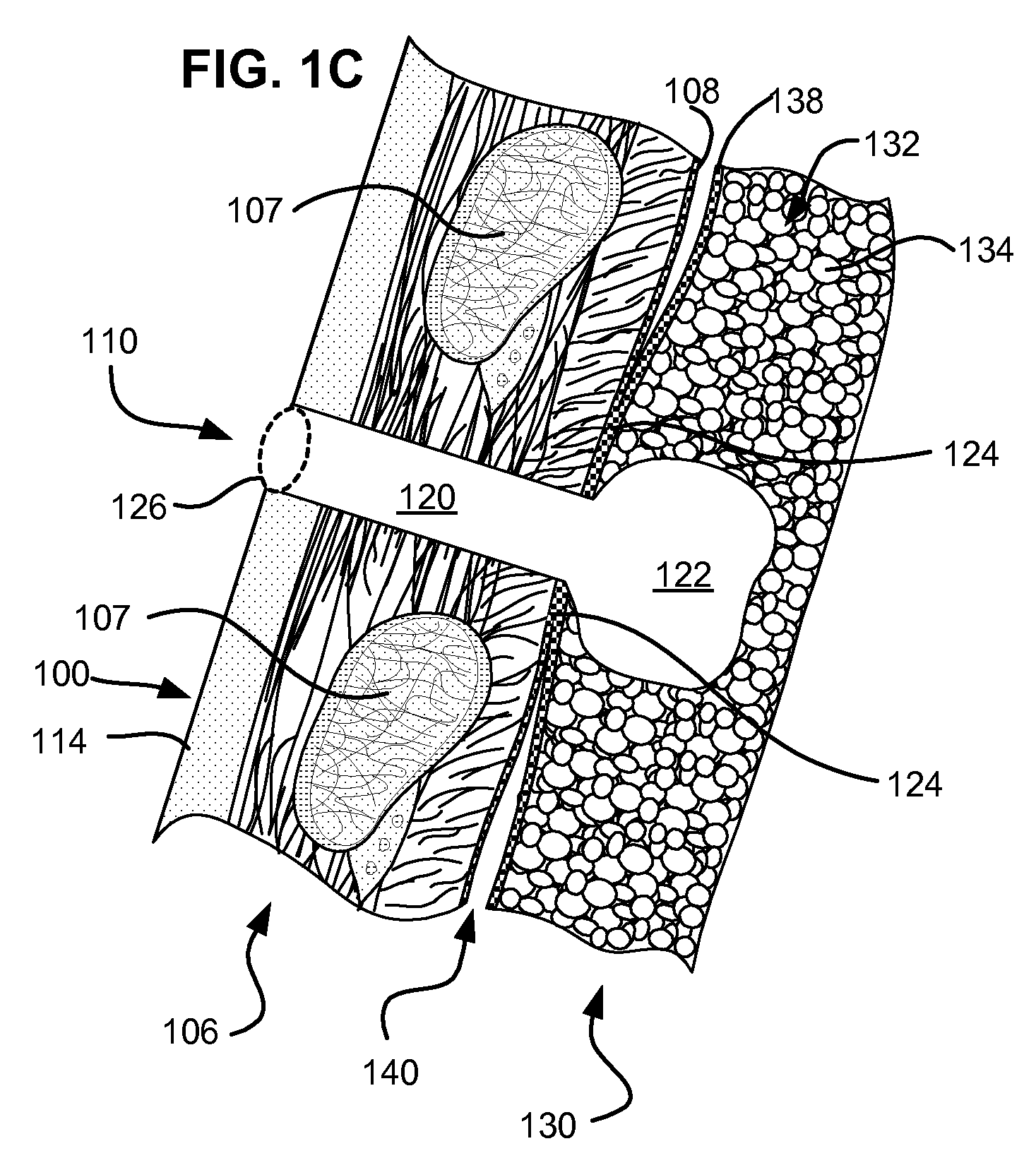
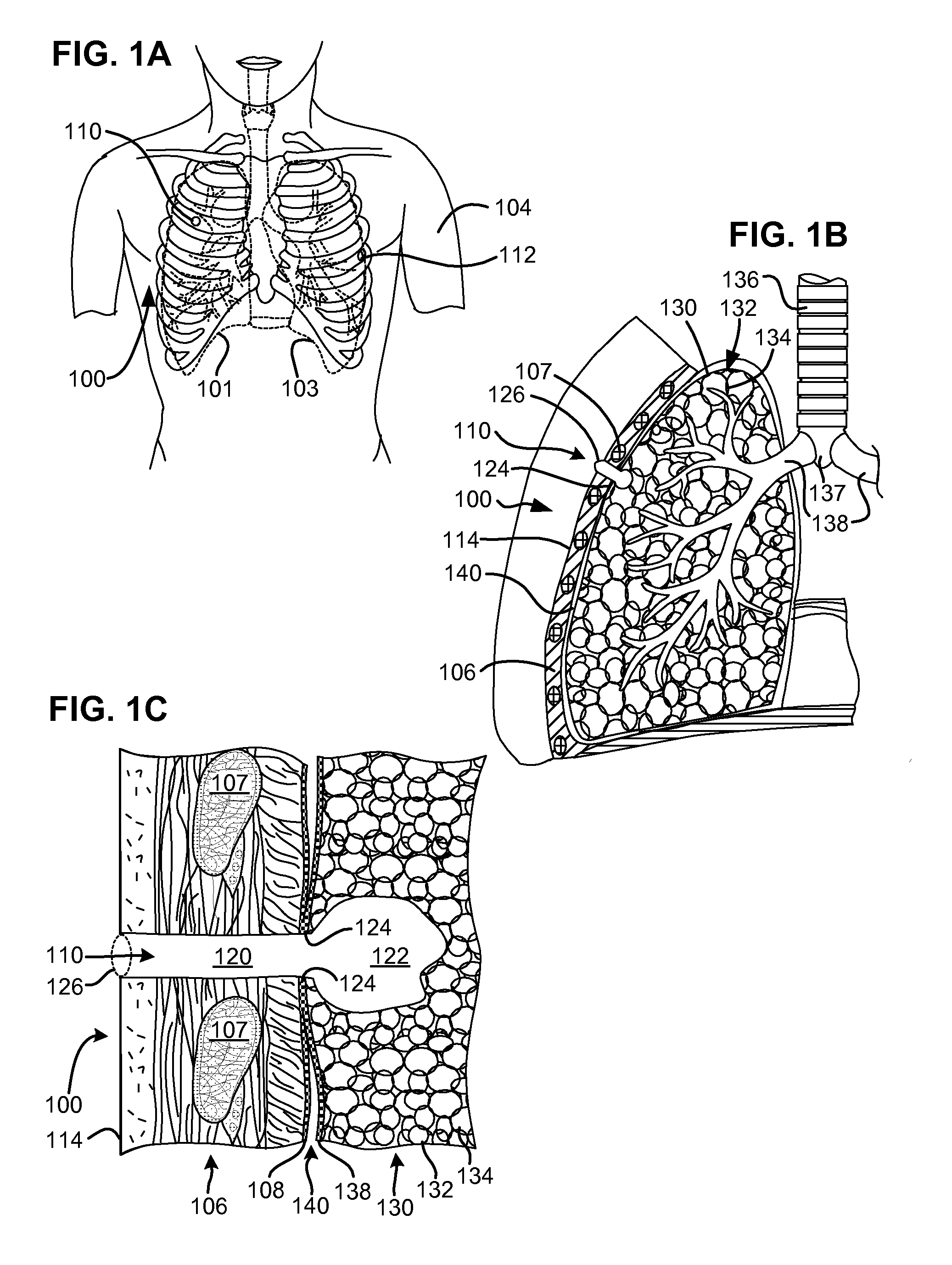
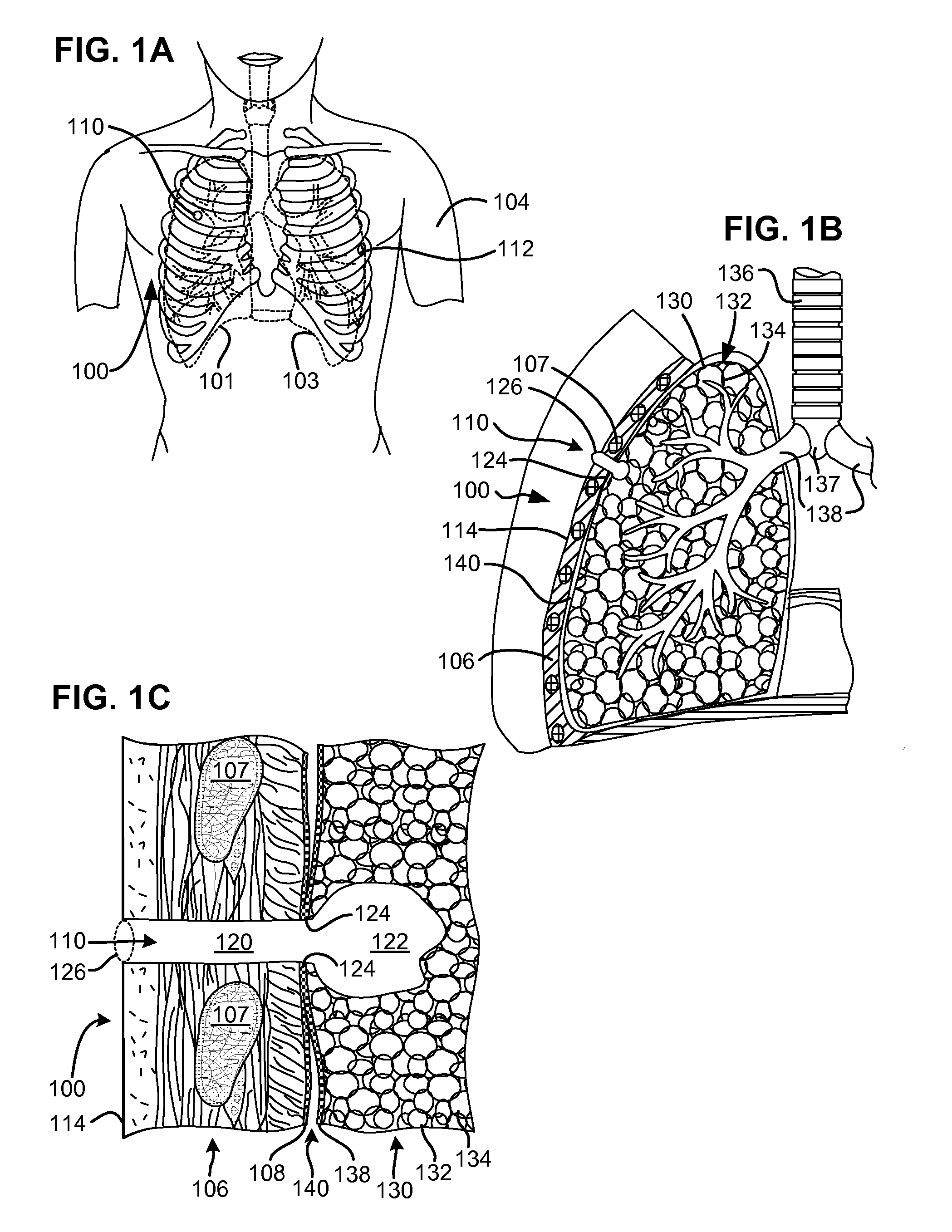
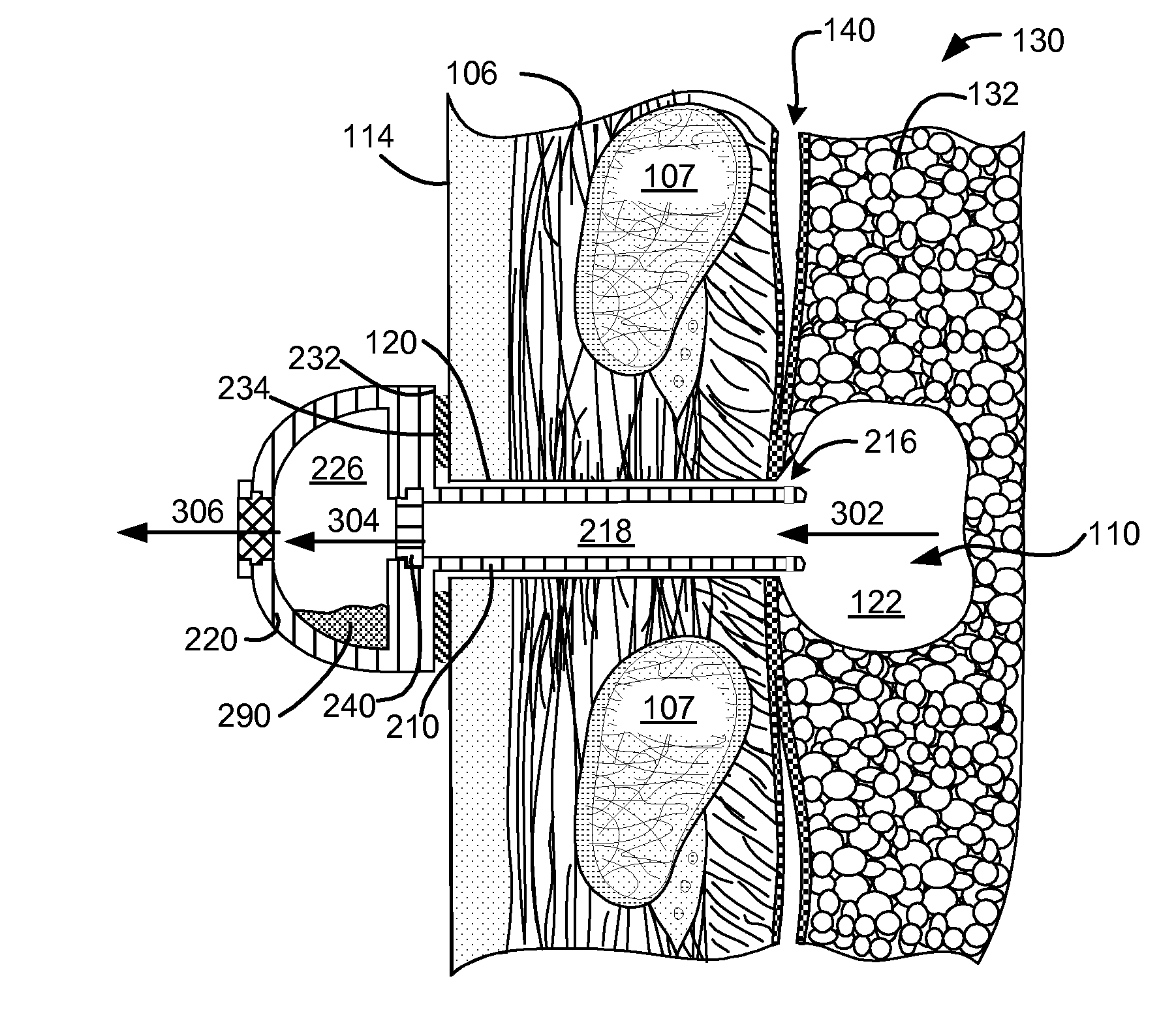
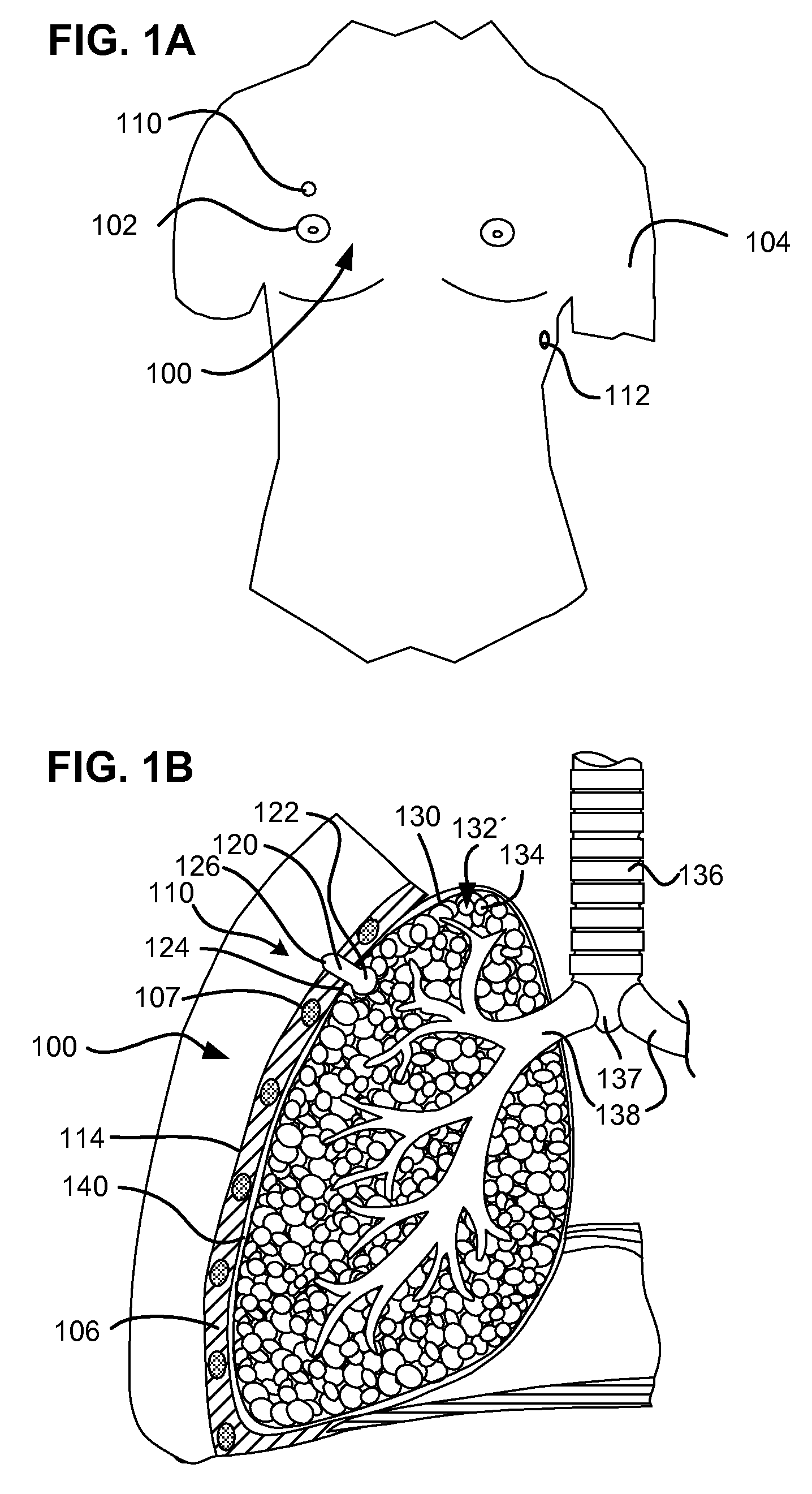
Surgical instruments for creating a pneumostoma and treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20100204707A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBalloon catheterEar treatmentSurgical instrumentPneumatocele
Surgical instruments and techniques are provided for creating a pneumostoma through the chest wall into the lung of a patient. The pneumostomy instruments and techniques may be used to create a pneumostoma which allows gases to escape from the lung through the chest wall and thereby treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:PORTAERO
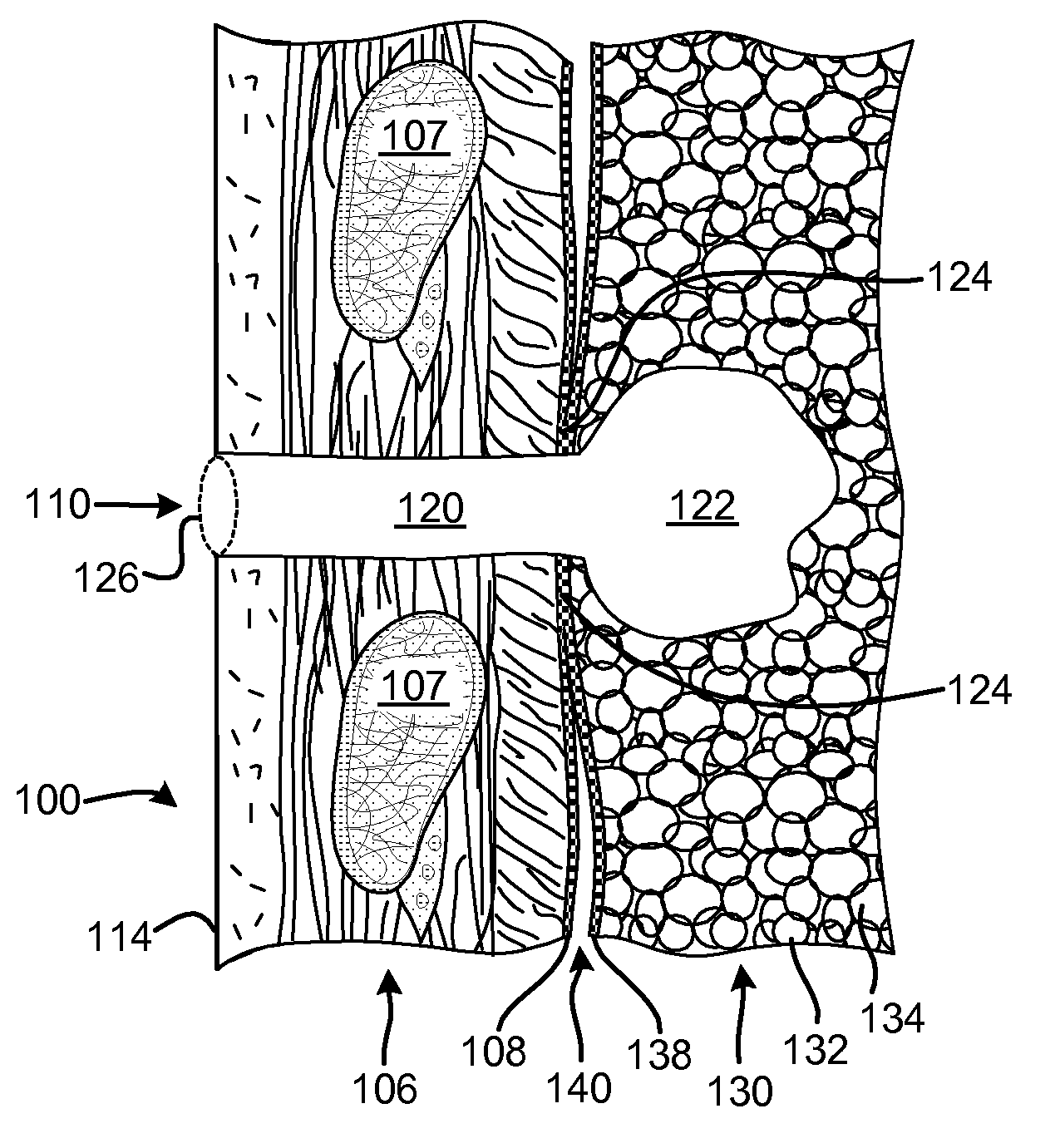
Single-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209970A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesEar treatmentBreathing masksObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesThoracic cavity
A single-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In a single-phase technique the pleurodesis is formed at the same time as the pneumostoma and does not require a separate step. The thoracic cavity is accessed to visualize the lung, the pneumostomy catheter is inserted into the lung and then the lung is secured to the channel through the chest wall creating a sealed anastomosis which matures into a pleurodesis after the procedure.
Owner:PORTAERO
Methods and devices for follow-up care and treatment of a pneumostoma
InactiveUS20090205665A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksFollow up carePneumatocele
A pneumostoma assessment and treatment system includes methods and devices for aftercare of a pneumostoma and for additional patient care utilizing a pneumostoma. The system utilizes a number of modalities to assess the health and functionality of the pneumostoma, the lungs and / or the patient as a whole. In response to an assessment of the health and functionality of the pneumostoma, lungs and patient, the tissues of pneumostoma may be treated with a treatment device and utilizing one or more different modalities to preserve or enhance the health and function of the pneumostoma and / or treat other conditions of the patient.
Owner:PORTAERO
Accelerated two-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205643A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing masksSurgeryObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesSurgical department
An accelerated two-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The first phase includes creation of a localized pleurodesis. The localized pleurodesis is created using chemical agents and / or mechanical fasteners to secure the visceral membrane to the pleural membrane. The second phase includes introduction of a surgical instrument into the lung via the pleurodesis to create the pneumostoma. The first and second phases are performed as parts of a single surgical procedure. The formation of a stable pleurodesis is to prevent pneumothorax during the procedure.
Owner:PORTAERO
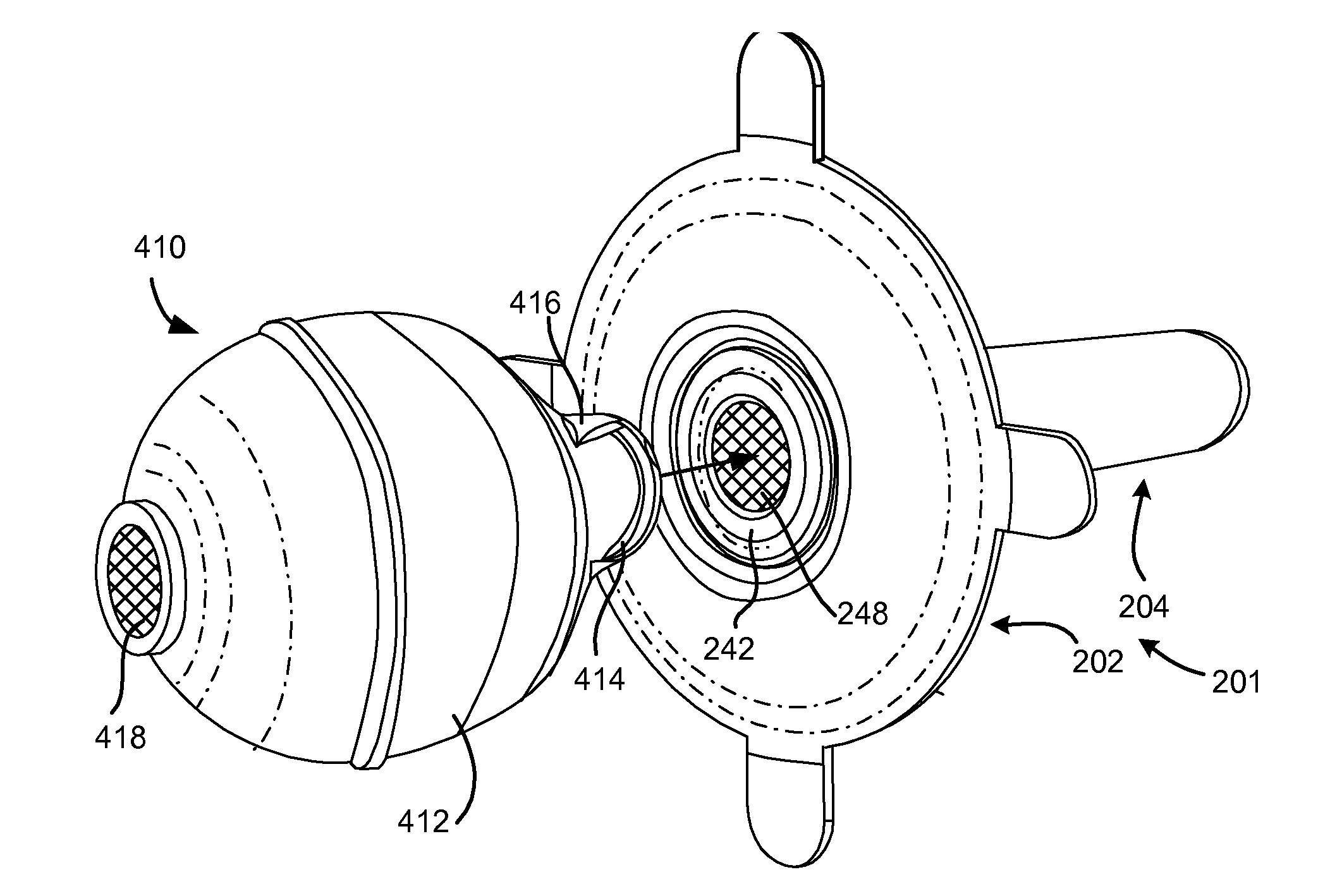
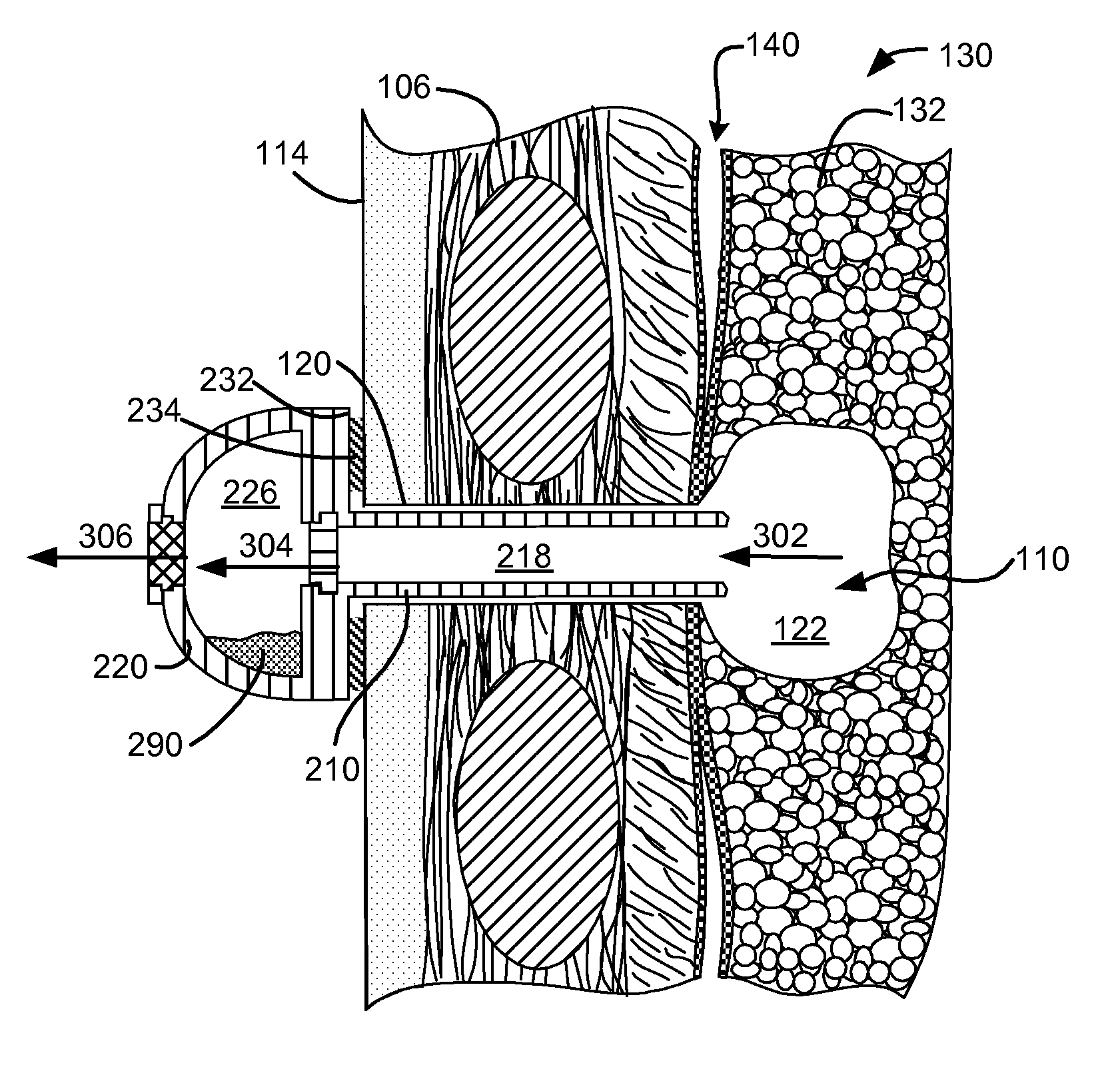
Aspirator for pneumostoma management
InactiveUS20090209917A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesEar treatmentSurgerySyringeManagement system
A pneumostoma management system includes a pneumostoma management device for maintaining the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma and a pneumostoma aspirator for pneumostoma care. The pneumostoma aspirator includes a bulb or syringe for applying positive or negative pressure, a tube for entering the pneumostoma and a limiting device for limiting the depth of insertion of the tube into a pneumostoma. The pneumostoma aspirator may also be used to introduce irrigation fluid into the pneumostoma and / or remove irrigation fluid and discharge from the pneumostoma.
Owner:PORTAERO
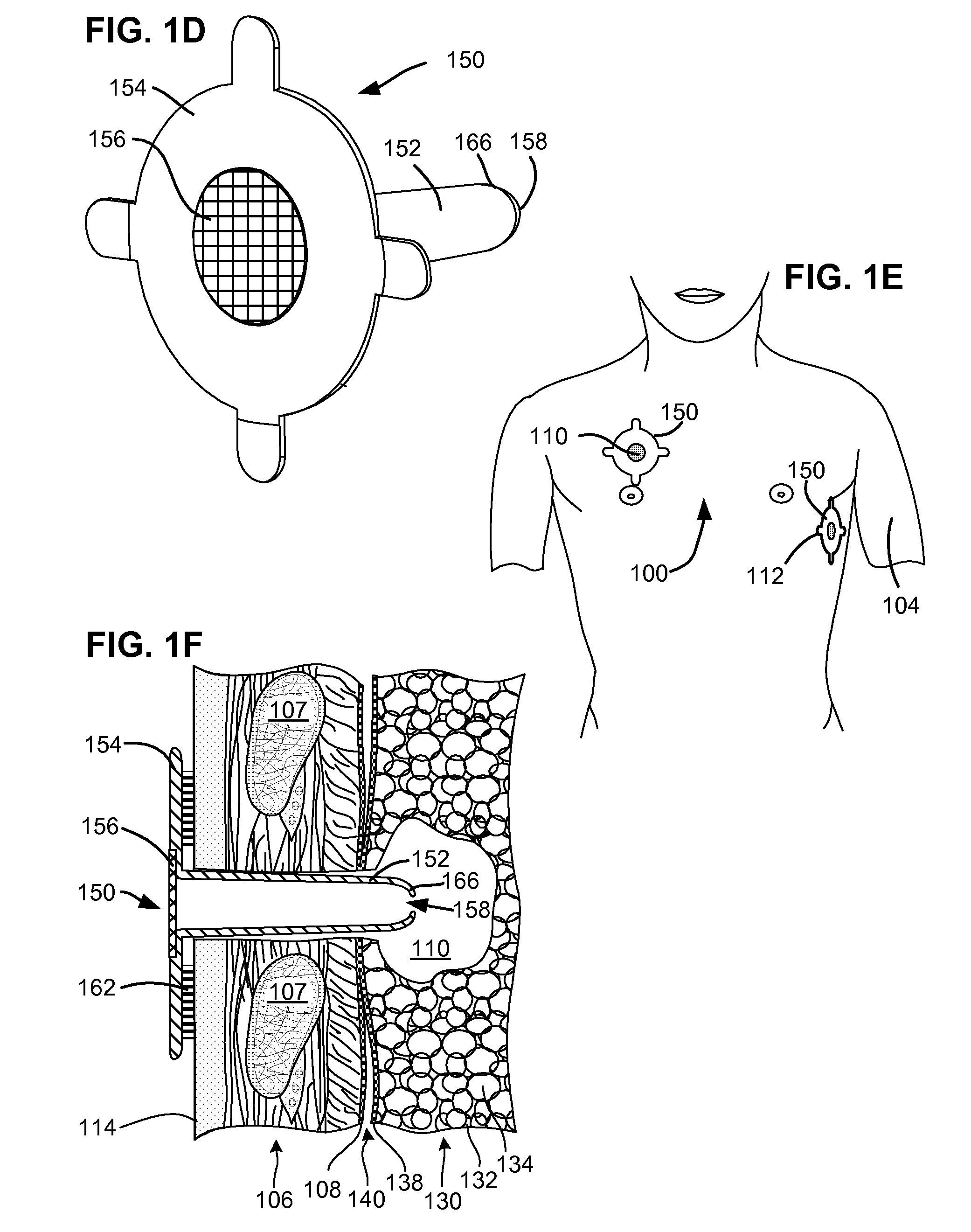
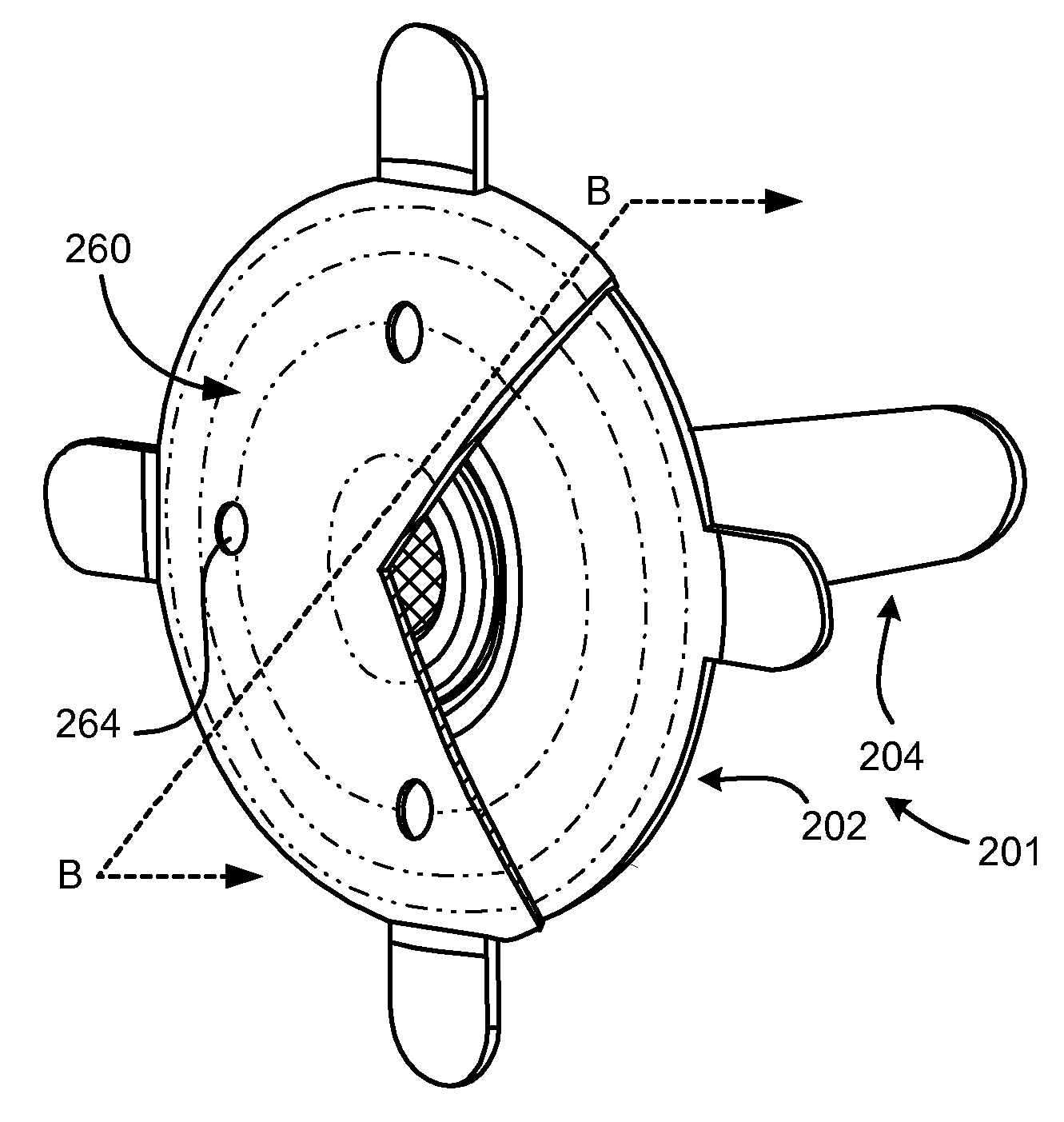
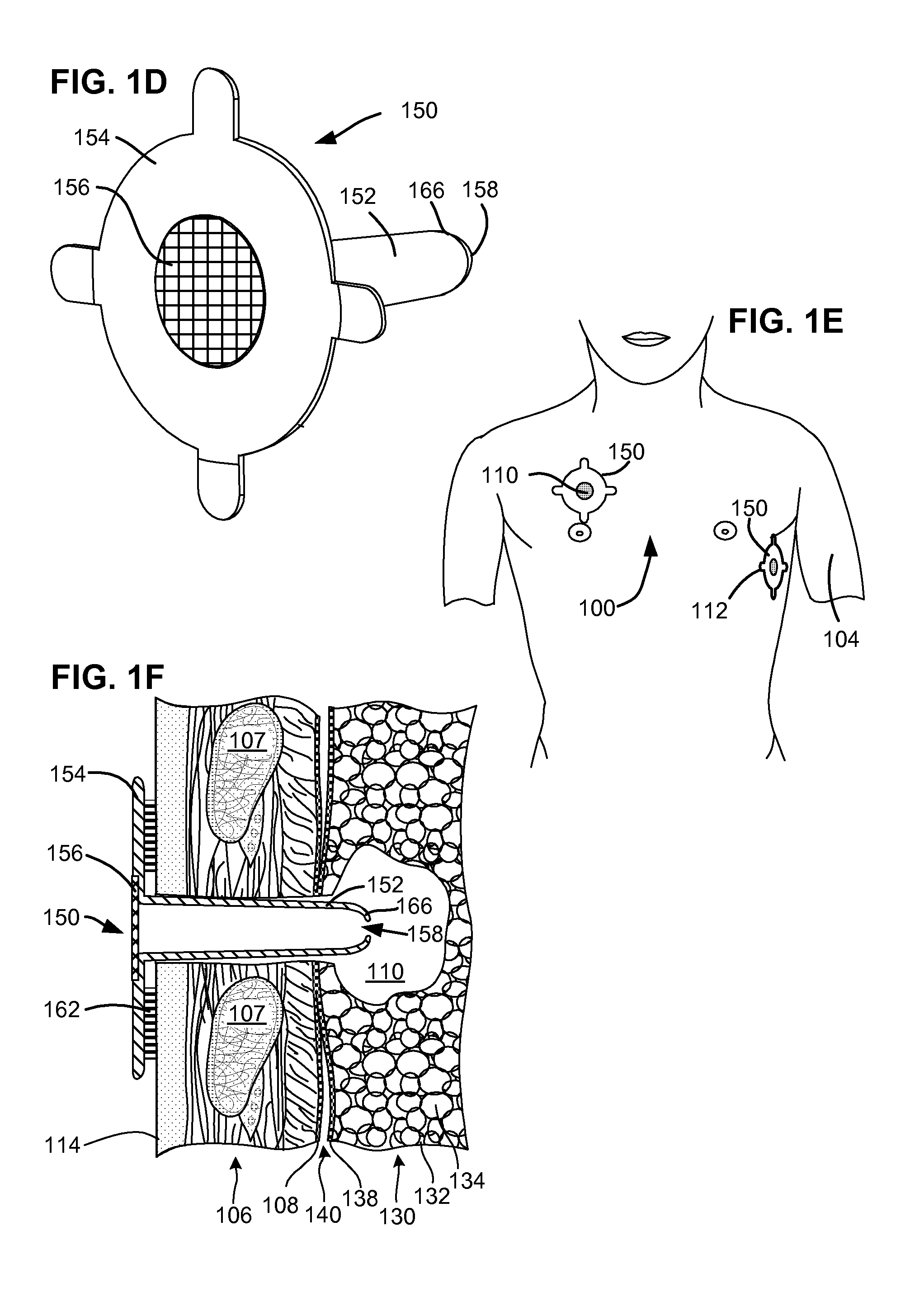
Flexible pneumostoma management system and methods for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205646A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesIntensive care medicine
A flexible pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent having a tube which enters the pneumostoma to allow gases to escape the lung, a flange and a filter / valve to control flow of materials through the tube. The flange is a thin flexible patch which conforms and attaches to the chest of the patient. The flange secures the tube in position in the pneumostoma.
Owner:PORTAERO
One-piece pneumostoma management system and methods for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205651A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesIntensive care medicine
A flexible pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent having a tube which enters the pneumostoma to allow gases to escape the lung, a flange and a filter / valve to control flow of materials through the tube. The flange is a thin flexible patch which conforms and attaches to the chest of the patient. The flange secures the tube in position in the pneumostoma. The flange is formed in one piece with the tube.
Owner:PORTAERO
Devices and methods for delivery of a therapeutic agent through a pneumostoma
InactiveUS20090205658A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesLiquid surface applicatorsPowdered material dispensingCollateral ventilationPositive pressure
A pneumostoma management system includes a pneumostoma management device for maintaining the patency of a pneumostoma and a drug delivery device for pneumostoma care. The drug delivery device includes a therapeutic agent dispenser for supplying a therapeutic agent and a propellant at positive pressure, a tube for entering the pneumostoma and a limiting device for limiting the depth of insertion of the tube into a pneumostoma. The drug delivery device may be used to introduce therapeutic agents into the pneumostoma for direct treatment of the pneumostoma, treatment of the lung by way of collateral ventilation, and / or treatment of non-lung tissues by diffusion into the bloodstream.
Owner:PORTAERO
Compositions and methods for treating cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases and disorders with apelin
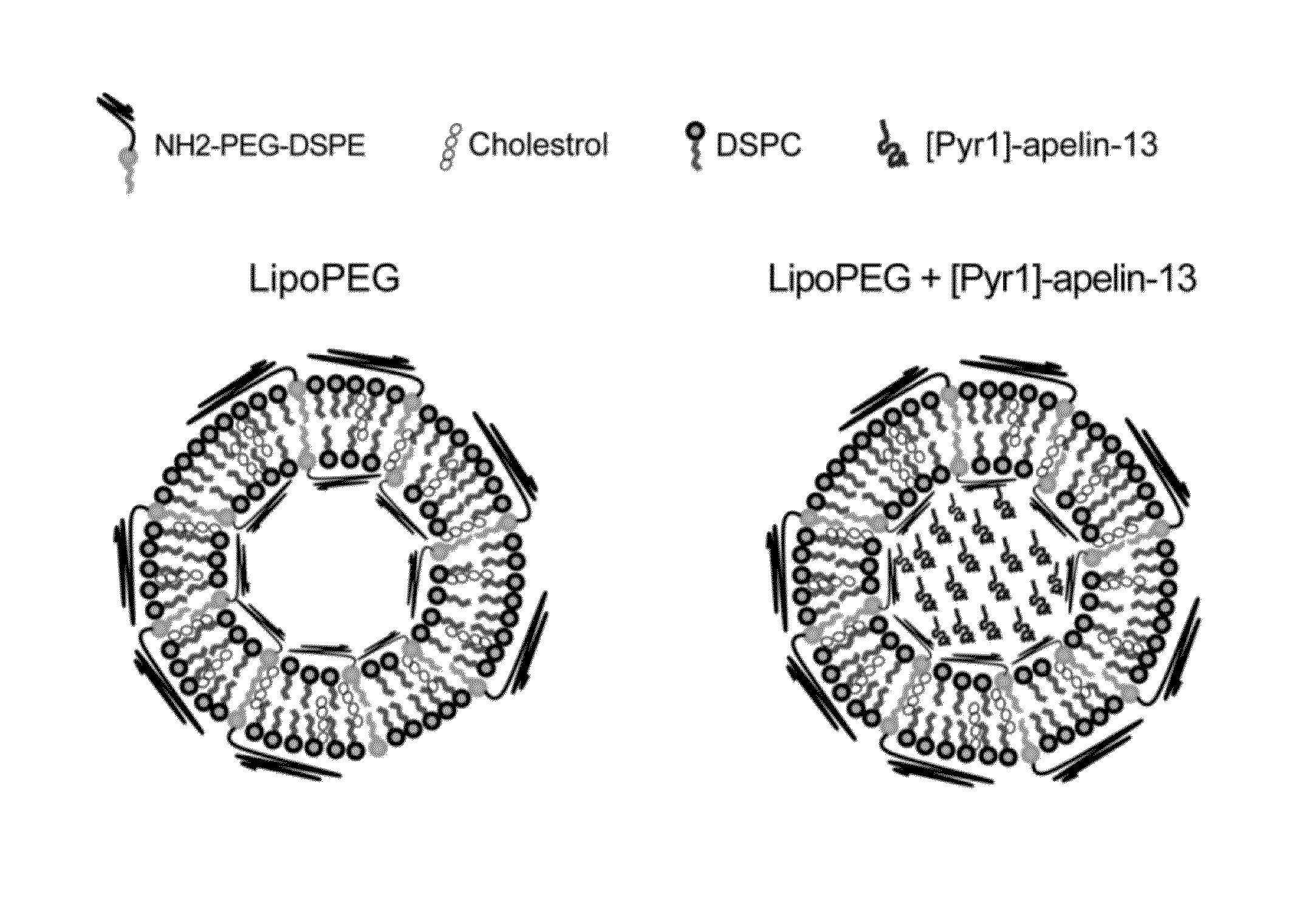
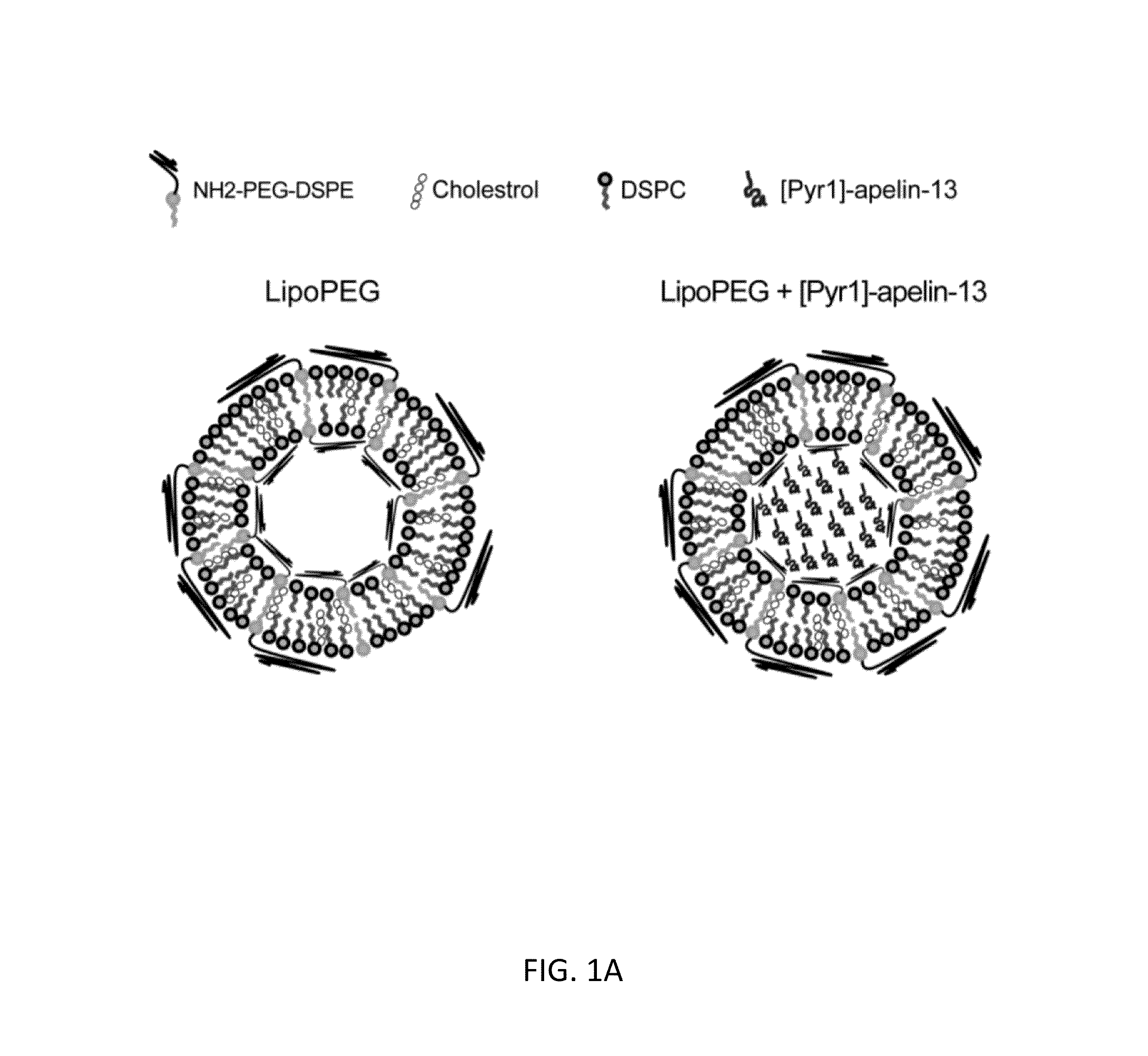
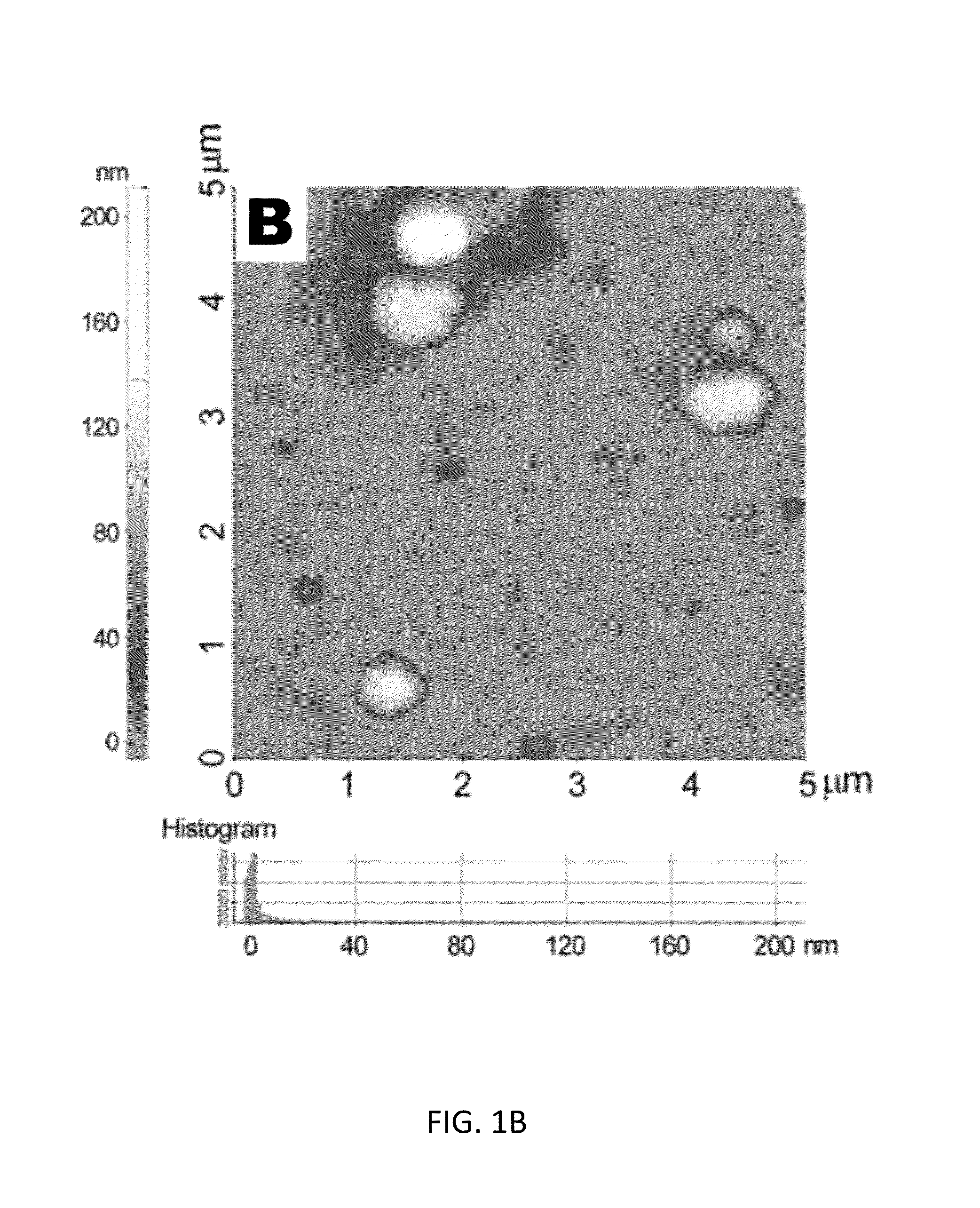
InactiveUS20160058705A1Improve stabilityPromote recoveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseNanocarriers
Compositions and methods for treating cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases and disorders with apelin are disclosed. In particular, the invention relates to formulations comprising apelin encapsulated in liposome nanocarriers conjugated with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and their use in treatment of cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases and disorders. Encapsulation of apelin in PEG-conjugated liposomes significantly enhances efficacy, improves cellular uptake of apelin, and allows for sustained and extended release of apelin under physiological conditions.
Owner:RAJADAS JAYAKUMAR +2
Percutaneous single-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209909A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesSuture equipmentsStapling toolsPleural cavityPleural part
A percutaneous single-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A pneumostomy instrument is introduced percutaneously through the thoracic wall, parietal membrane, visceral membrane and into the parenchymal tissue of the lung. The pneumostomy instrument crosses the pleural cavity between the parietal membrane and visceral membrane there being no pleurodesis between the membranes prior to passage of the pneumostomy instrument. A pneumoplasty device at the distal end of the pneumostomy instrument displaces and engages the parenchymal tissue of the lung and the pneumostomy instrument is used to secure the lung and visceral membrane in contact with the parietal membrane and chest wall. The pneumostomy instrument is left in place while a pneumostoma tract heals and pleurodesis occurs between the pleural membranes surrounding the pneumostomy instrument.
Owner:PORTAERO
Self-sealing device and method for delivery of a therapeutic agent through a pneumostoma
InactiveUS20090209906A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesRespiratorsStentsCollateral ventilationPositive pressure
A pneumostoma management system includes a pneumostoma management device for maintaining the patency of a pneumostoma and a drug delivery device for pneumostoma care. The drug delivery device may be used to introduce therapeutic agents into the pneumostoma for direct treatment of the pneumostoma, treatment of the lung by way of collateral ventilation, and / or treatment of non-lung tissues by diffusion into the bloodstream. The drug delivery device includes a therapeutic agent dispenser for supplying a therapeutic agent and a propellant at positive pressure, an outlet and a connector for correctly positioning the outlet relative to a pneumostoma management device. The drug delivery device includes a self-centering and self-sealing connector for engaging the pneumostoma management device.
Owner:PORTAERO
Variable length pneumostoma management system for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205650A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesVariable length
A flexible pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes flange attaches to the chest of the patient to secure the device in position. The pneumostoma management device also includes a tube which enters the pneumostoma to allow gases to escape the lung. The length of the tube is selected to match the dimensions of the pneumostoma of a patient. In order to manufacture devices having different tube lengths, the tube is formed at a longer length than required, cut to size and tipped. The tube may be formed by molding or extrusion.
Owner:PORTAERO
Surgical instruments for creating a pneumostoma and treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS8518053B2Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBalloon catheterEar treatmentObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesPneumatocele
Surgical instruments and techniques are provided for creating a pneumostoma through the chest wall into the lung of a patient. The pneumostomy instruments and techniques may be used to create a pneumostoma which allows gases to escape from the lung through the chest wall and thereby treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:PORTAERO
Pneumostoma management system with secretion management features for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205648A1StableStable artificial apertureBreathing filtersBreathing masksManagement systemPneumatocele
A flexible pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent having a tube which enters the pneumostoma to allow gases to escape the lung, a flange and a filter / valve to control flow of materials through the tube. The flange is a thin flexible patch which conforms and attaches to the chest of the patient. The flange secures the tube in position in the pneumostoma. The device has features to control secretions from the pneumostoma. The secretion management features include, ridges, pores, absorbent materials, and combinations thereof.
Owner:PORTAERO
Multi-layer pneumostoma management system and methods for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205649A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksThin layerObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
A flexible pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent having a tube which enters the pneumostoma to allow gases to escape the lung, a flange and a filter / valve to control flow of materials through the tube. The flange is a thin flexible patch comprises of multiple thin layers of materials and which conforms and attaches to the chest of the patient. The flange includes a filter, a protective outer layer and an inner hydrocolloid layer. The flange secures the tube in position in the pneumostoma.
Owner:PORTAERO
Pneumostoma management method for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205645A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing masksSurgeryMedicineObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
A method for maintaining the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. A pneumostoma management system includes a two-part pneumostoma management device and associated insertion and removal tools. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent and a chest mount for positioning and securing the vent into a pneumostoma. To use the system, the chest is first cleaned and the chest mount secured to the chest adjacent the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma vent is then inserted into the pneumostoma through an aperture in the chest mount until it is engaged and secured by a coupling of the chest mount. The pneumostoma vent may be replaced periodically such as daily. The chest mount may be changed less frequently such as weekly.
Owner:PORTAERO
Two-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209856A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesRespiratorsStentsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesSurgical department
A two-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease The first phase is a procedure to induce creation of a localized pleurodesis and is preferably performed as an outpatient procedure. The second phase is a procedure to introduce a surgical instrument into the lung via the pleurodesis to create the pneumostoma. An interval of about one of more days between the first and second phases allows the formation of a stable pleurodesis to prevent pneumothorax during the procedure.
Owner:PORTAERO
Pneumostoma management system having a cosmetic and/or protective cover
InactiveUS20090205647A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksPatient complianceManagement system
Owner:PORTAERO
Aspirator and method for pneumostoma management
InactiveUS20090209936A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesSurgeryMedical devicesMedicineIrrigation fluids
A method for treating a pneumostoma by applying suction to the pneumostoma in order to remove solid or liquid discharge. A pneumostoma aspirator including a bulb or syringe is used to apply negative pressure to a tube which enters the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma aspirator may be used in conjunction with a pneumostoma management device. Alternatively, the pneumostoma aspirator may be used after the pneumostoma management device has been removed. The pneumostoma aspirator may also be used to introduce irrigation fluid into the pneumostoma and / or remove irrigation fluid and discharge from the pneumostoma.
Owner:PORTAERO
Pneumostoma management device and method for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205641A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesElectrotherapyBreathing filtersObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesIntensive care medicine
A pneumostoma management device for maintaining the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of gases and discharge through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes a bulb connected to a tube which enters the pneumostoma. A flow control device regulates air flow in and out of the pneumostoma via the tube. A hydrophobic filter traps discharge in the bulb while allowing gases to escape.
Owner:PORTAERO
Pneumostoma management system for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090205644A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesBreathing filtersBreathing masksObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesIntensive care medicine
A pneumostoma management system for maintaining the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management system includes a two-part pneumostoma management device and associated insertion and removal tools. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent and a chest mount for positioning and securing the vent into a pneumostoma. The pneumostoma vent includes a hydrophobic filter and / or a one-way valve.
Owner:PORTAERO
Surgical instruments for creating a pneumostoma and treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209971A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesEar treatmentMedical devicesObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesPneumatocele
Surgical instruments and techniques are provided for creating a pneumostoma through the chest wall into the lung of a patient. The pneumostomy instruments and techniques may be used to create a pneumostoma which allows gases to escape from the lung through the chest wall and thereby treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:PORTAERO
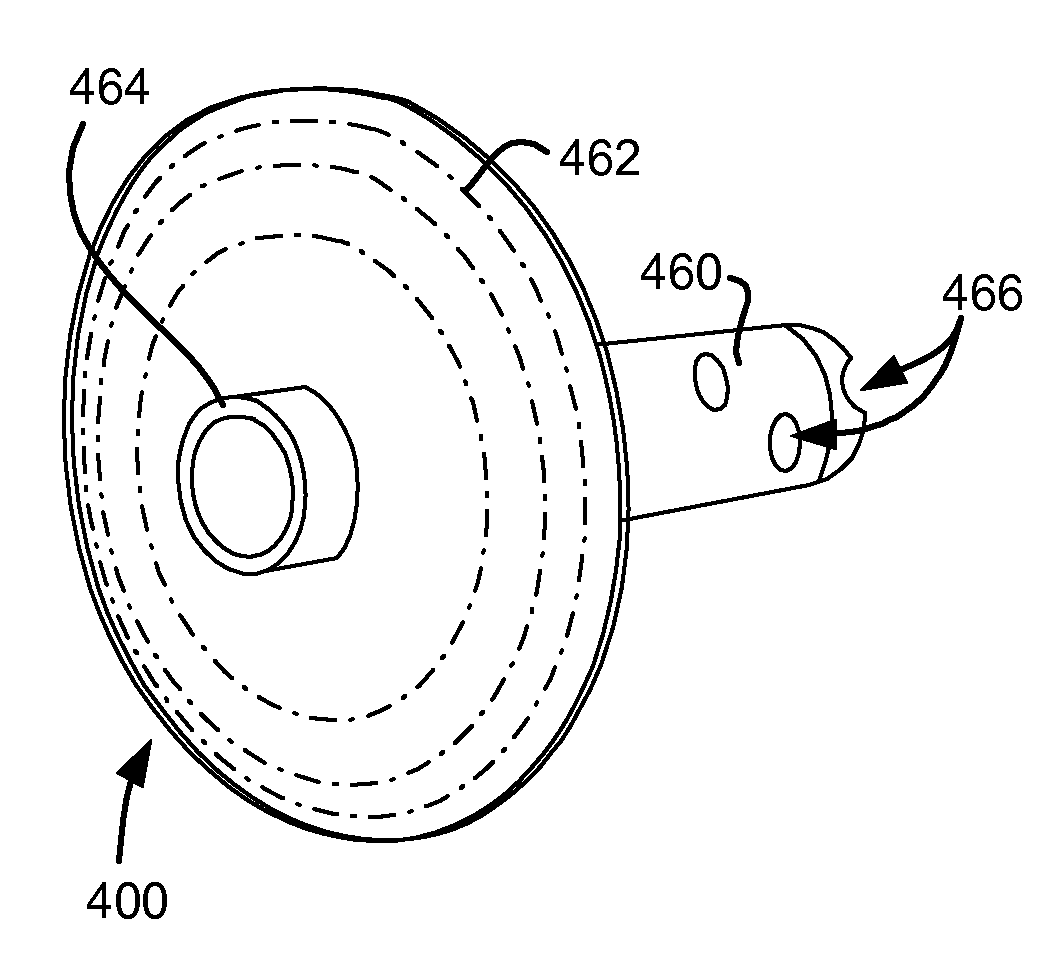
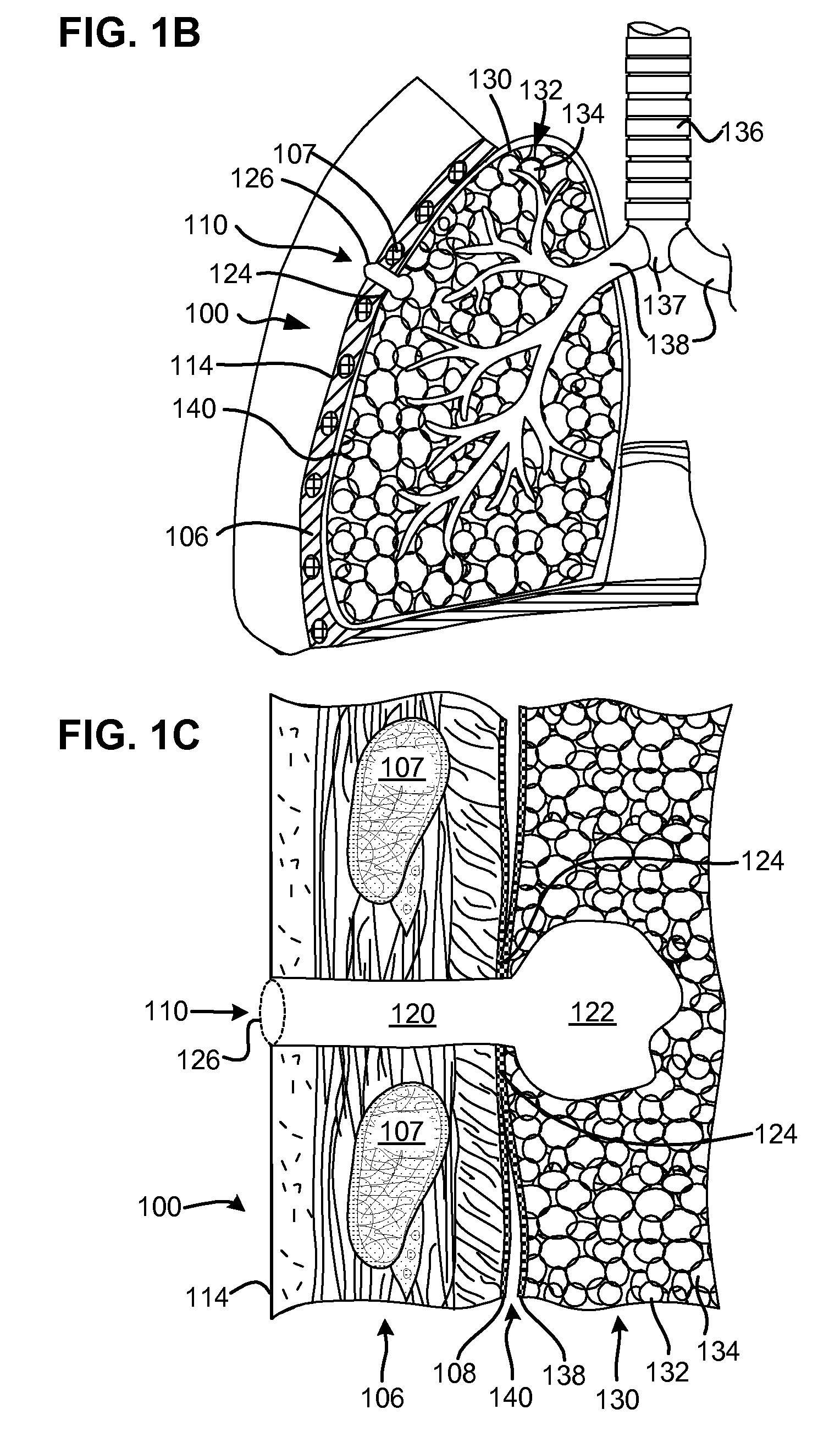
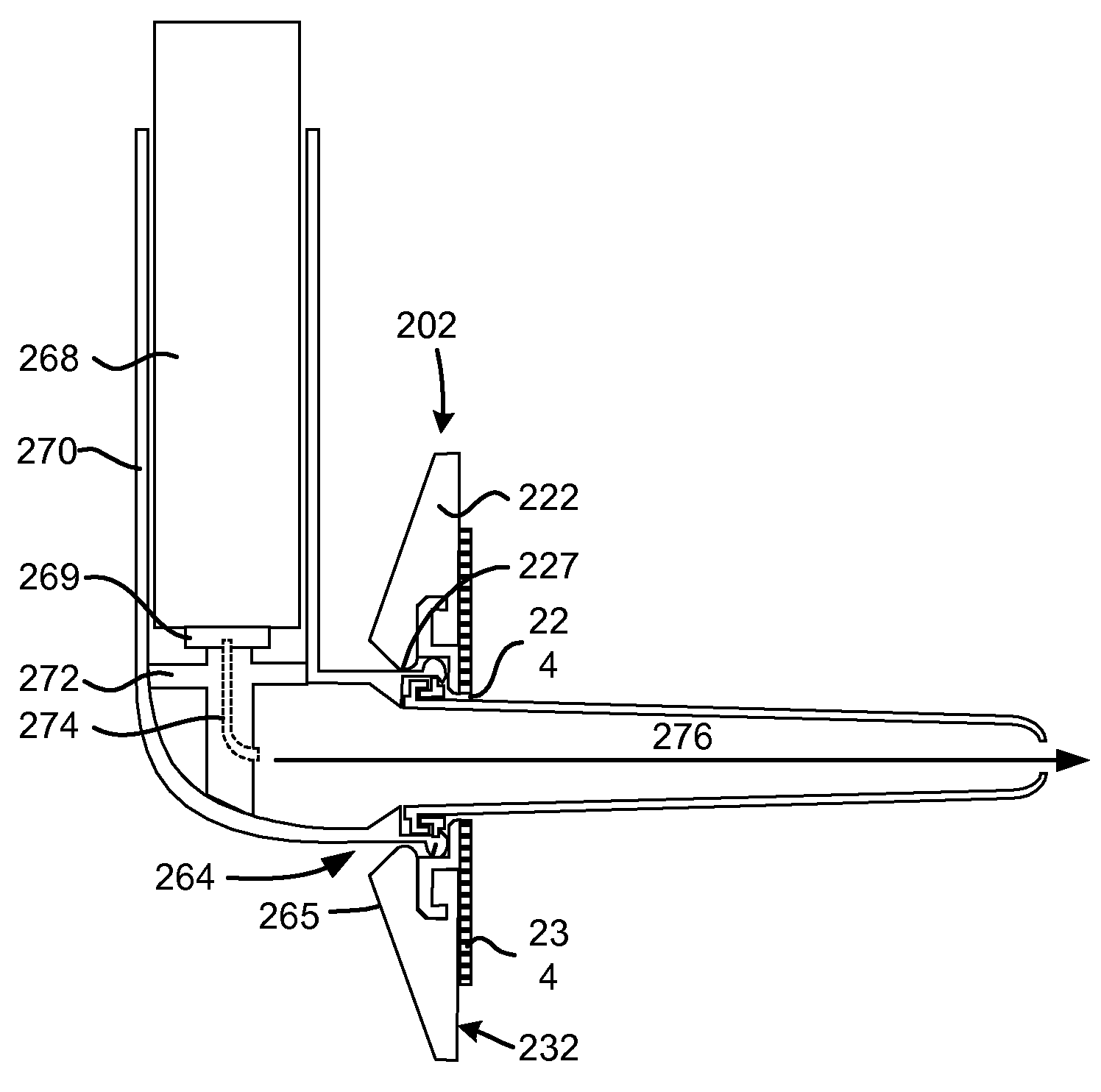
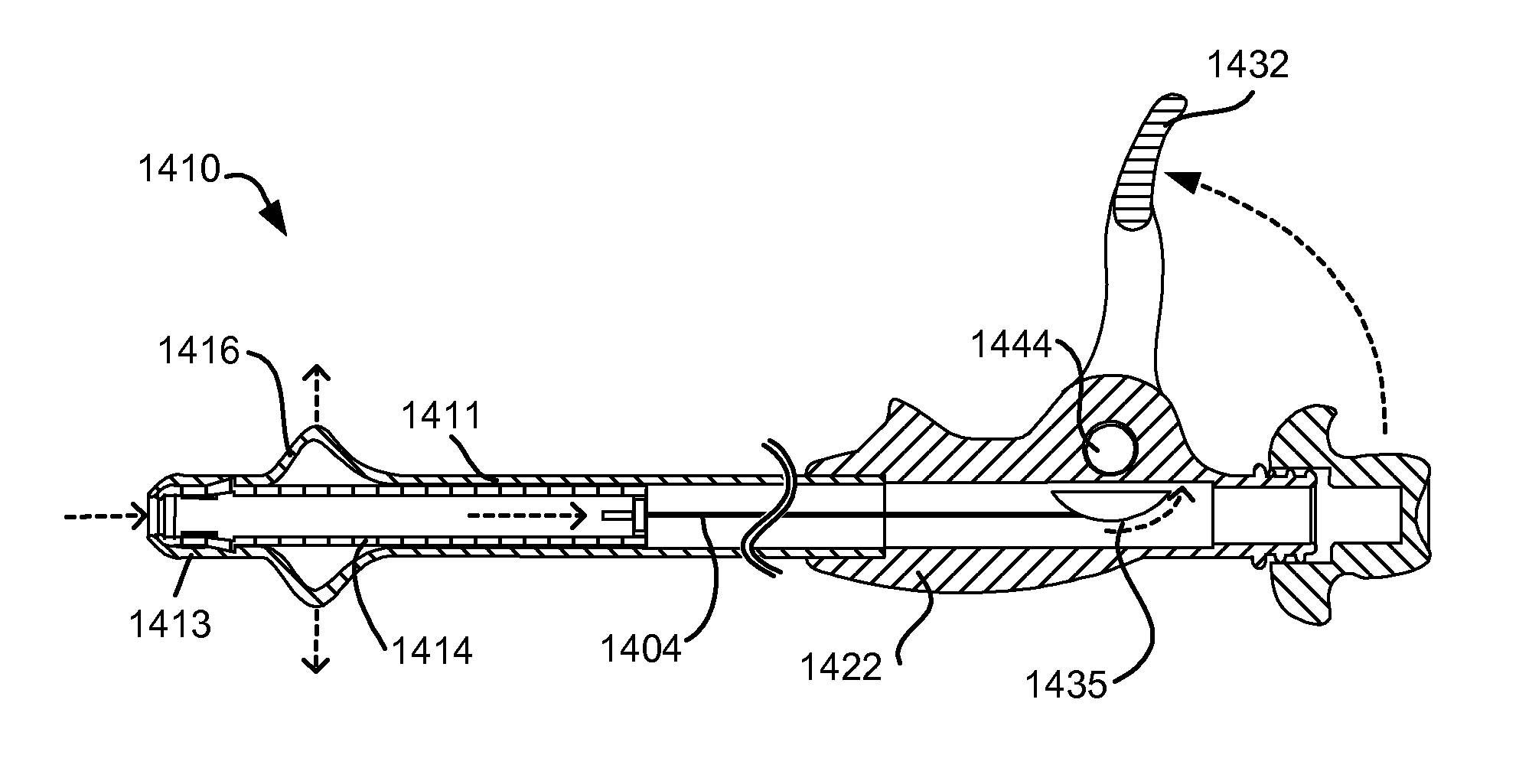
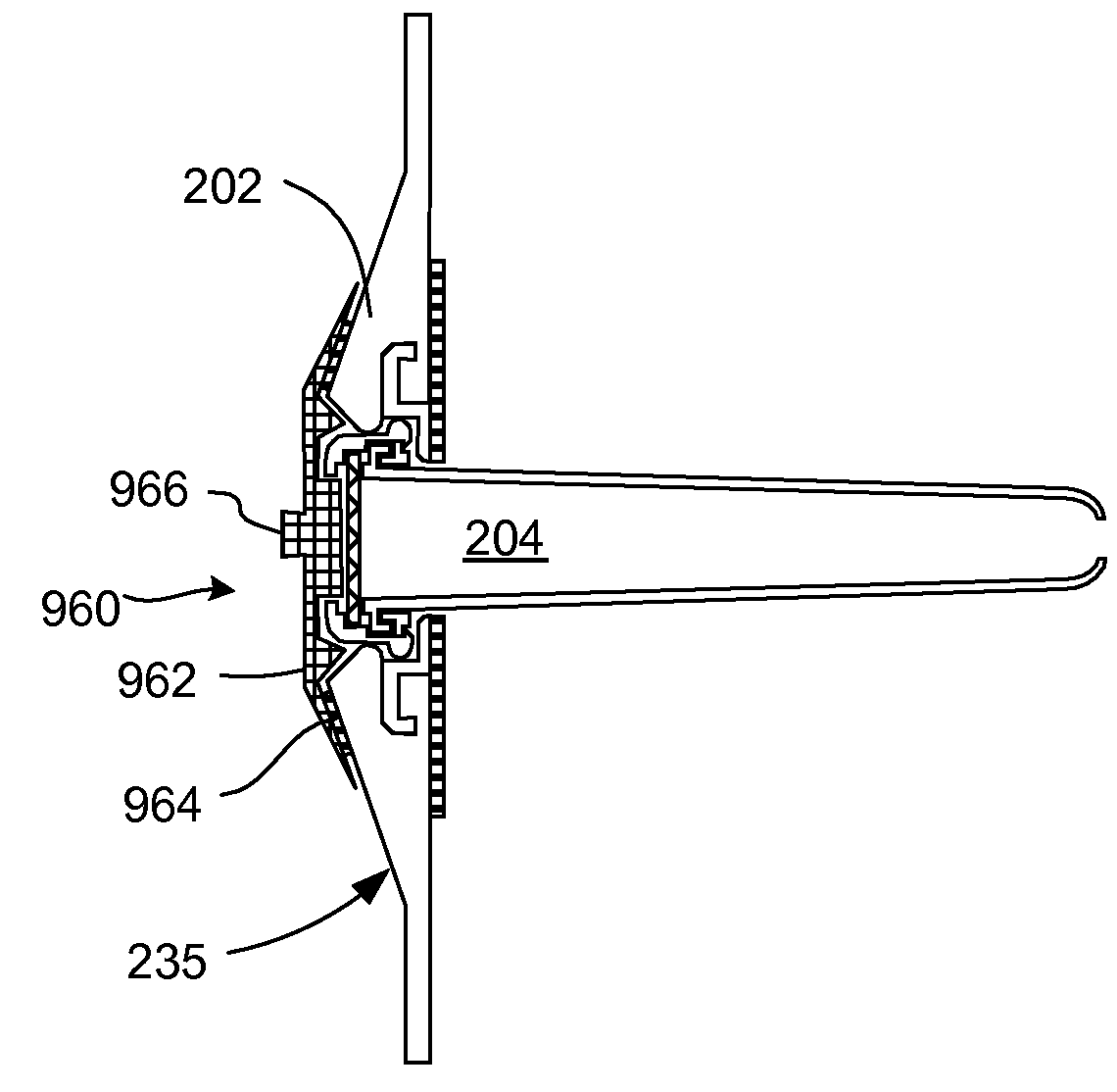
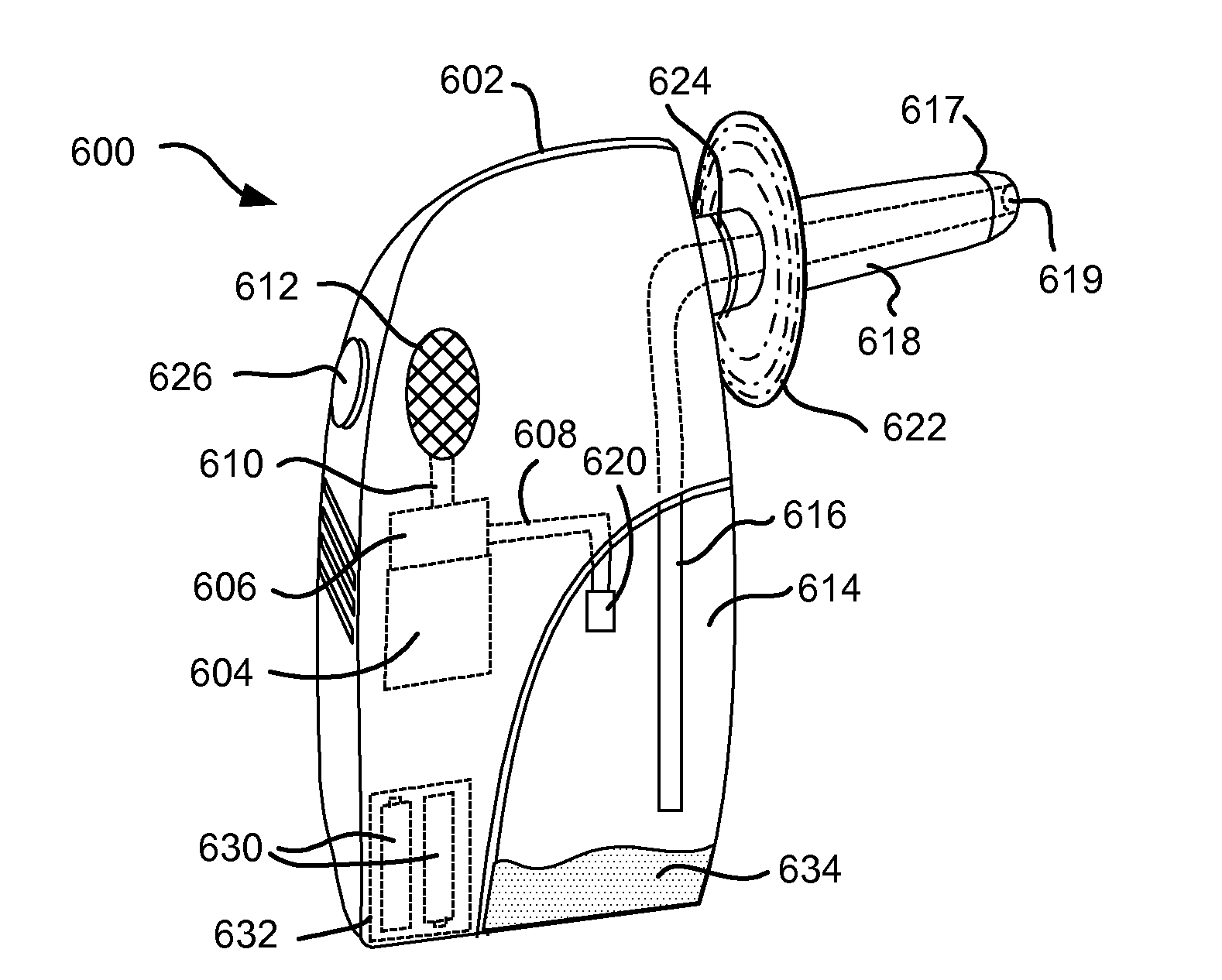
Enhanced pneumostoma management device and methods for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209924A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesRespiratorsStentsIrritationObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
A partially-implantable pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. A tube of the pneumostoma management device is placed through the chest wall into the lung. The tube comprises a plurality of holes in the distal end to allow the entry of gases and non-gaseous discharge from the lung. A contact surface prevents over-insertion of the tube while releasably securing the device to the chest of the patient. The contact surface has features to reduce irritation of the skin of the chest.
Owner:PORTAERO
Methods and devices for follow-up care and treatment of a pneumstoma
InactiveUS20110180064A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBronchoscopesFollow up careTreatment modality
A pneumostoma assessment and treatment system includes methods and devices for aftercare of a pneumostoma and for additional patient care utilizing a pneumostoma. The system utilizes a number of modalities to assess the health and functionality of the pneumostoma, the lungs and / or the patient as a whole. In response to an assessment of the health and functionality of the pneumostoma, lungs and patient, the tissues of pneumostoma may be treated with a treatment device and utilizing one or more different modalities to preserve or enhance the health and function of the pneumostoma and / or treat other conditions of the patient. Particular treatment modalities may be utilized to reduce tissue growth in and around the pneumostoma in order to prevent stenosis and maintain patency of the pneumostoma.
Owner:PORTAERO
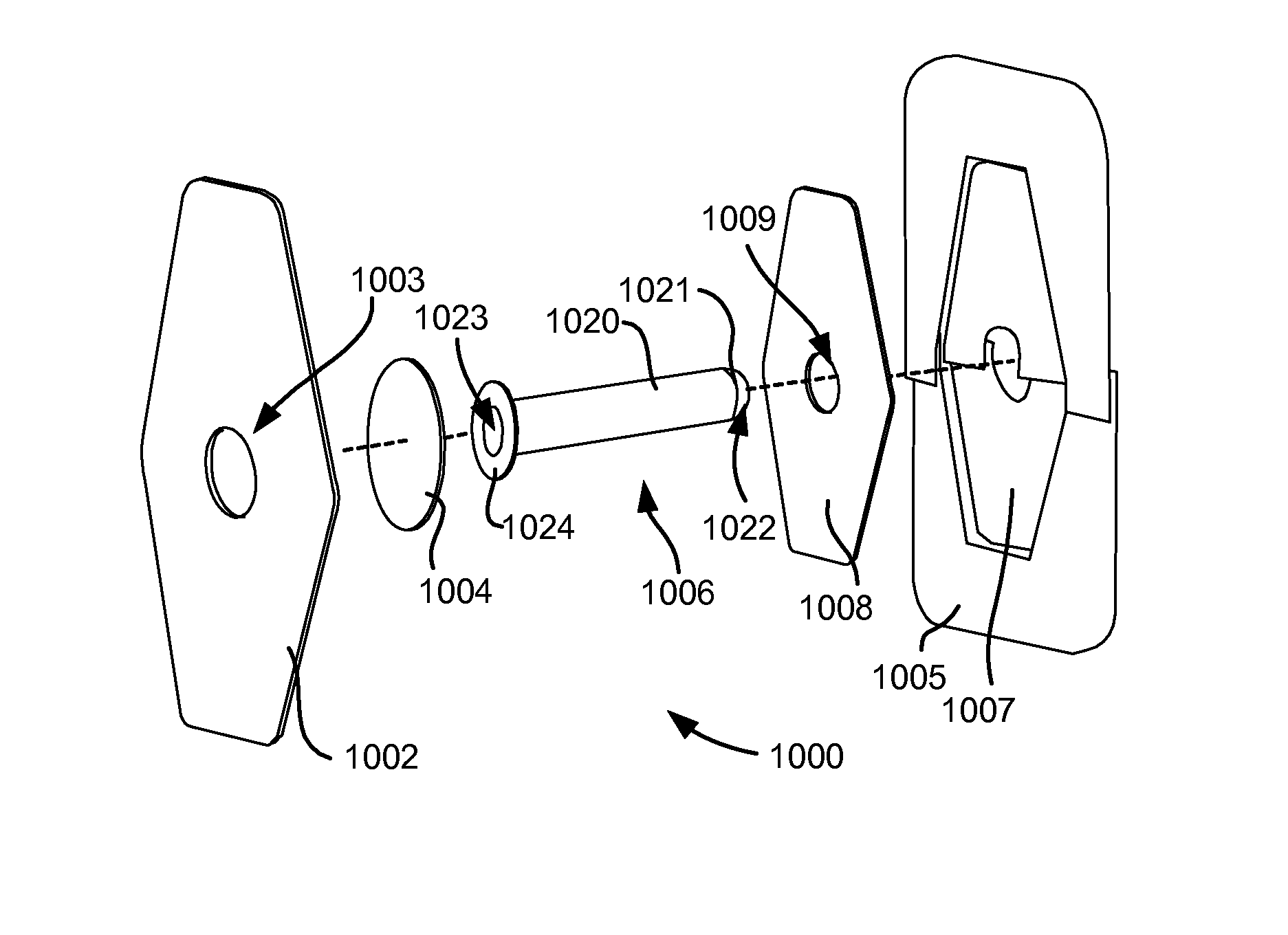
Pneumostoma management device with integrated patency sensor and method
InactiveUS8347881B2Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesElectrotherapyRespiratory device testingEngineeringPneumatocele
A flexible pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. The pneumostoma management device includes a pneumostoma vent having a tube which enters the pneumostoma to allow gases to escape the lung, a flange and a filter / valve to control flow of materials through the tube. The flange is a thin flexible patch comprises of multiple thin layers of materials and which conforms and attaches to the chest of the patient. The flange includes a filter, a protective outer layer and an inner hydrocolloid layer. The flange secures the tube in position in the pneumostoma. An indicator responsive to gases exiting the pneumostoma is integrated into the device and provides and external indicia of the patency and efficacy of the pneumostoma.
Owner:PORTAERO
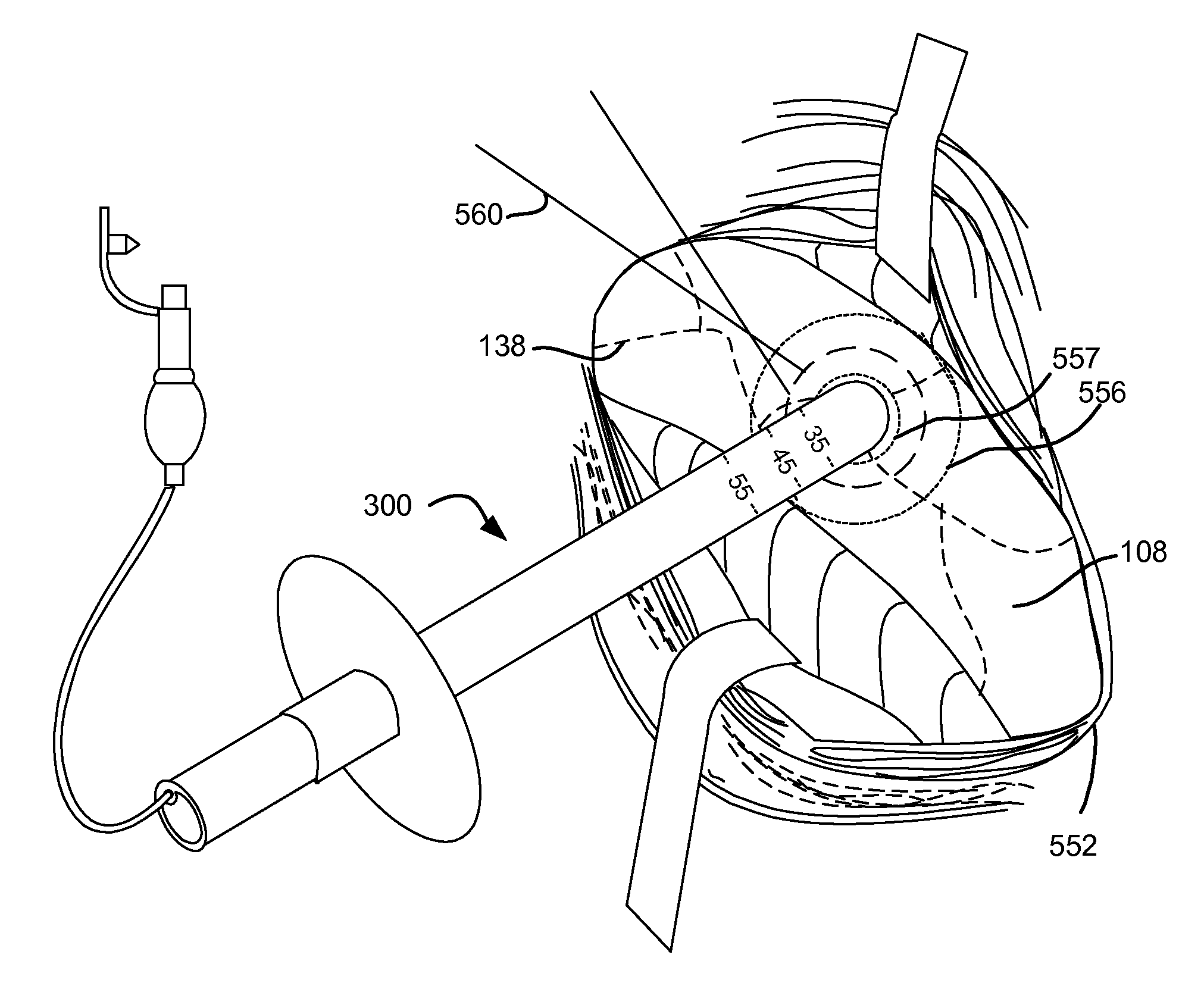
Apparatus to treat cardiopulmonary disease
InactiveUS20190343579A1Suppressing nerve signal transmissionReduce deliverySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesCardiopulmonary bypassTherapeutic Devices
A treatment apparatus including: a bronchoscope including a flexible shaft having working channel; a transbronchial ablation probe configured to extend from a distal end of the working channel and extend thru a wall of a trachea and into tissue outside of the trachea; and a stabilization element mounted to a distal portion of the flexible shaft, wherein the stabilization element is configured to brace the distal portion against the wall of the trachea while the transbronchial ablation probe is extended through the wall of the trachea.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method of treating tuberculosis with interferons
ActiveUS20080292559A1Increase appetiteReduction in wheezingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsInterferon therapyInterferon alpha
A method of treating tuberculosis comprising administering an aerosolized interferon such as interferon α, interferon β or interferon γ in a therapeutically effective amount is provided herein. Also, pharmaceutical compositions of one or more aerosolized interferon(s) are provided.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Method and apparatus to treat cardiopulmonary disease
ActiveUS10842556B1Modulate its functionReduces dyspneaEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingCardiopulmonary diseaseEngineering
Methods and devices for treating patients having cardiopulmonary disease such as cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular arrhythmias, pulmonary hypertension, or heart failure comprising a tracheal approach. The method includes ablating a deep cardiac plexus of a patient by advancing an treatment apparatus into a trachea of the patient, extending an ablative energy delivery element of the treatment apparatus through a wall of the trachea at a level of the trachea proximate a tracheal bifurcation, positioning the ablative energy delivery element at a target space between the trachea, an aorta and a pulmonary artery, and ablating, by the ablative energy delivery element, tissue within the target space to substantially disable the deep cardiac plexus.
Owner:CORIDEA +1
Enhanced pneumostoma management device and methods for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS7909803B2Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesRespiratorsStentsIrritationObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
A partially-implantable pneumostoma management device maintains the patency of a pneumostoma while controlling the flow of material through the pneumostoma. A tube of the pneumostoma management device is placed through the chest wall into the lung. The tube comprises a plurality of holes in the distal end to allow the entry of gases and non-gaseous discharge from the lung. A contact surface prevents over-insertion of the tube while releasably securing the device to the chest of the patient. The contact surface has features to reduce irritation of the skin of the chest.
Owner:PORTAERO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com